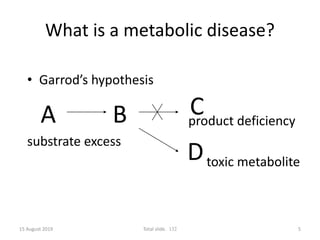
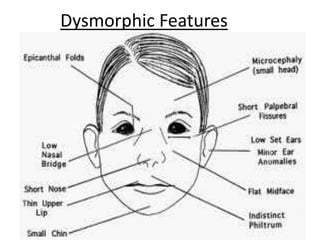
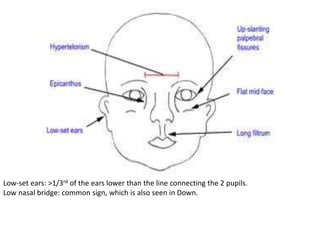
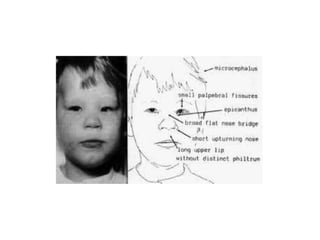
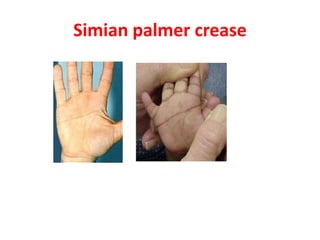
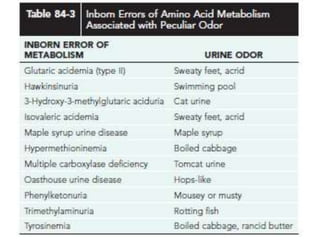
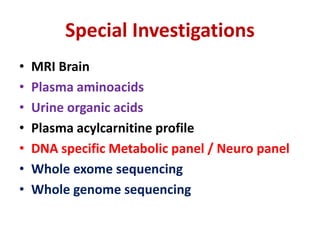
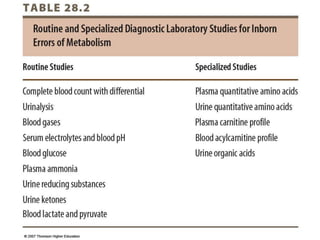
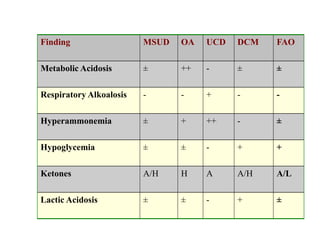
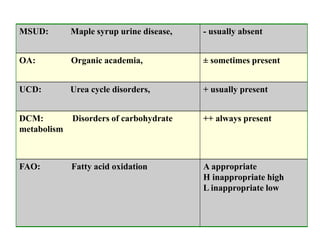
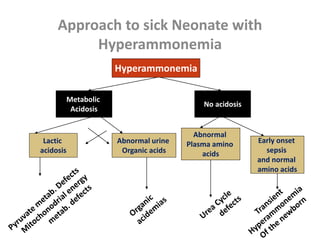
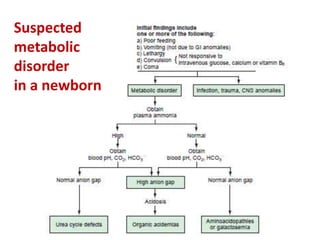
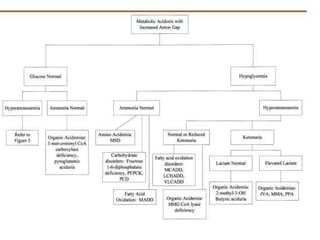
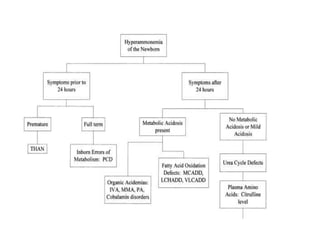
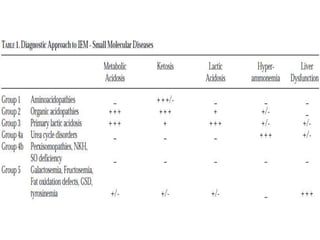
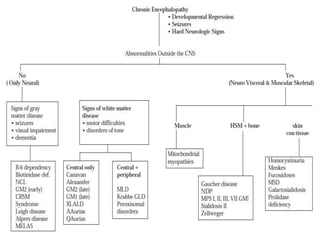
This document discusses the diagnosis and presentation of inborn errors of metabolism. It begins by defining inborn errors of metabolism as inherited enzyme deficiencies that disrupt normal metabolism. There are three main types of clinical presentation: silent disorders, acute metabolic crises, and progressive neurological deterioration. For diagnosis, the document outlines important history and examination factors and provides guidance on initial laboratory tests and specialized investigations. Common metabolic presentations like metabolic acidosis and hypoglycemia are reviewed. Specific disorders are then discussed in terms of their typical diagnostic considerations and laboratory findings.