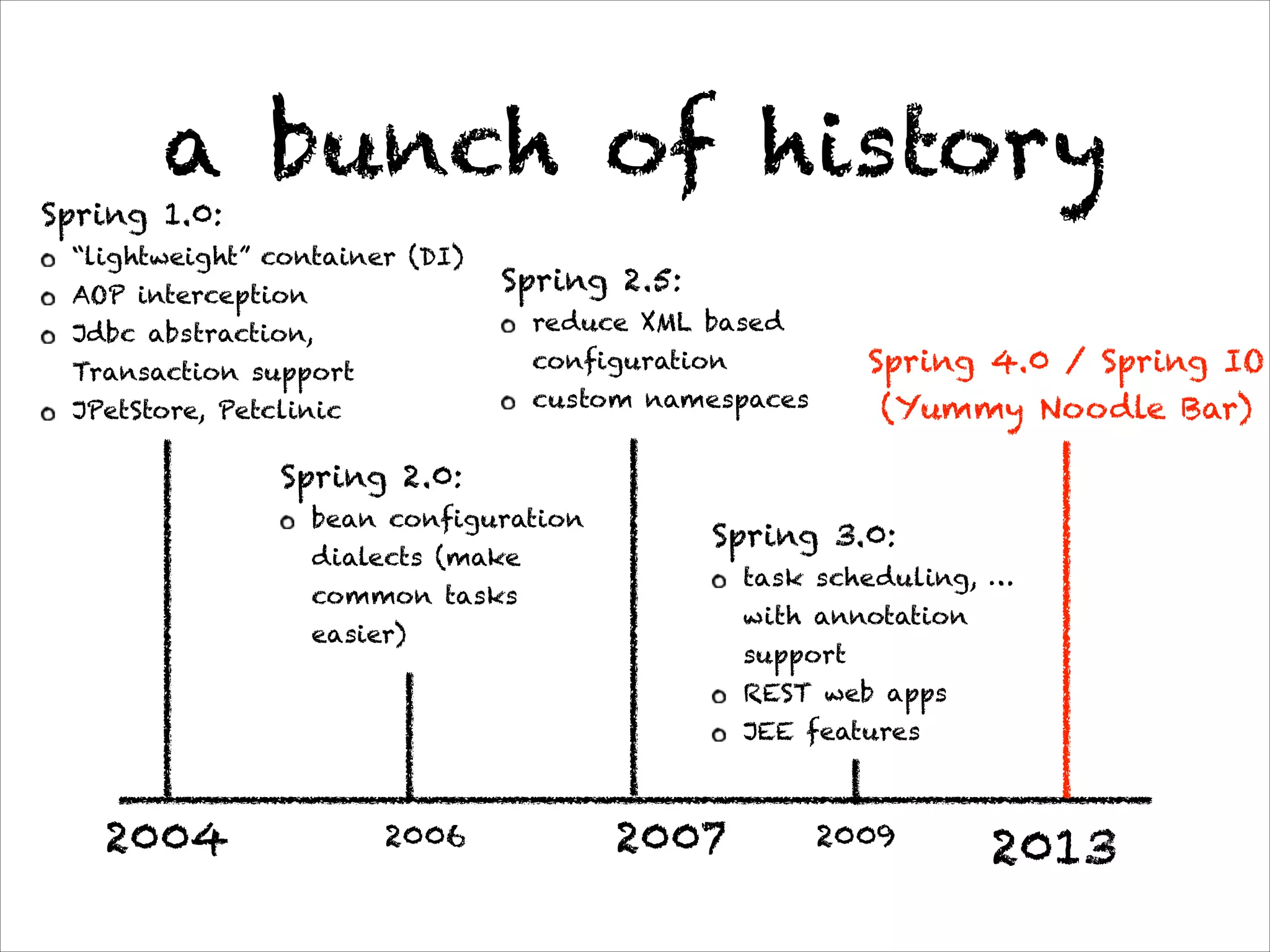
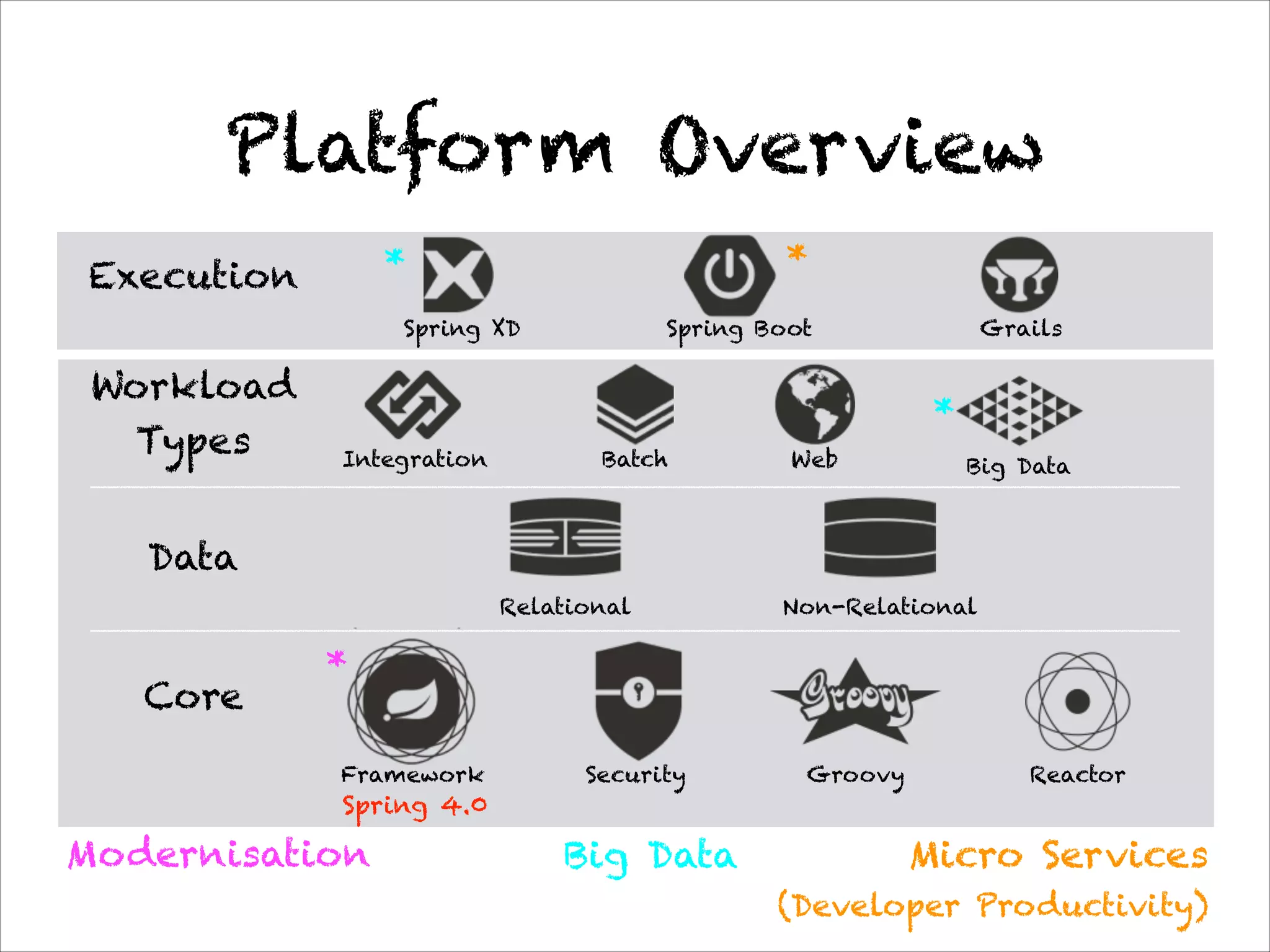
