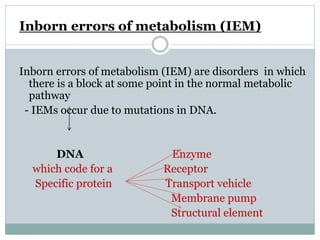
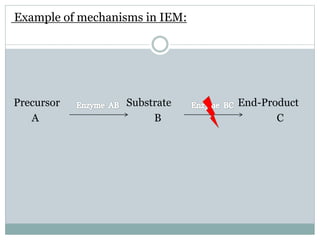
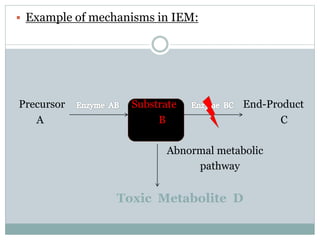
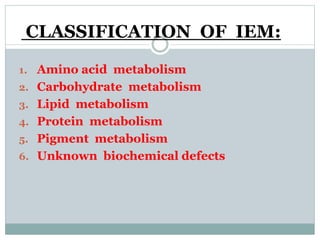
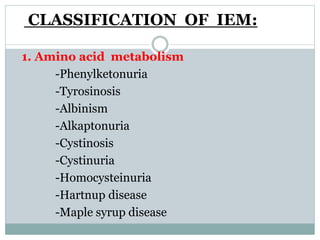
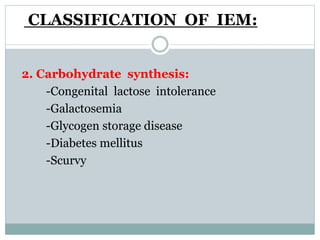
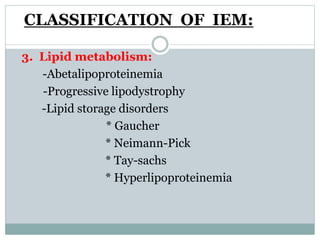
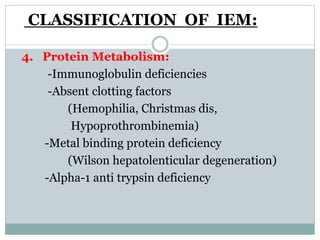
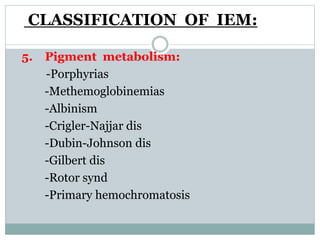
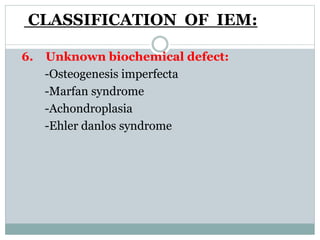
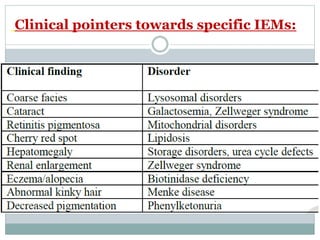
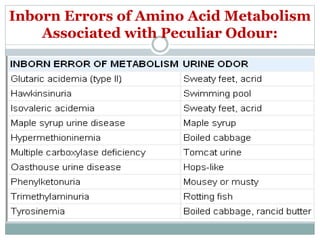
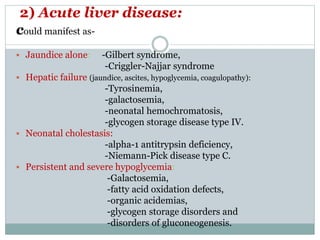
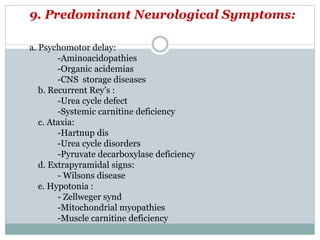
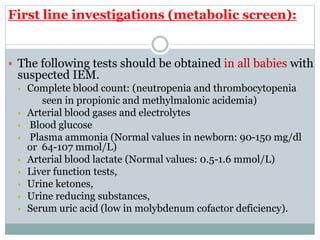
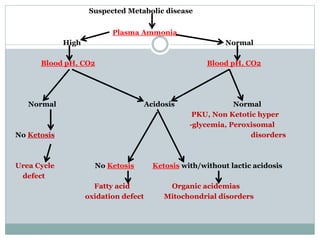
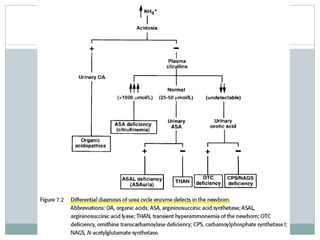
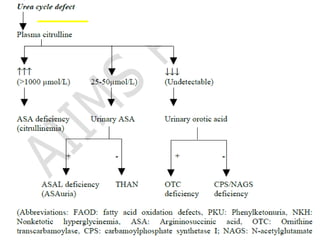
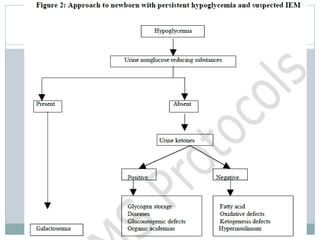
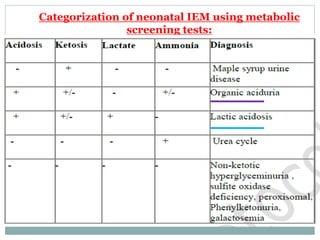
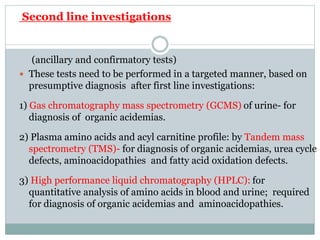
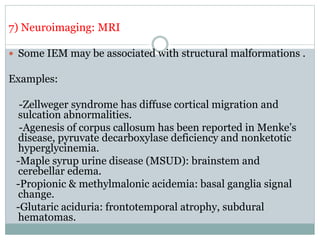
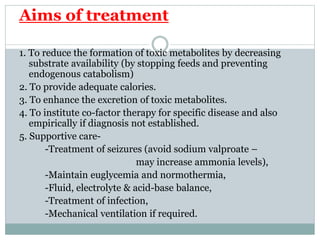
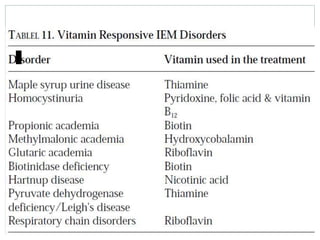
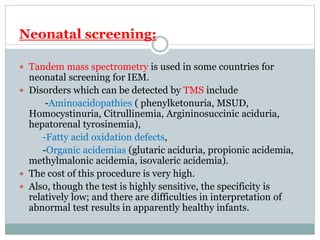
This document discusses inborn errors of metabolism (IEM), which are genetic disorders that block normal metabolic pathways. IEMs are caused by mutations that affect enzymes and proteins involved in metabolism. Symptoms vary depending on the specific pathway affected but may include developmental delay, seizures, liver disease, hypoglycemia, and dysmorphic features. The document outlines classifications of IEMs and provides examples. It also describes approaches to investigating and initially treating patients with suspected IEMs prior to establishing a specific diagnosis. These include metabolic screening tests, targeted further testing, and empirical management strategies to reduce toxic metabolites and support organ function.