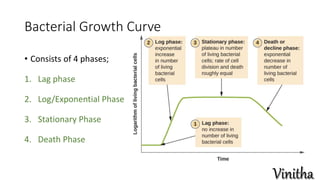
Microbes are microscopic organisms, categorized into five groups: bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and algae. Microbial growth reflects changes in population through binary fission and requires specific physical and chemical factors, including temperature, pH, nutrients, and oxygen levels. The bacterial growth curve consists of four phases: lag, log/exponential, stationary, and death phases.