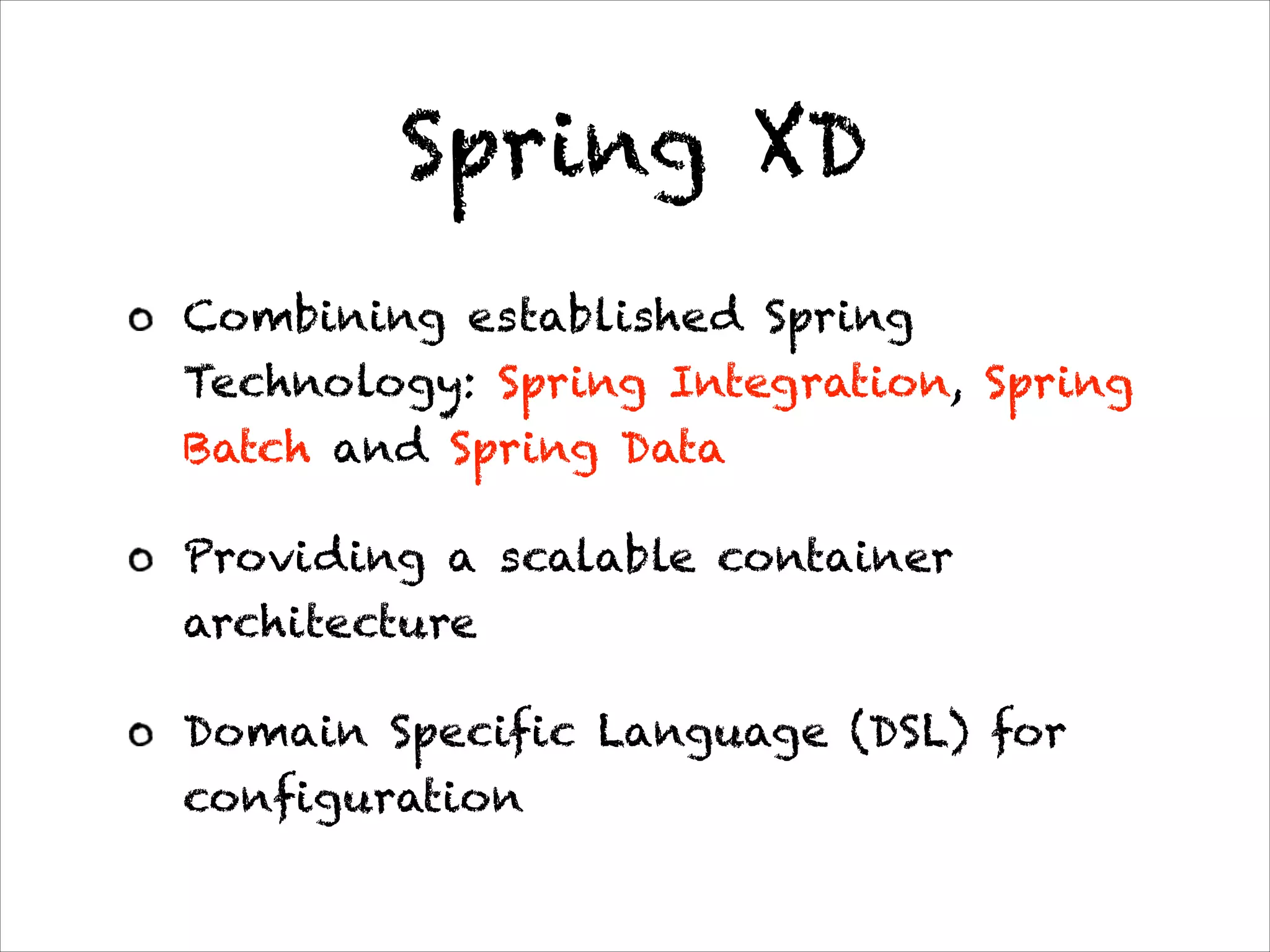
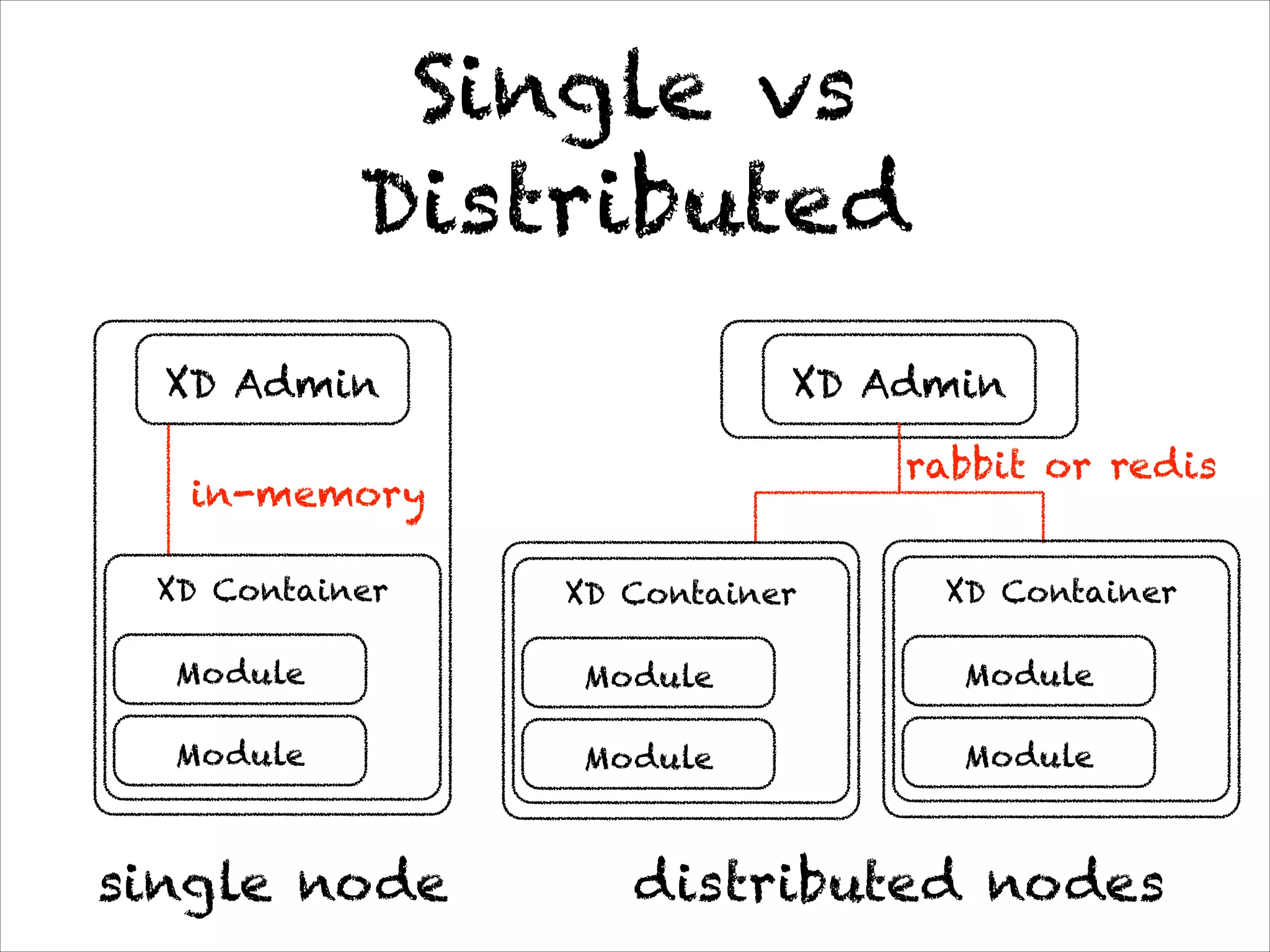
