This document provides an overview of neurometabolic disorders, including:
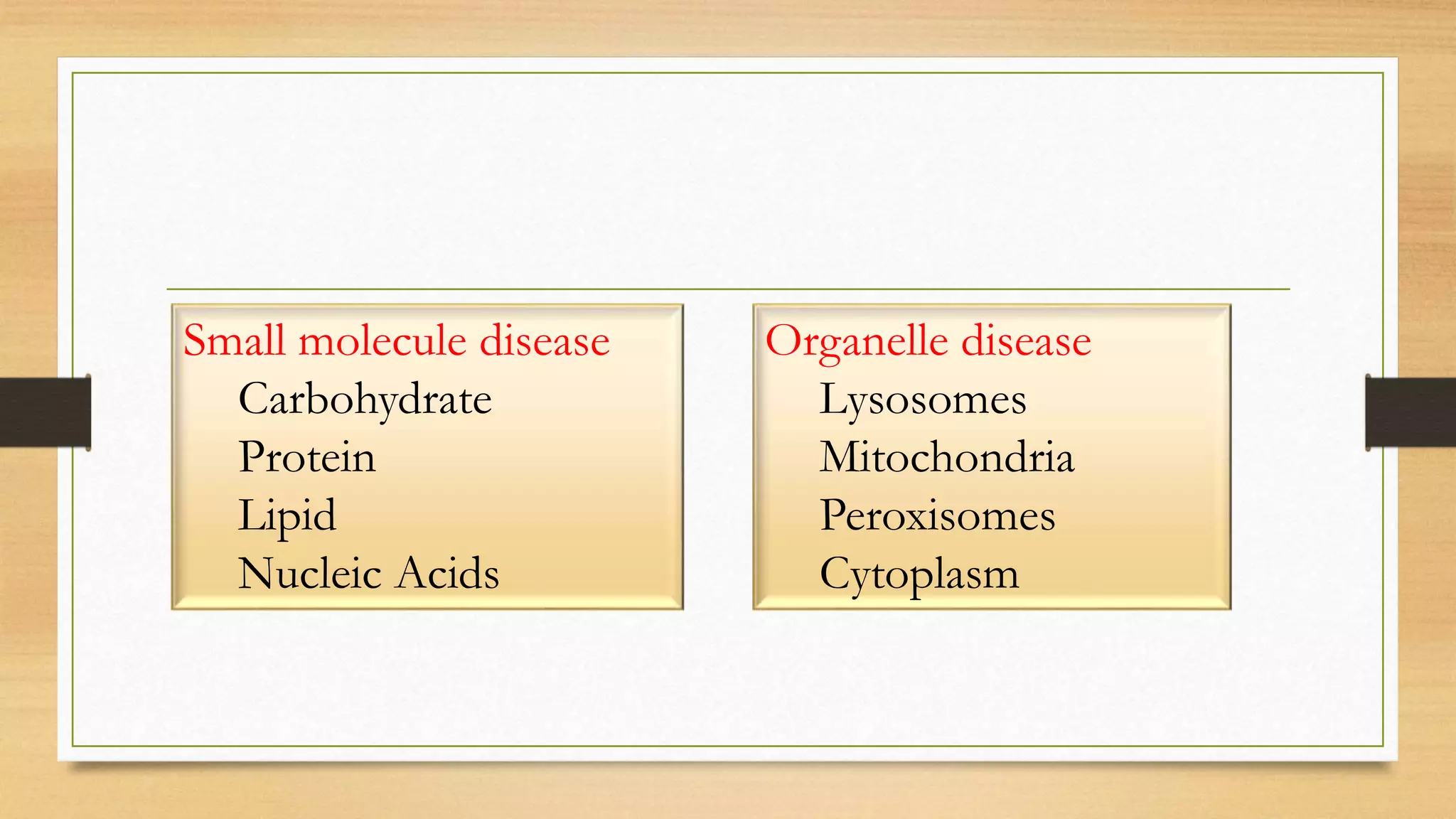
1. It discusses Garrod's hypothesis and how metabolic disorders can be classified into groups related to intoxication, energy metabolism, and complex molecules.
