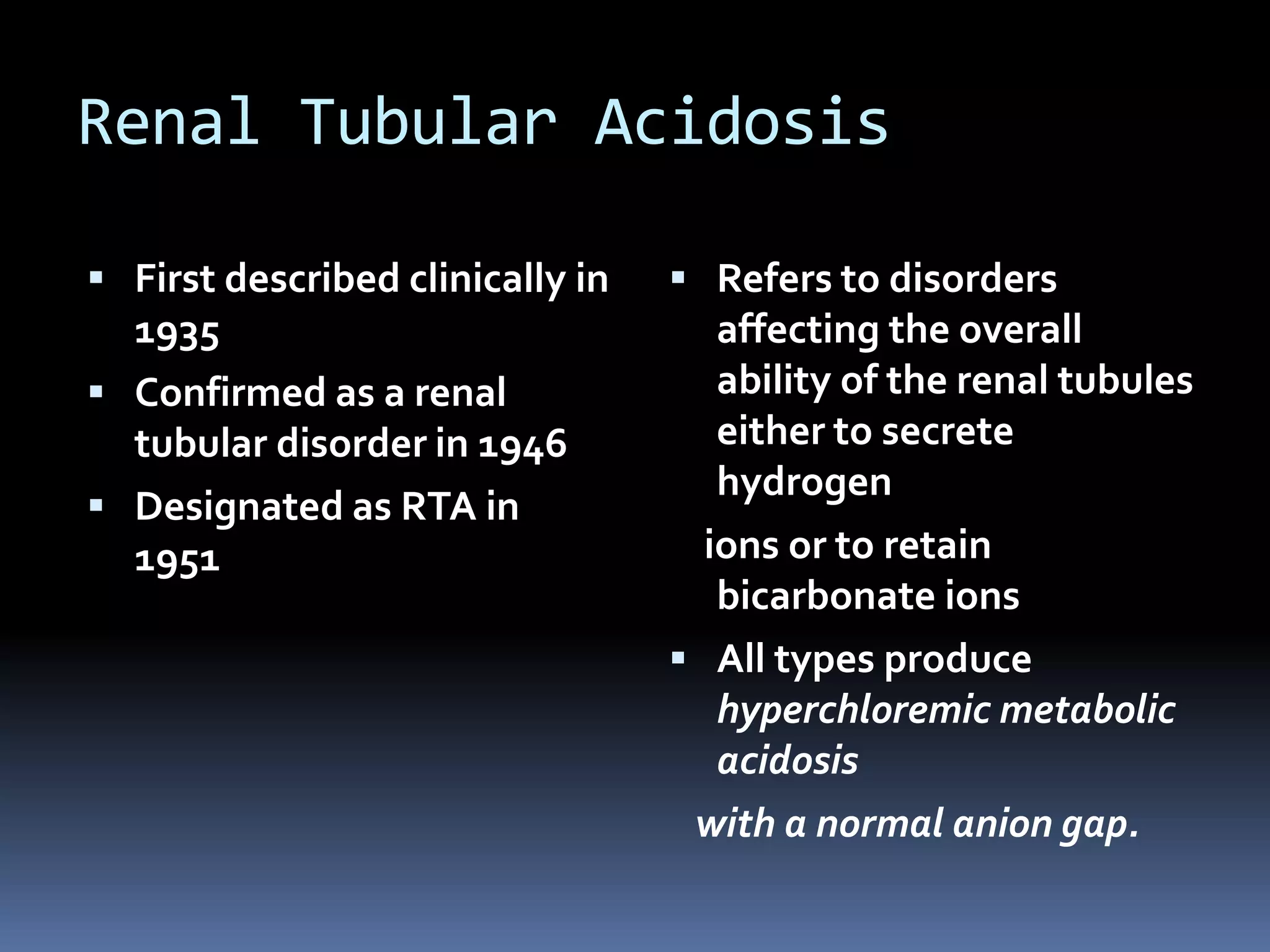
