This document discusses trauma to the hand, specifically extensor tendon injuries and flexor tenosynovitis.
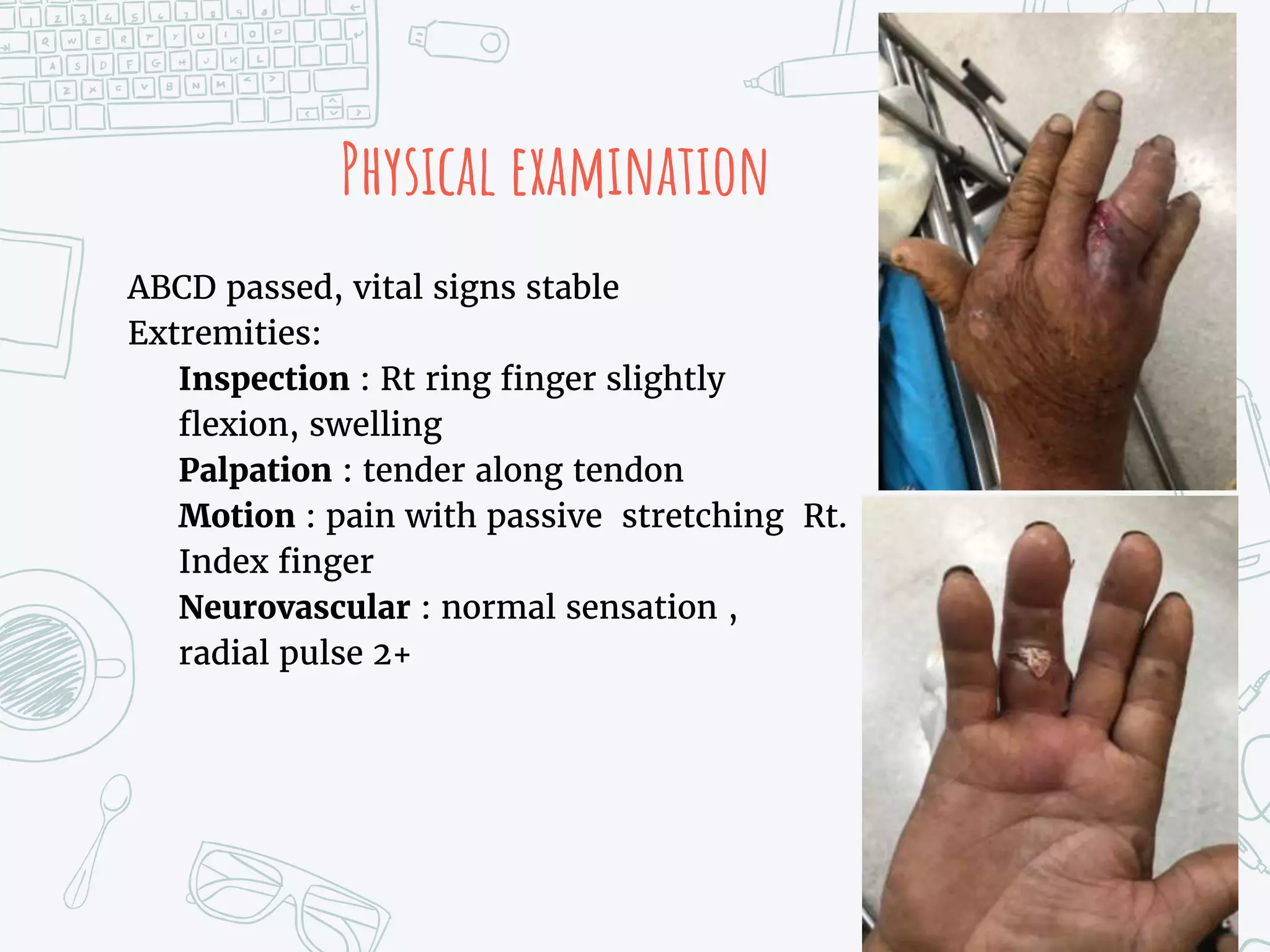
It describes two cases - the first involving a laceration to the extensor tendon of the right thumb requiring surgical repair. The second case involves flexor tenosynovitis of the right ring finger from a fishhook injury, requiring IV antibiotics and possible surgery.