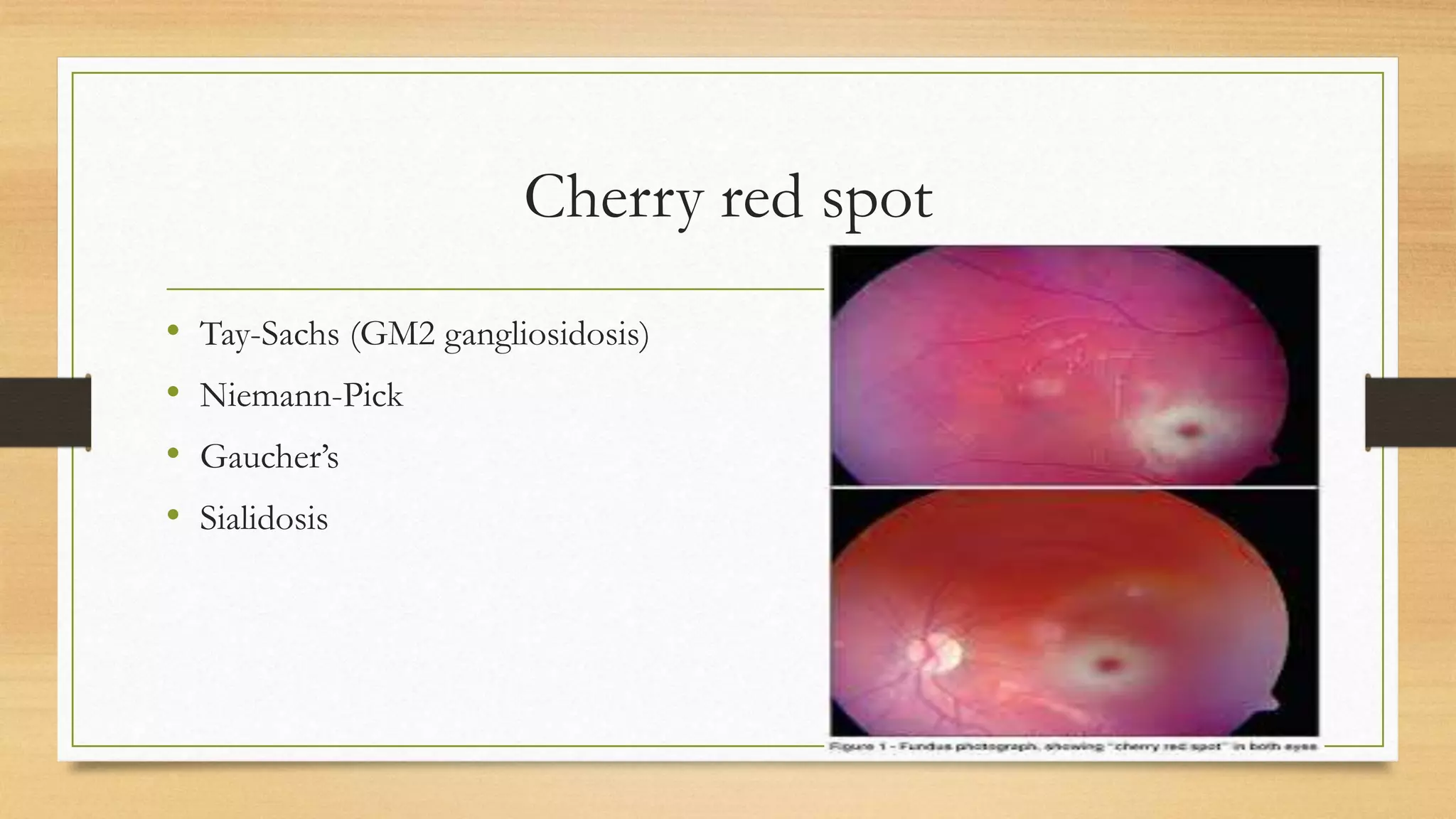
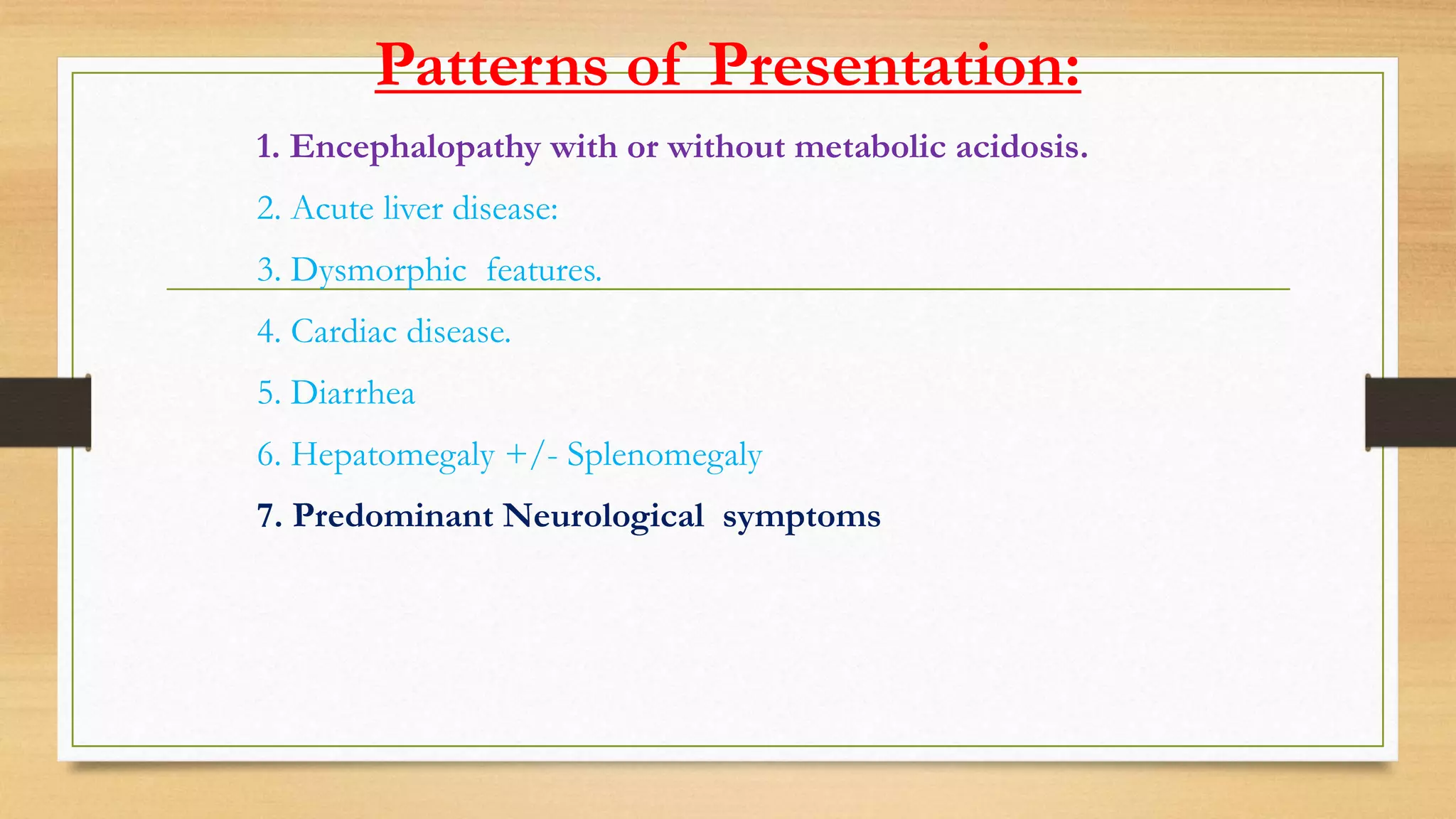
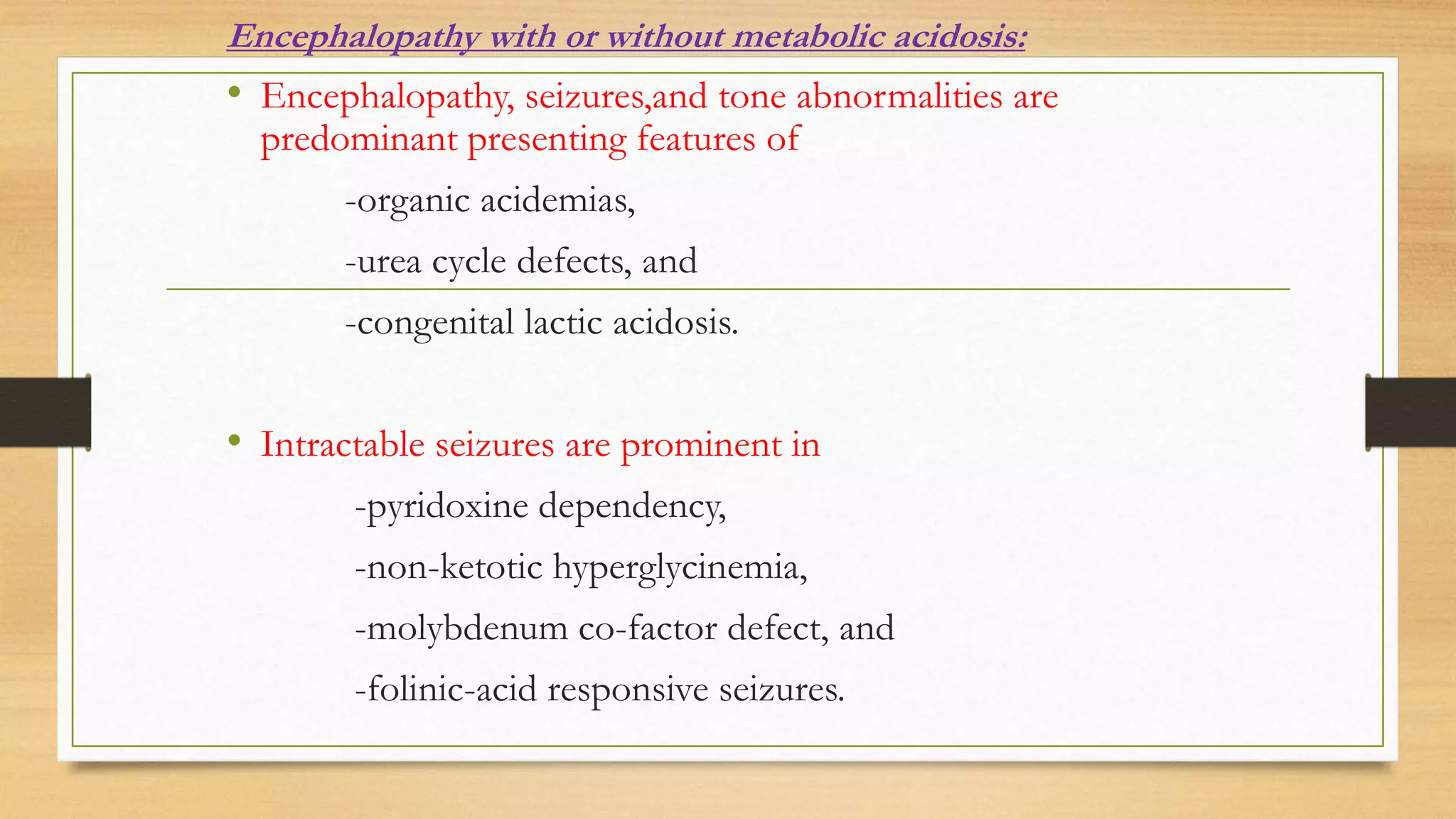
2. The different presentations of neurometabolic disorders are outlined, including encephalopathy, liver disease, cardiac issues, and predominant neurological symptoms.