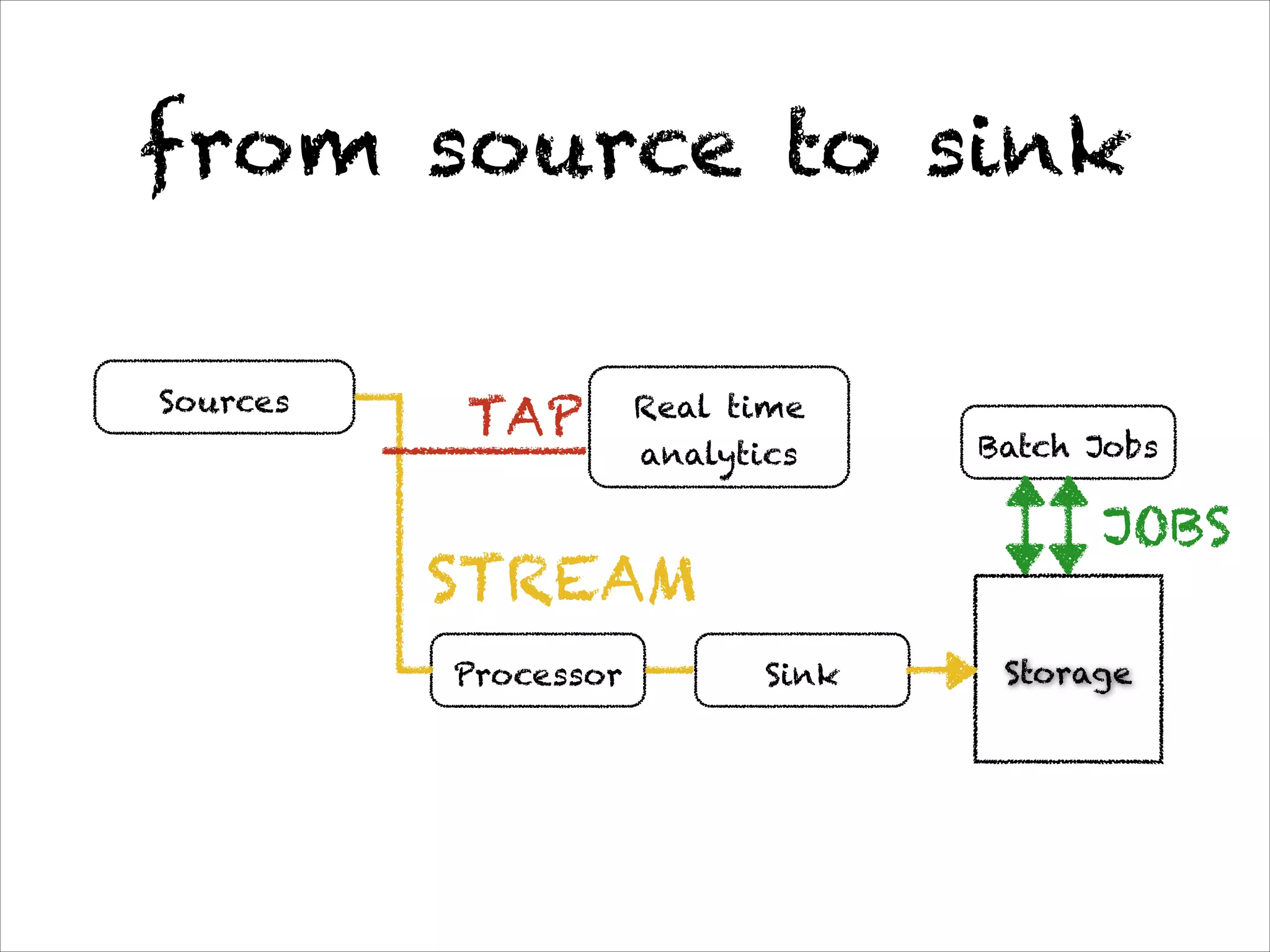
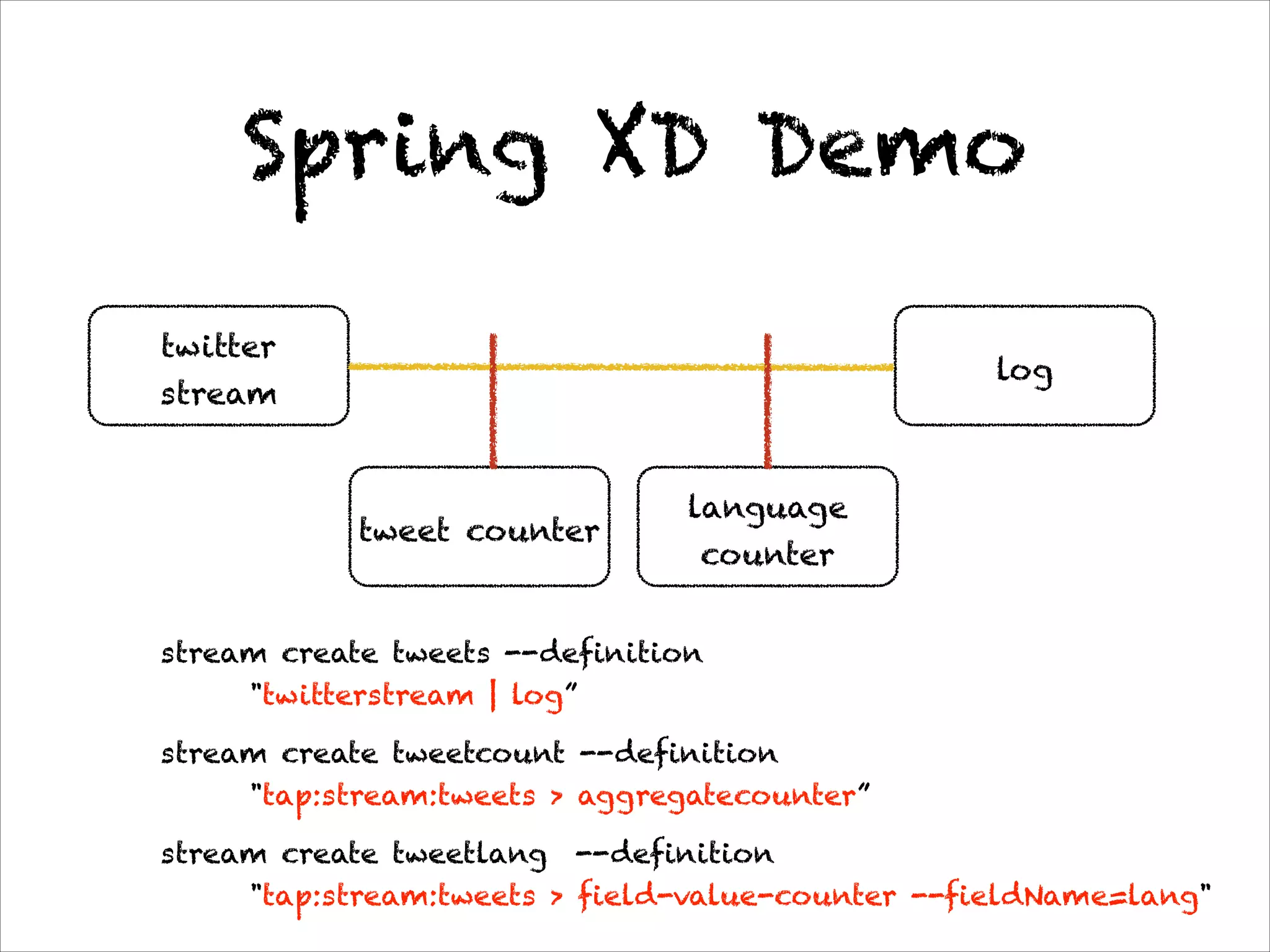