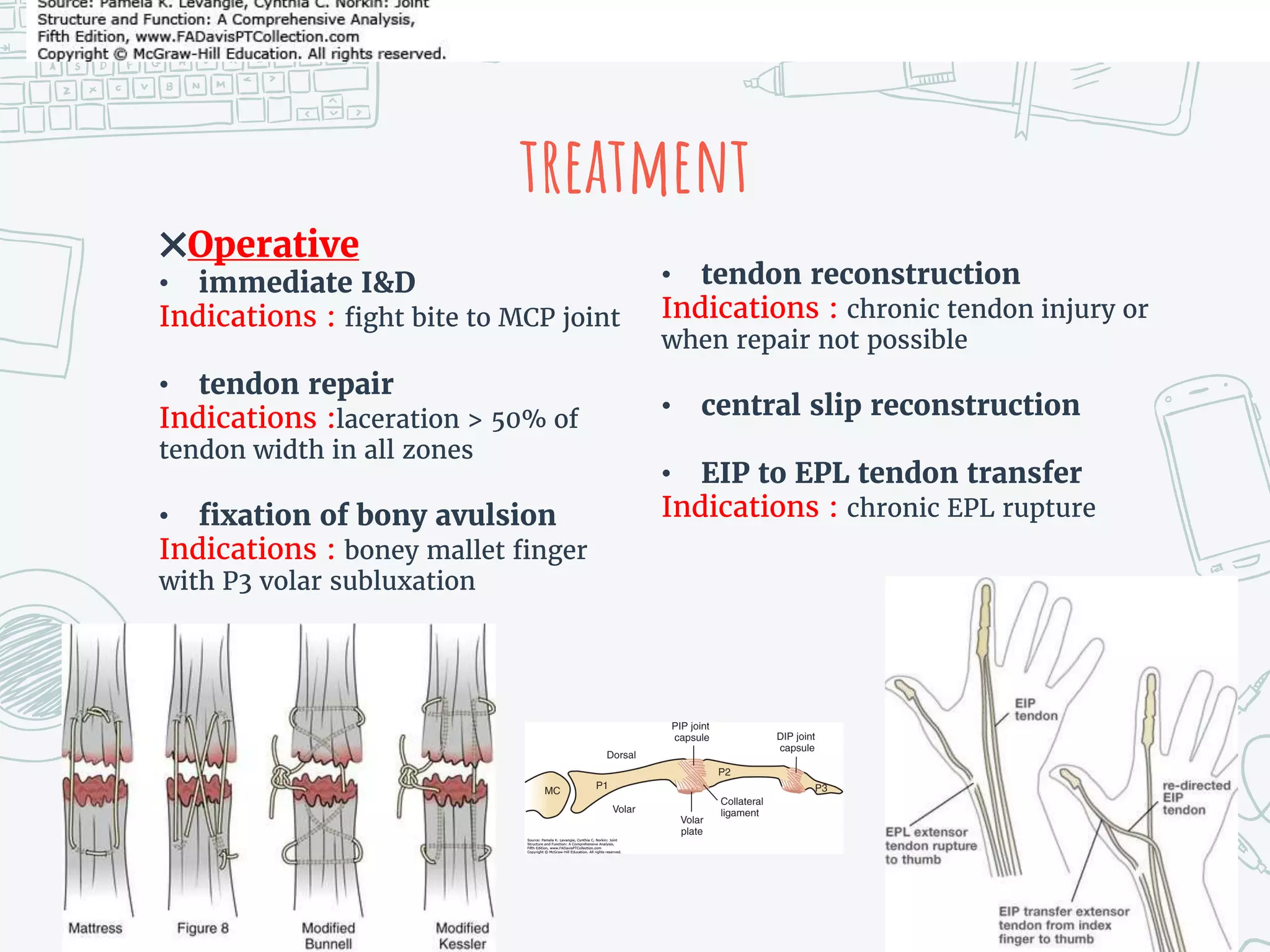
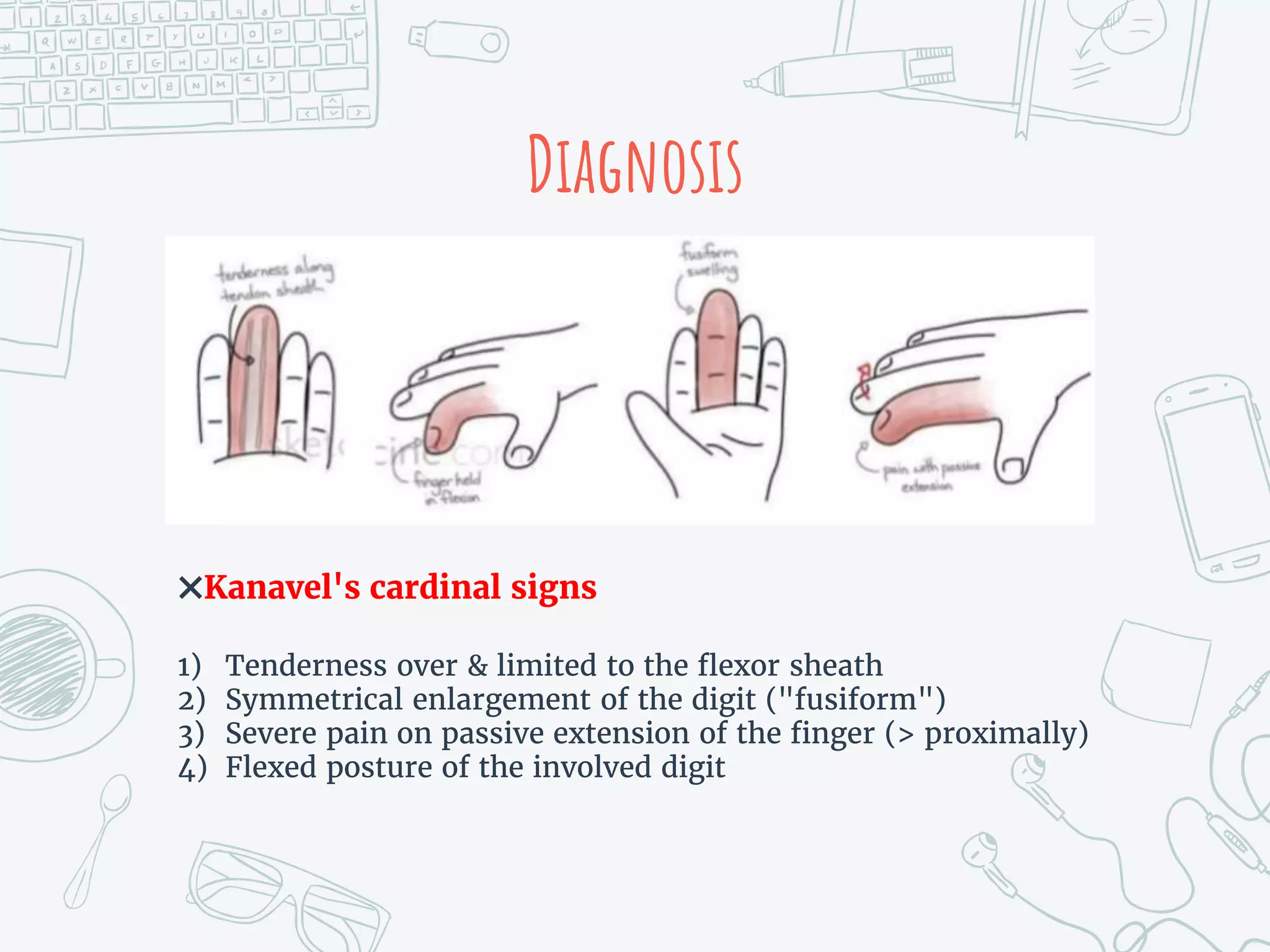
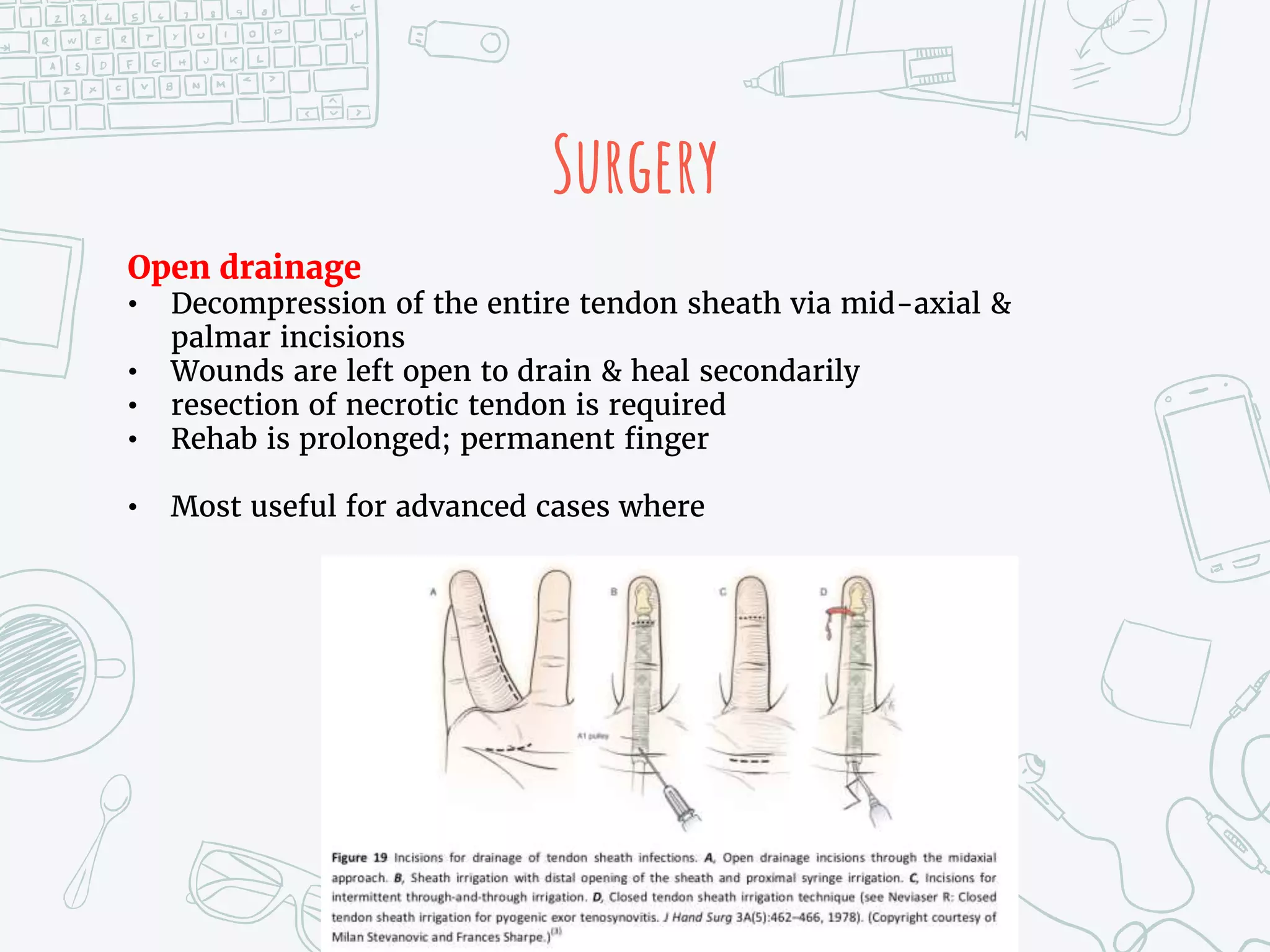