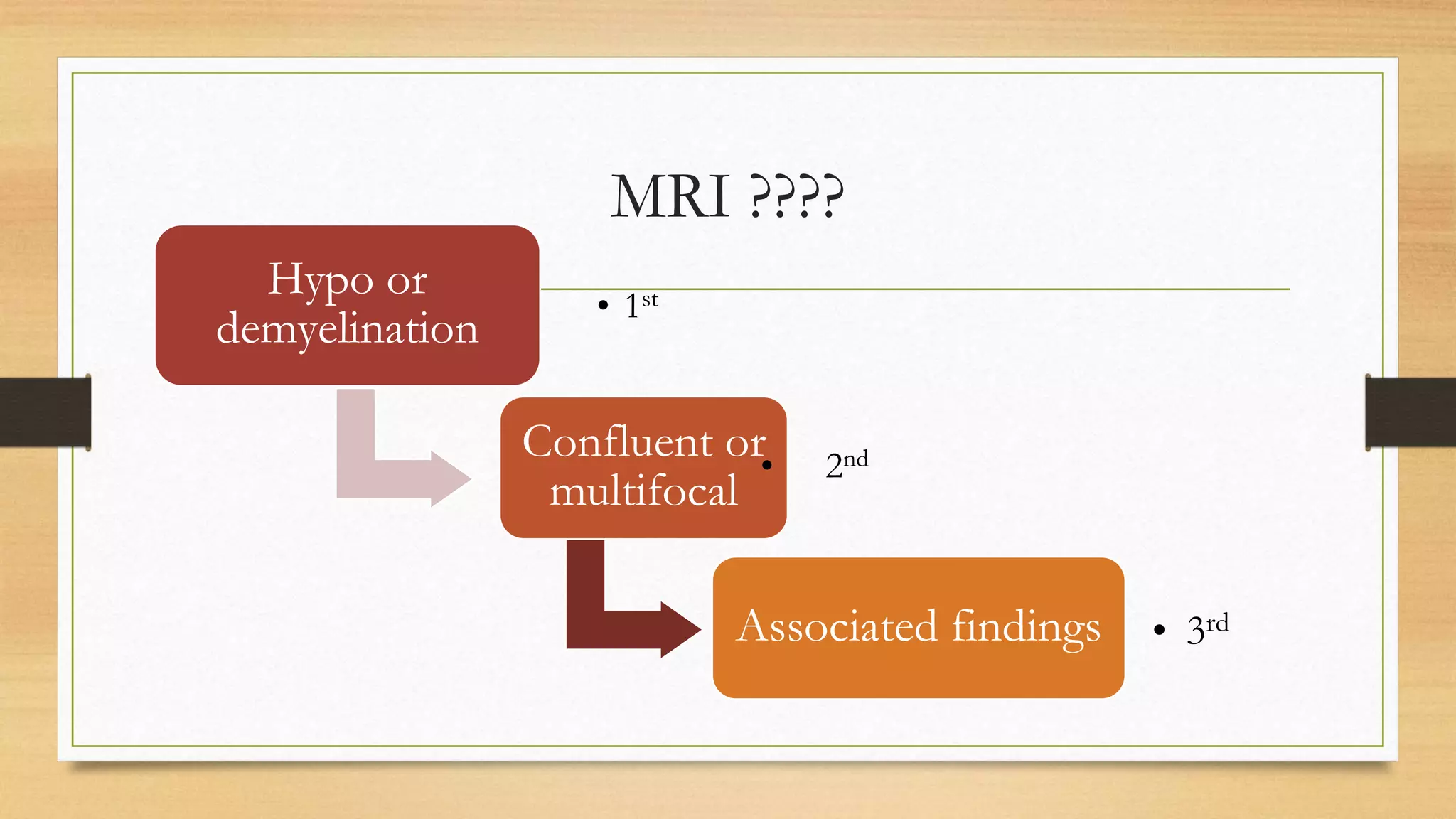
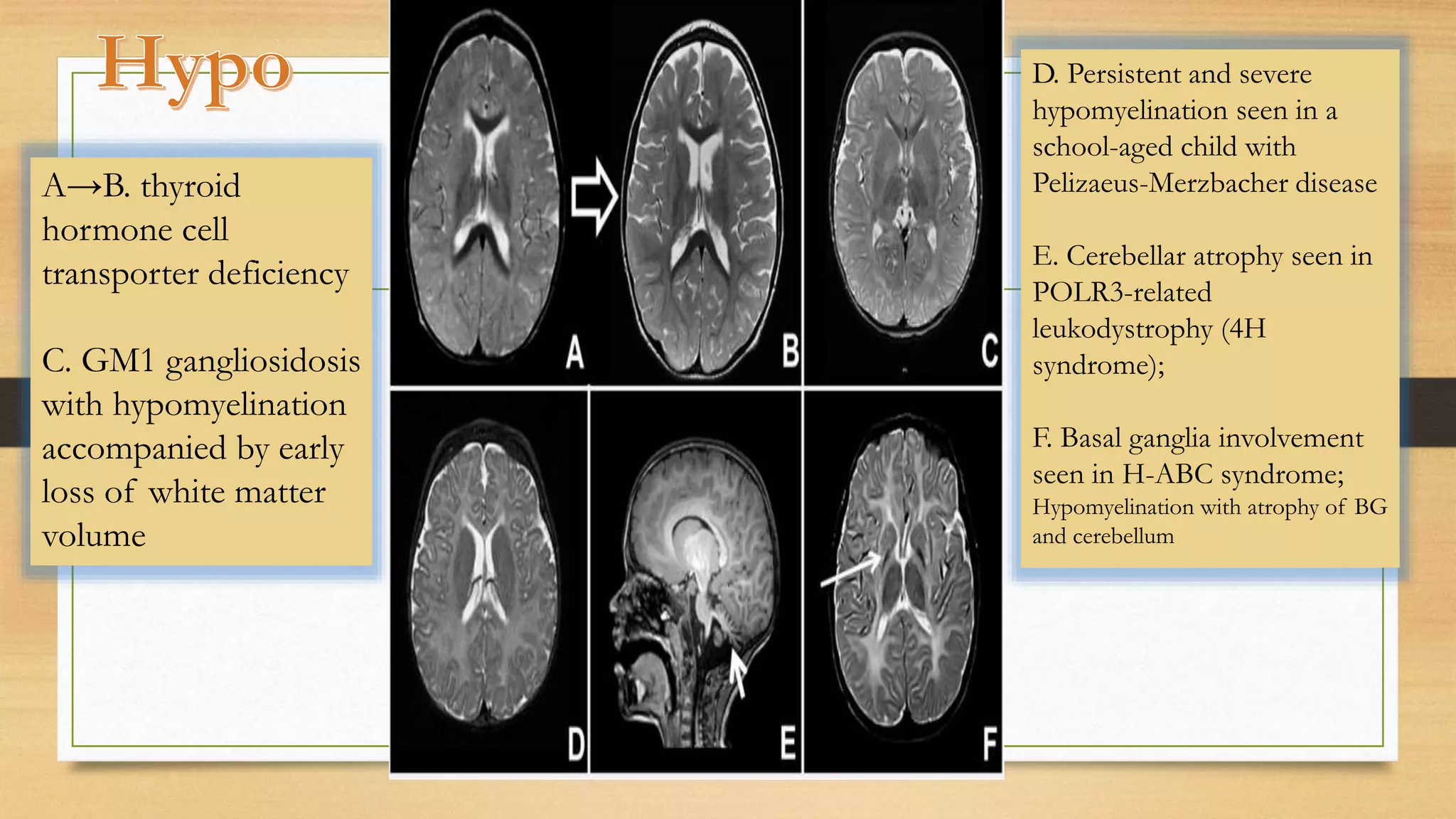
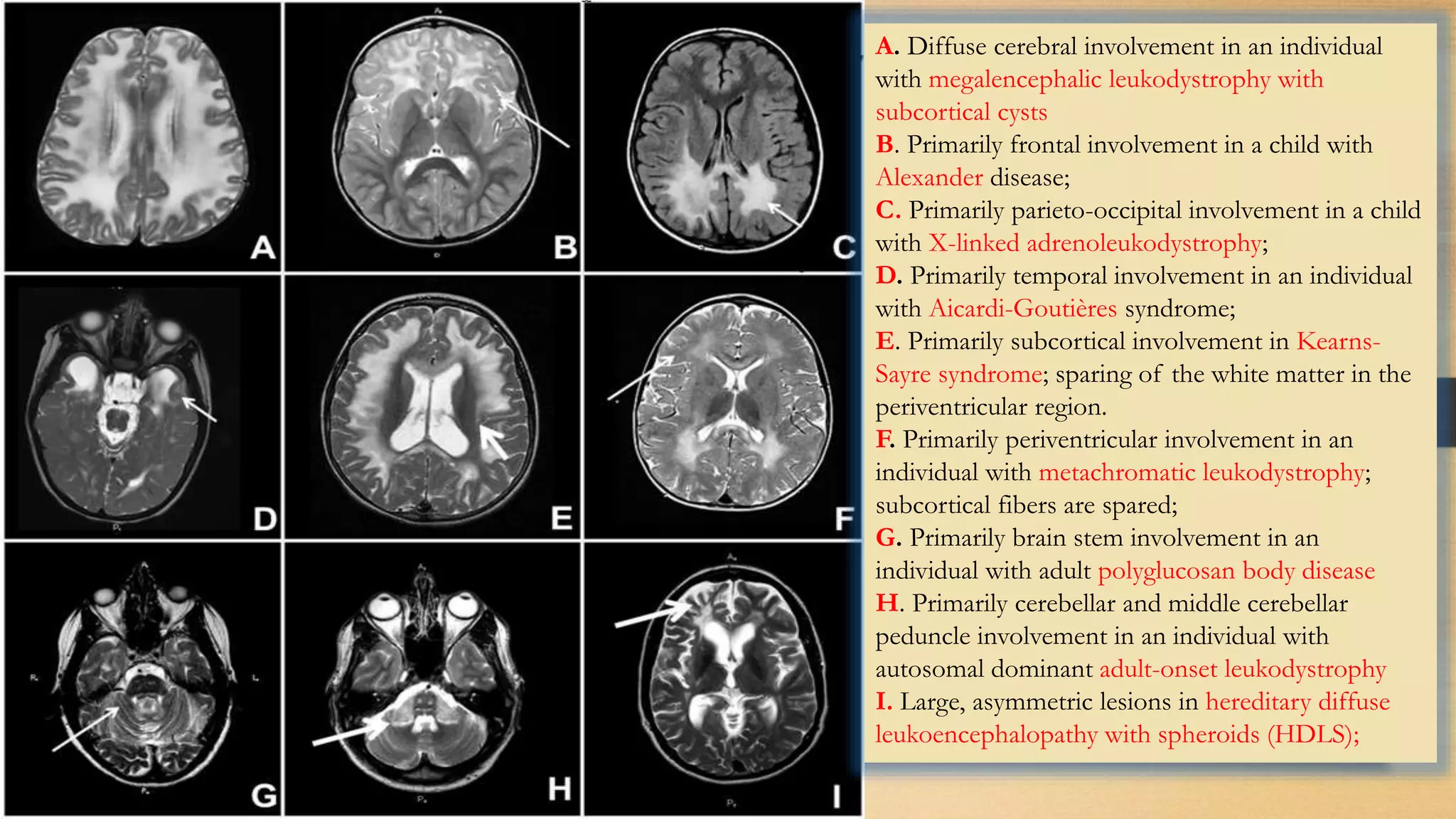
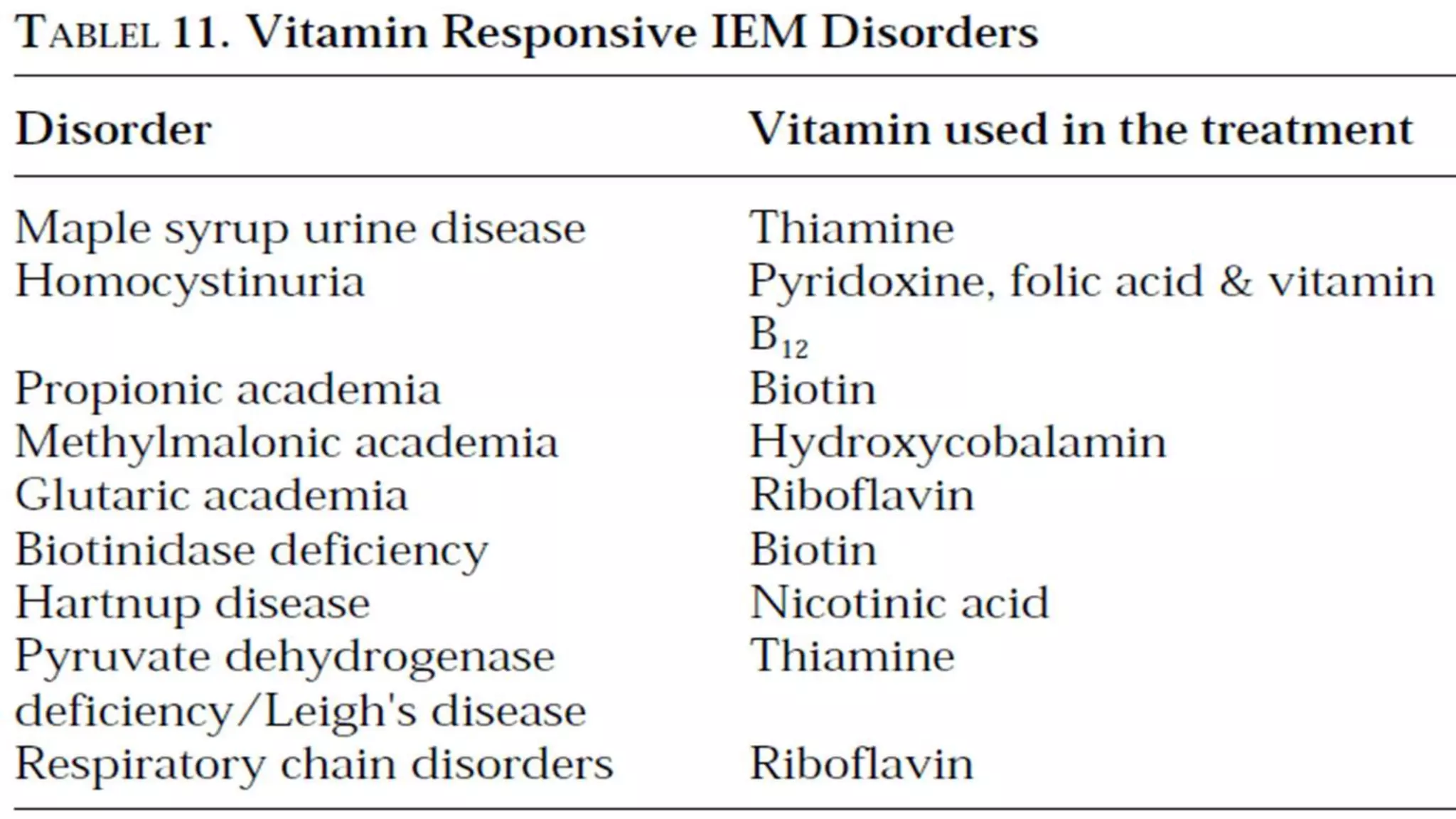
3. Guidance is provided on when to suspect a neurometabolic disorder and how to conduct initial investigations including metabolic screening tests and MRI patterns.
