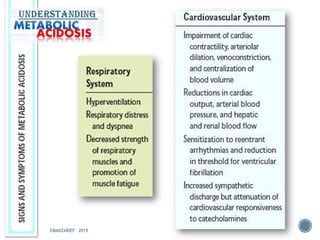
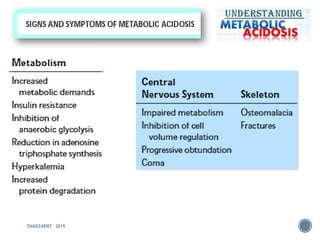
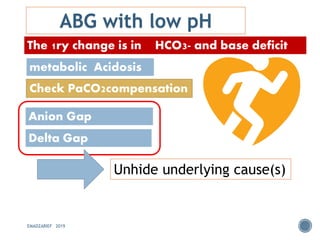
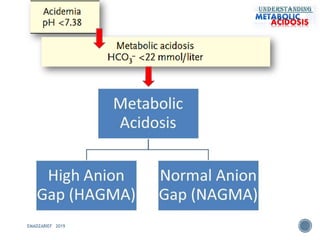
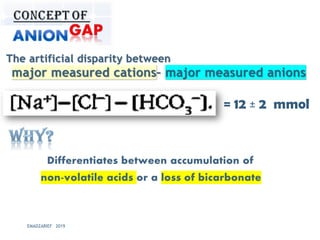
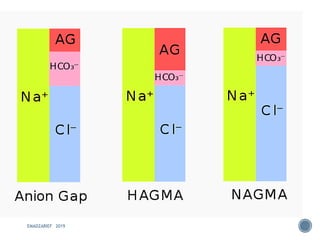
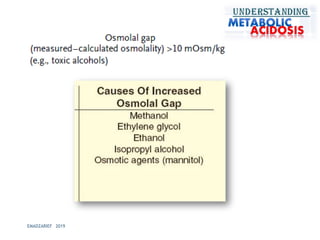
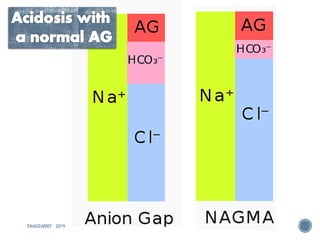
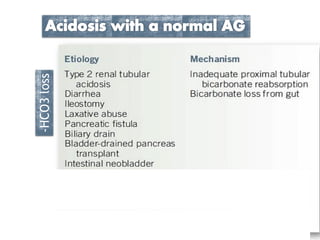
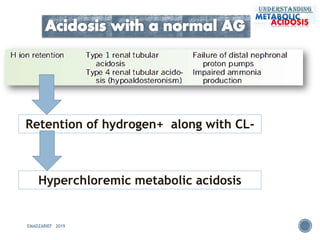
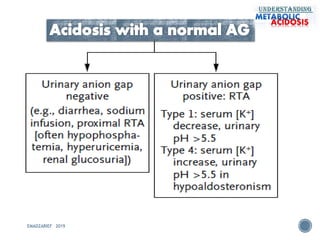
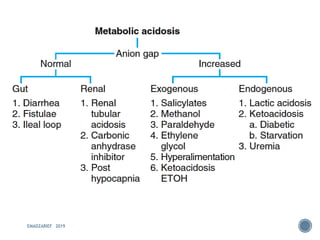
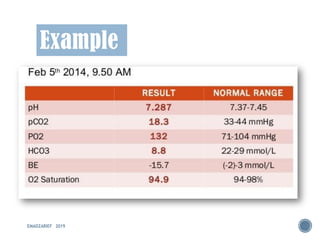
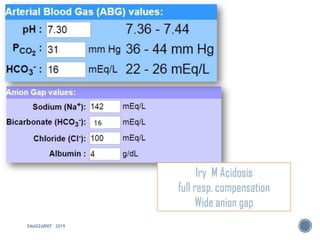
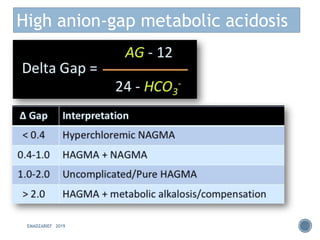
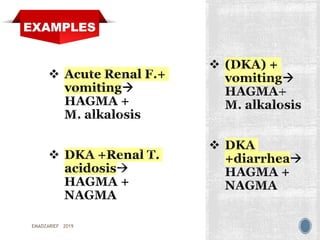
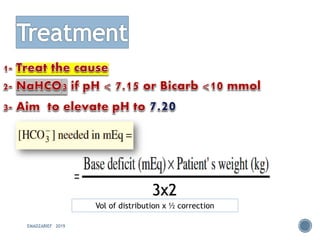
This document discusses metabolic acidosis, including its underlying causes, effects on the body, and diagnostic steps. It notes that metabolic acidosis can be caused by conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis, renal failure, intoxication, or shock. The 6 key steps for arterial blood gas interpretation are outlined, including evaluating pH, pCO2, HCO3, and determining the primary cause. Mixed disorders can complicate the diagnosis and treatment. Anion gap and delta gap help identify underlying causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis. Respiratory compensation and renal responses are also addressed.