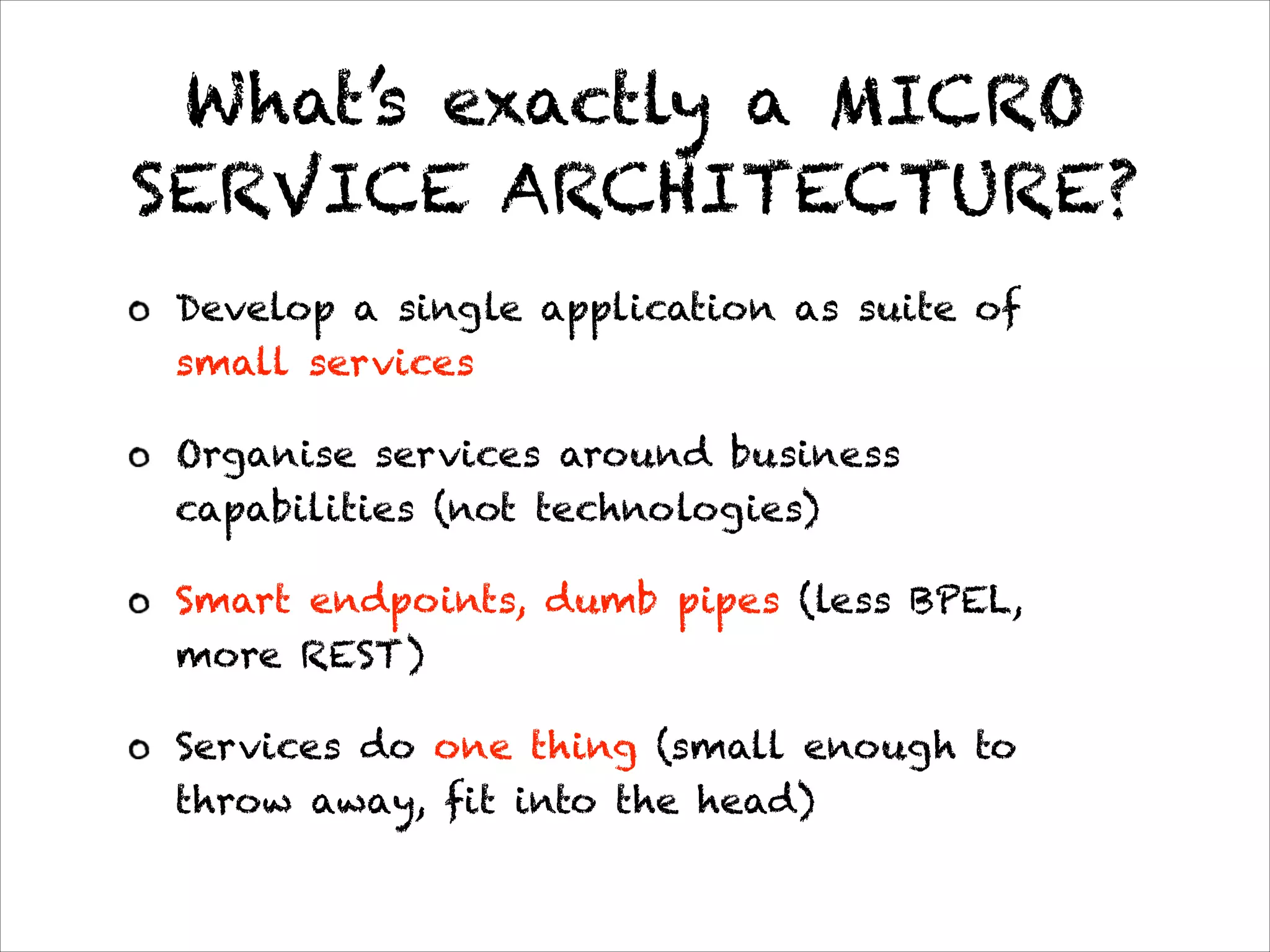
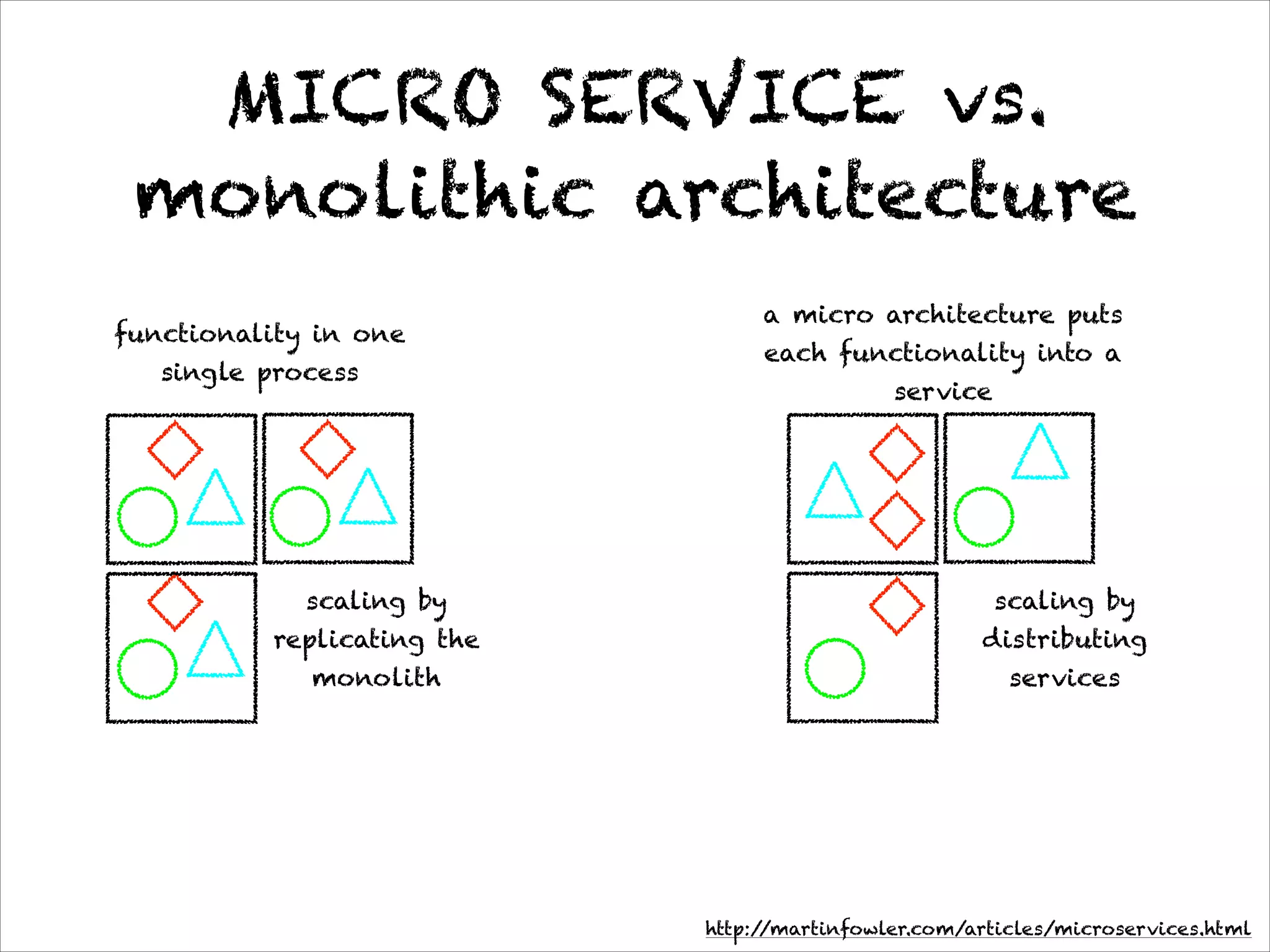
This document discusses the evolution of Spring 4.0 and related technologies. It covers new features in Spring 4.0 like support for Java 8 lambdas and date/time API. It also discusses Spring projects for big data like Spring XD for data ingestion and analytics. Finally, it covers microservice architecture and how Spring Boot helps develop standalone microservices.