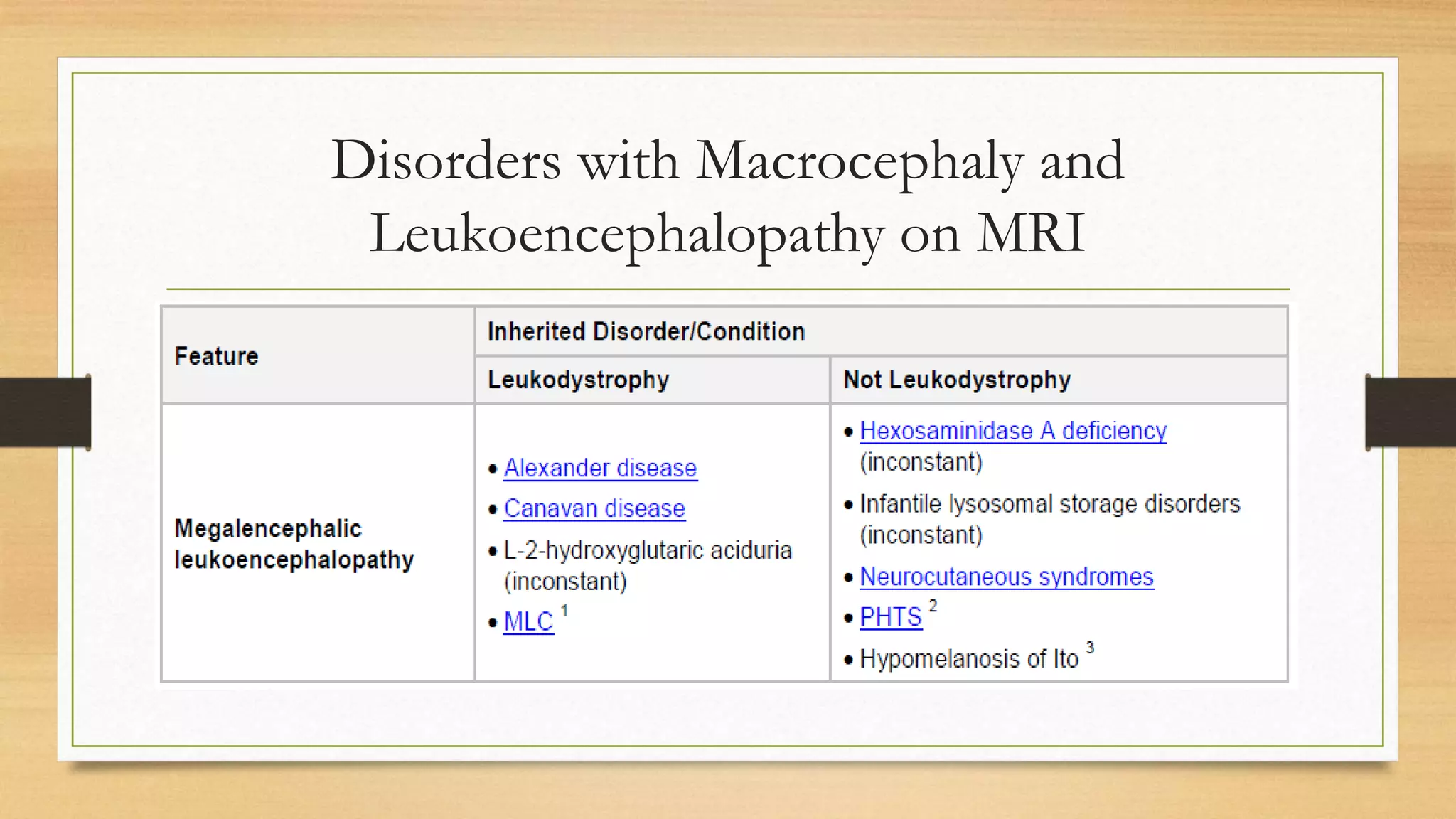
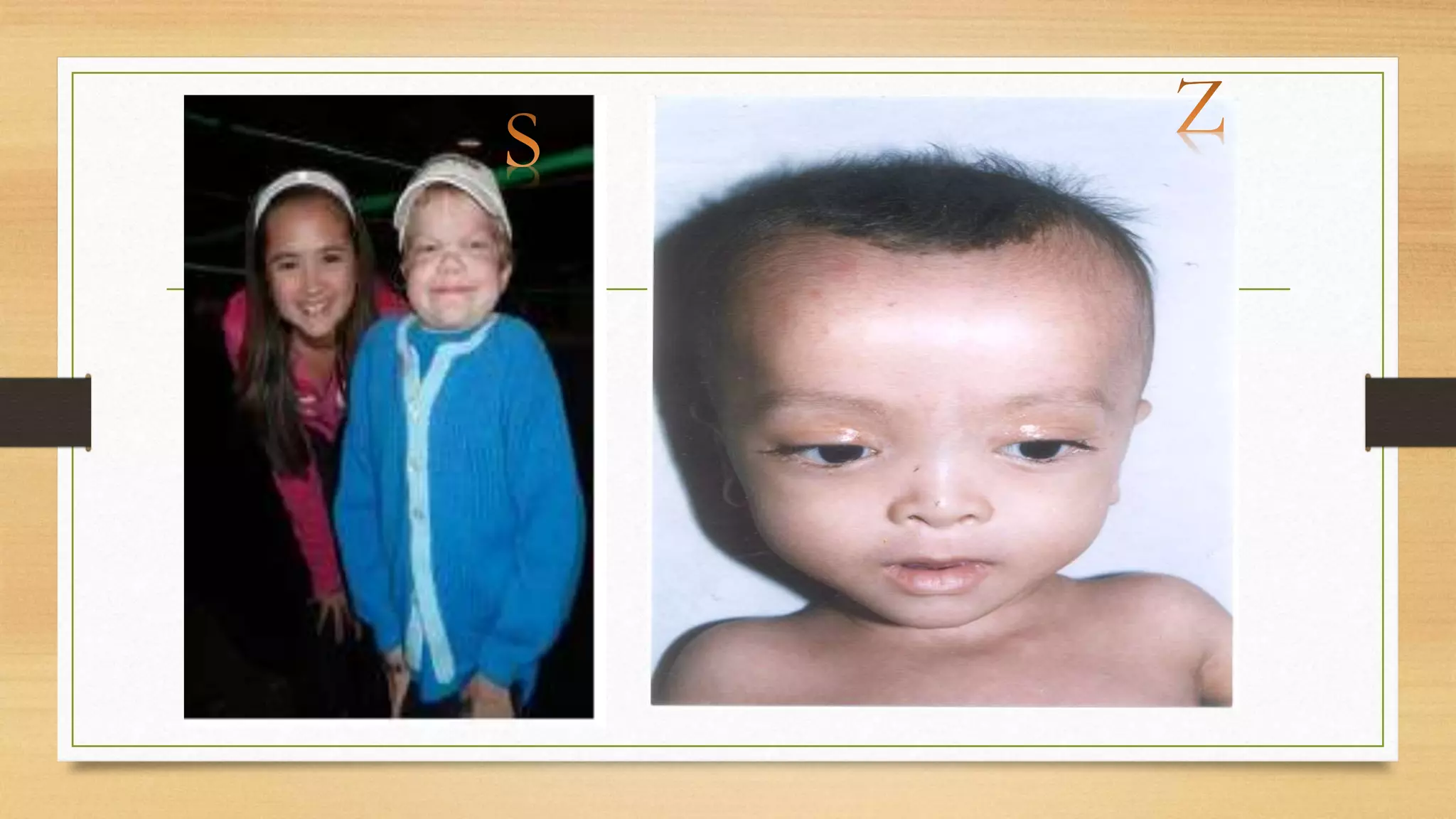
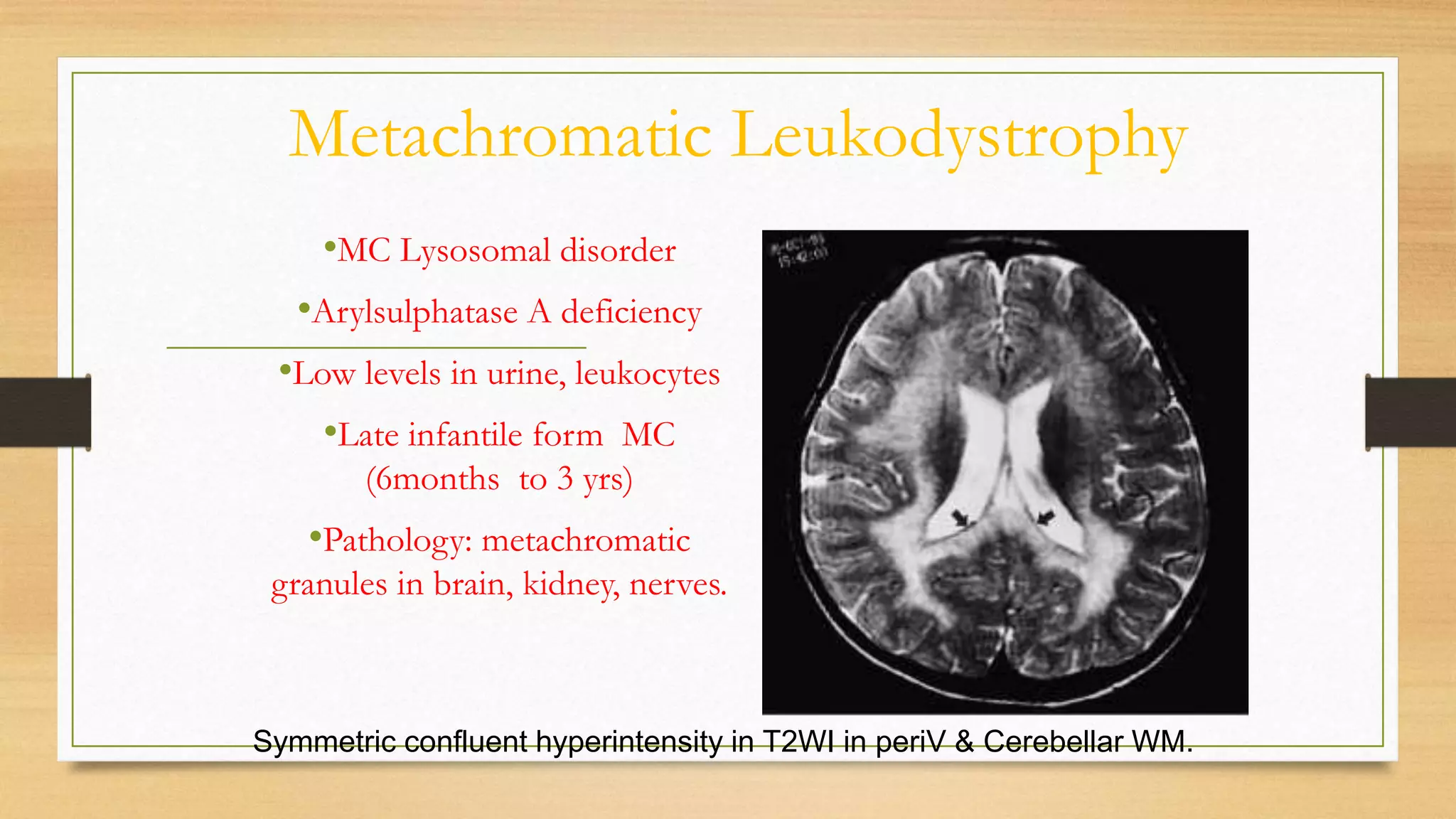
