The document provides an introduction to metadata, including definitions of metadata, how it relates to digital libraries, its purposes and uses. It discusses the structure, semantics and syntax of metadata, how metadata is created through workflows and quality processes, and why high quality metadata is important for functions like interoperability and resource discovery.





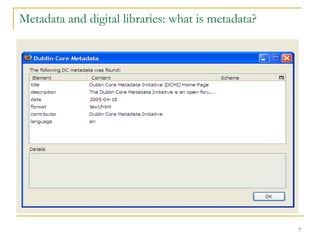
![Metadata and digital libraries: what is metadata? Firefox plug-in [bottom right]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadata-101public-1209635649242273-9/85/Metadata-101public-6-320.jpg)


![Metadata and digital libraries: what is metadata (part 2)? Definition from Weibel (1998) how to think about data… Structure : ‘a data model […] for specifying semantic schemas’ e.g. Dublin Core Semantic : ‘agreed content description standards’ e.g. author name conventions; controlled vocabularies Syntax : ‘syntax for expressing metadata’ e.g. XML binding for Dublin Core](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadata-101public-1209635649242273-9/85/Metadata-101public-10-320.jpg)








![The end Questions now? Questions later – contact: [email_address] Rm 12:12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metadata-101public-1209635649242273-9/85/Metadata-101public-22-320.jpg)