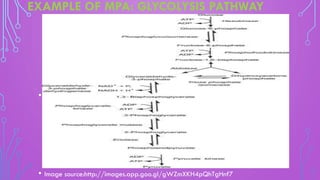
This document discusses metabolic pathway analysis. It defines metabolic pathways as series of consecutive enzyme reactions that produce specific products. It notes that pathways are irreversible and compartmentalization allows different cycles to operate in eukaryotes. The document outlines several methods to analyze pathways, including isotope labeling, genome-scale metabolic modeling, and structural kinetic modeling. It provides the example of glycolysis and describes applications like finding high yield pathways and determining active reactions.