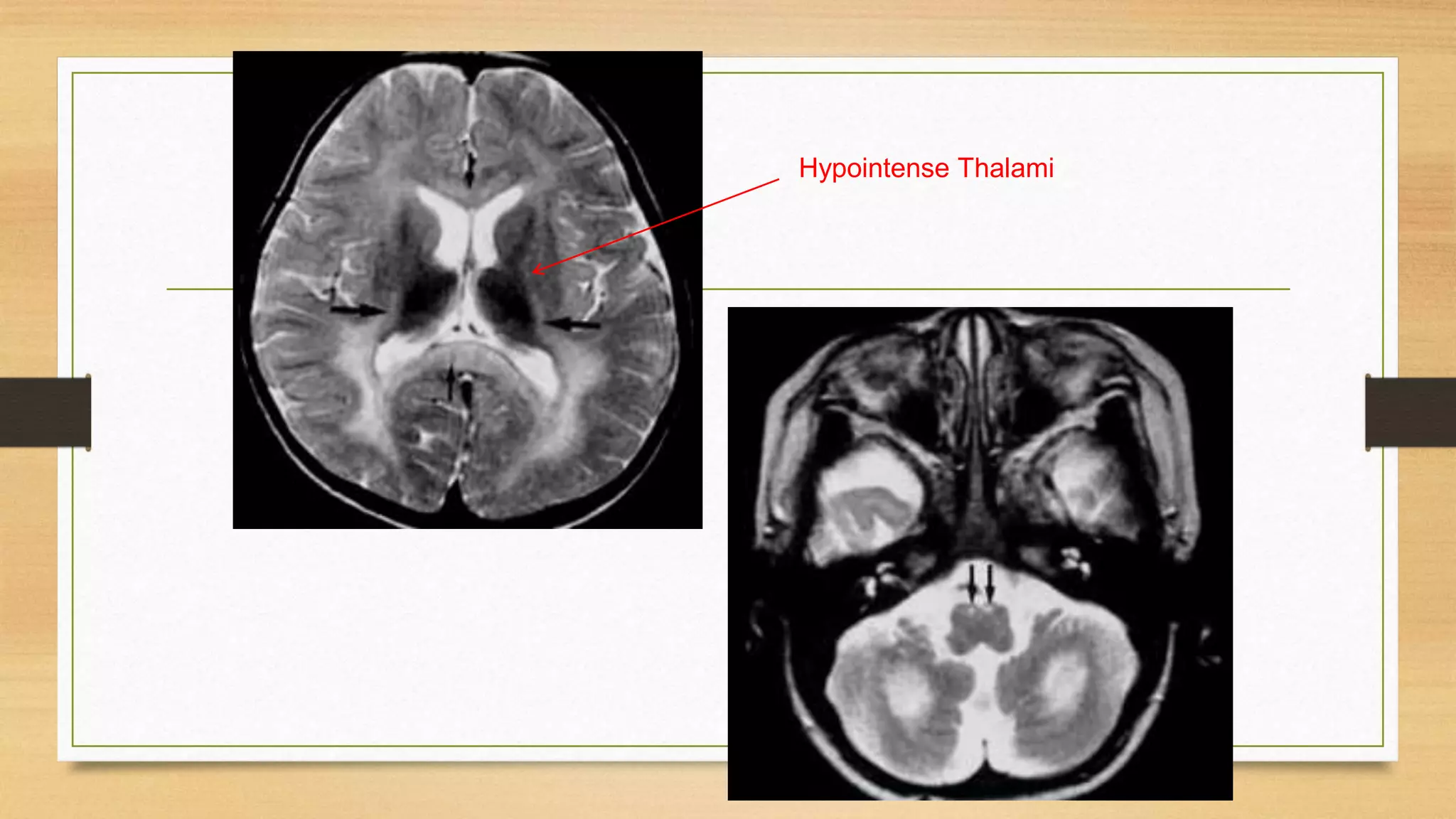
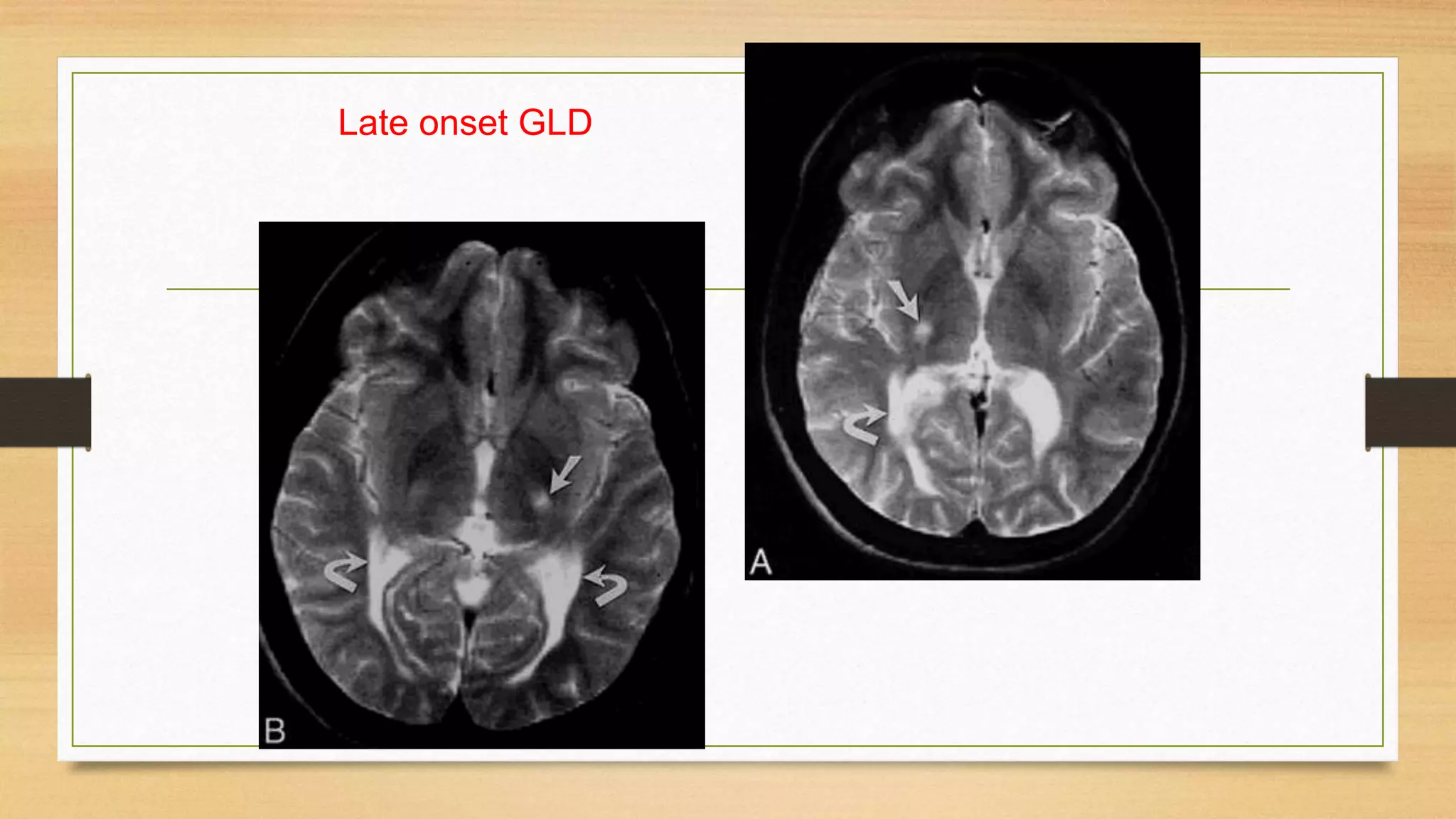
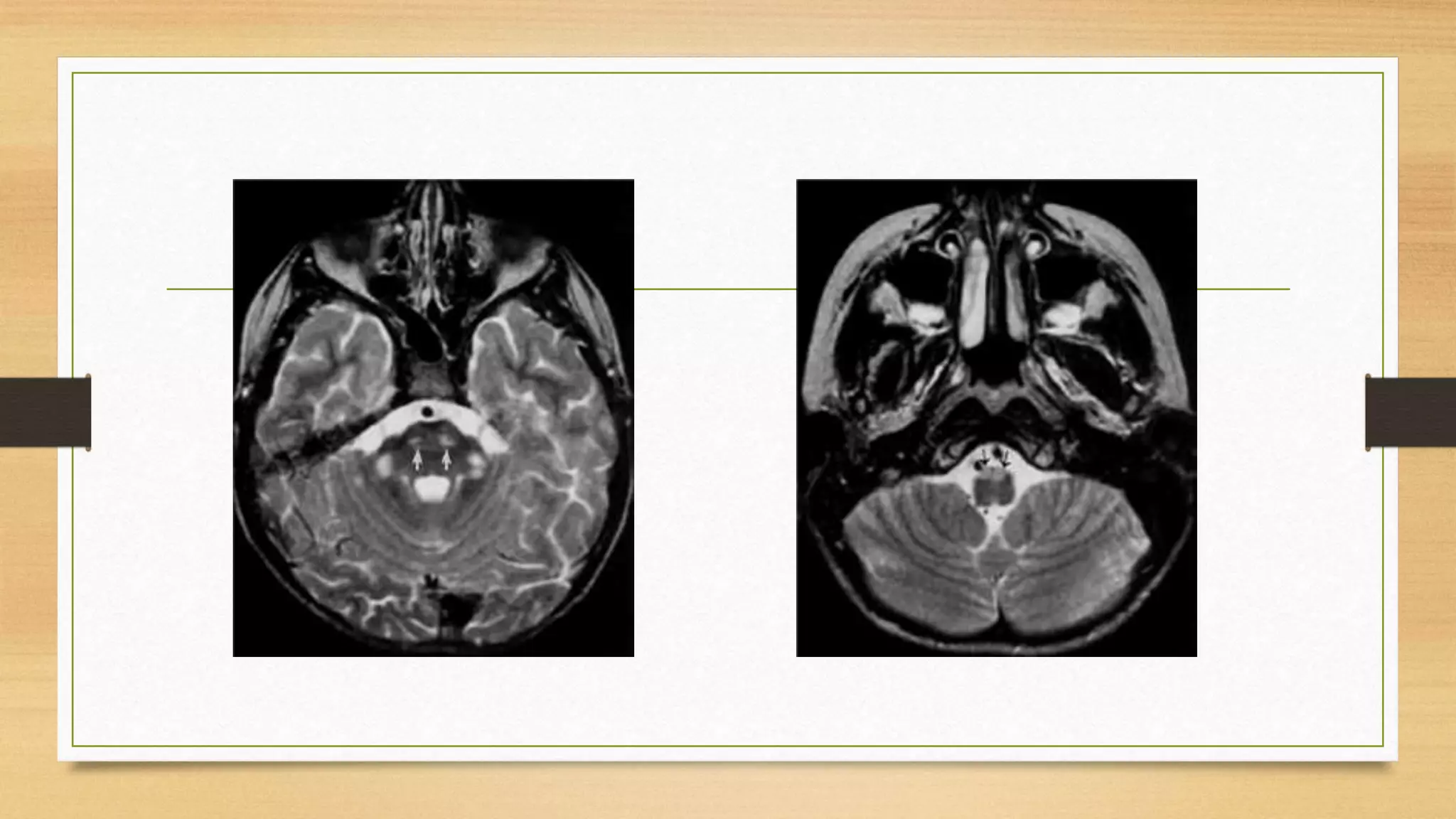