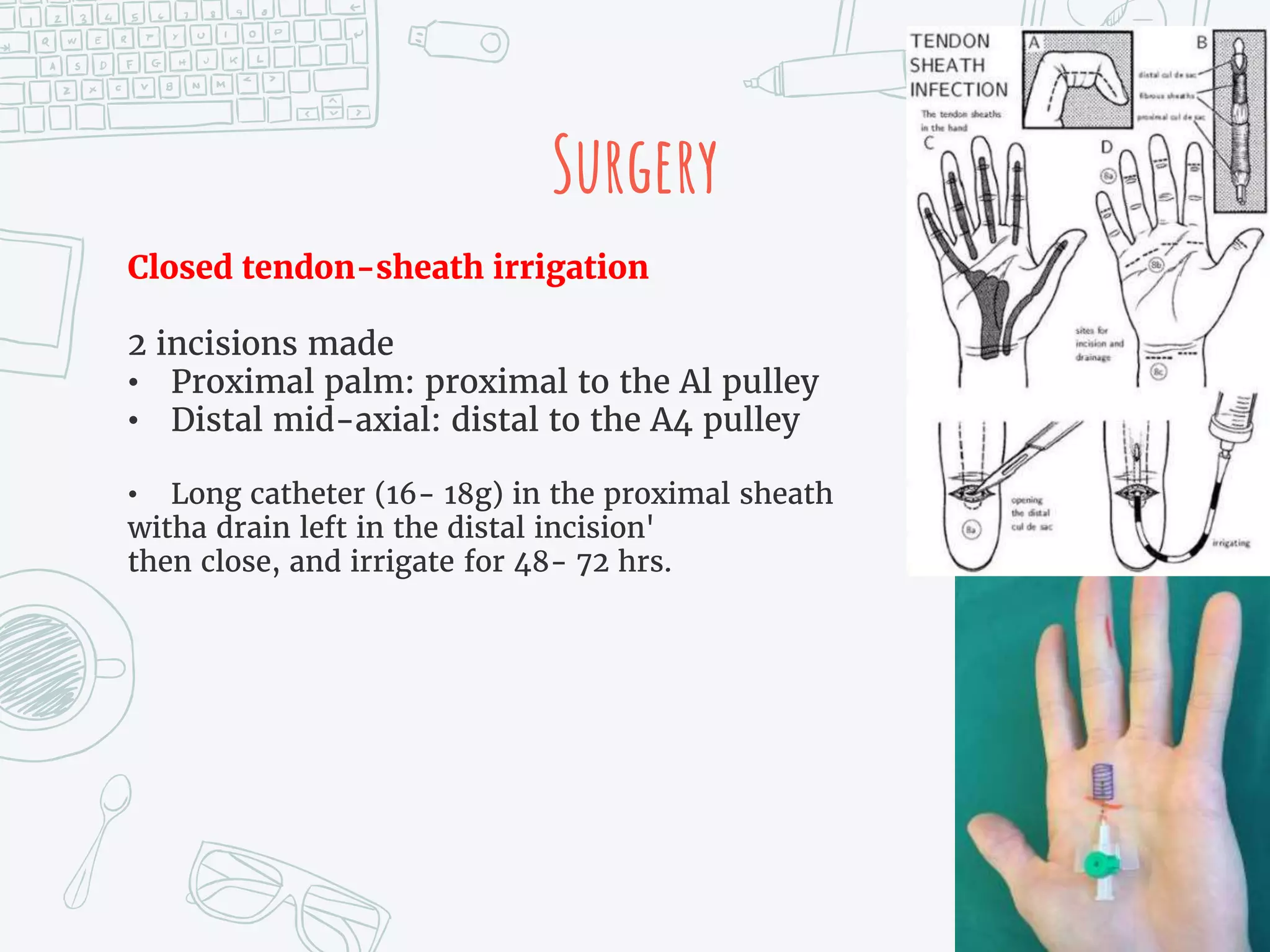
It provides details on the anatomy, mechanisms of injury, clinical presentations, diagnostic criteria, non-operative and operative treatment options, post-operative care and potential complications for both extensor tendon injuries and flexor tenosynovitis. Surgical management focuses on debridement, irrigation and repair or reconstruction depending on the