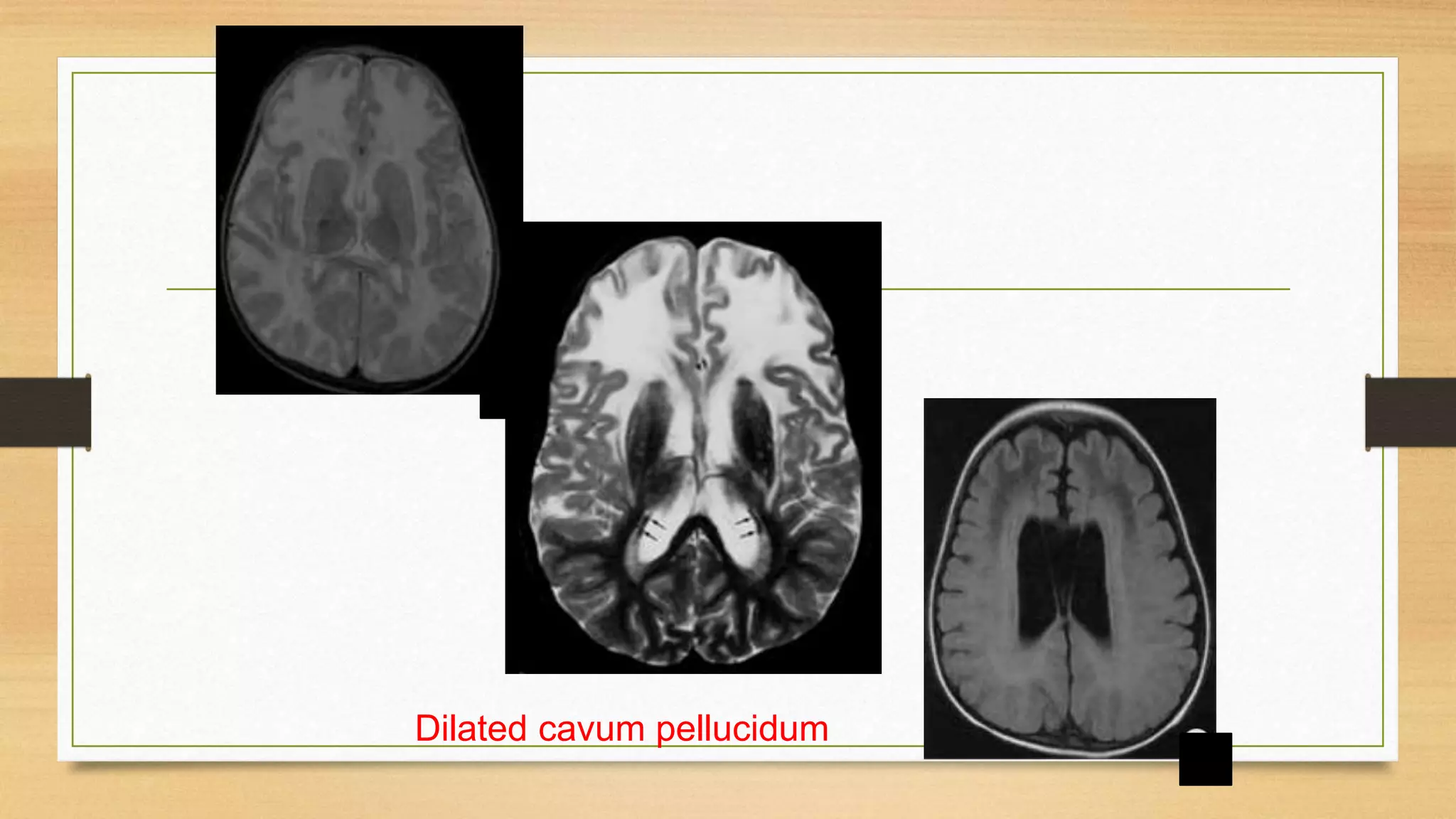
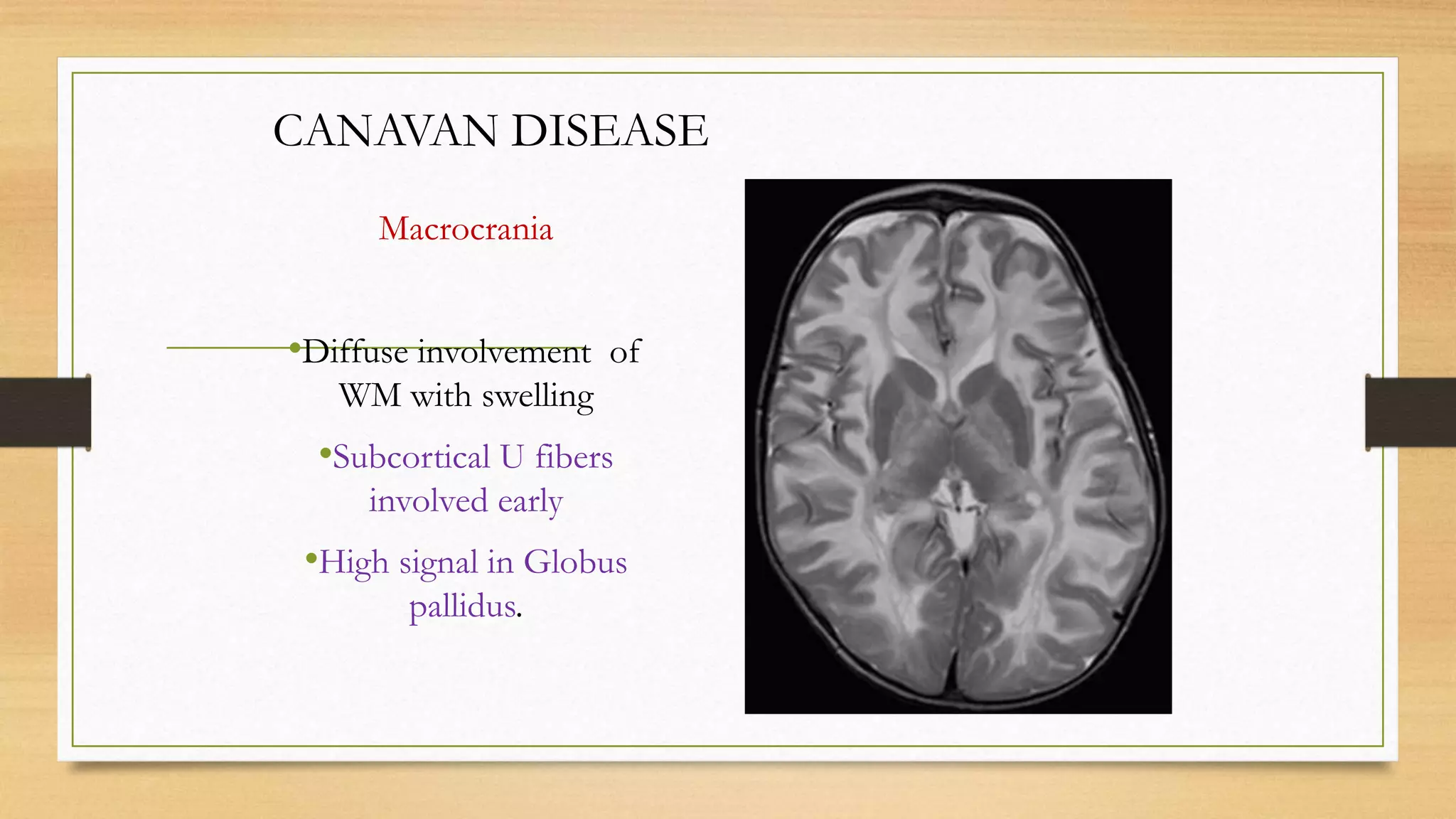
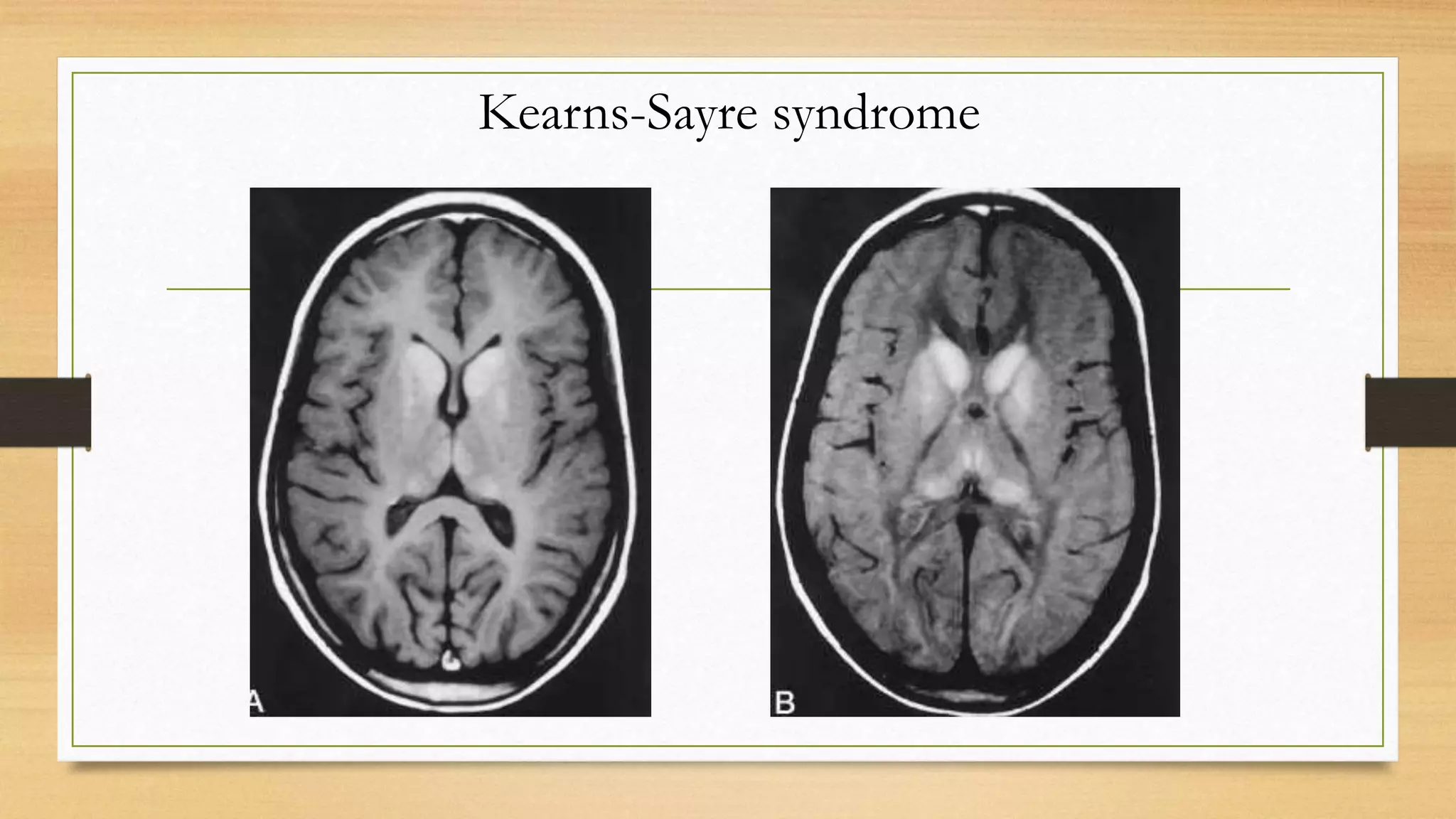
4. Specific white matter leukoencephalopathies are examined in detail including their genetics, organelle involvement, and distinguishing imaging features.