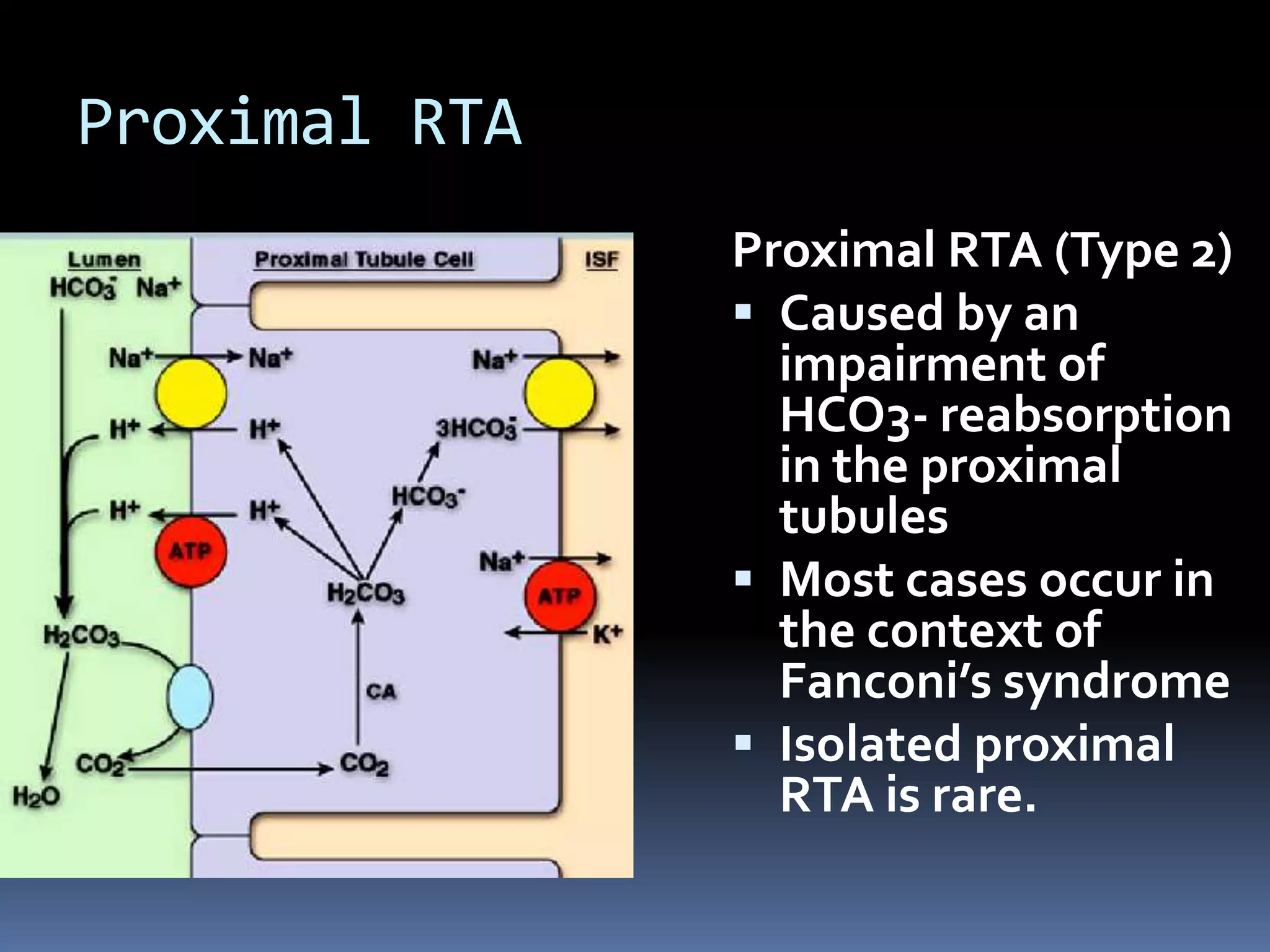
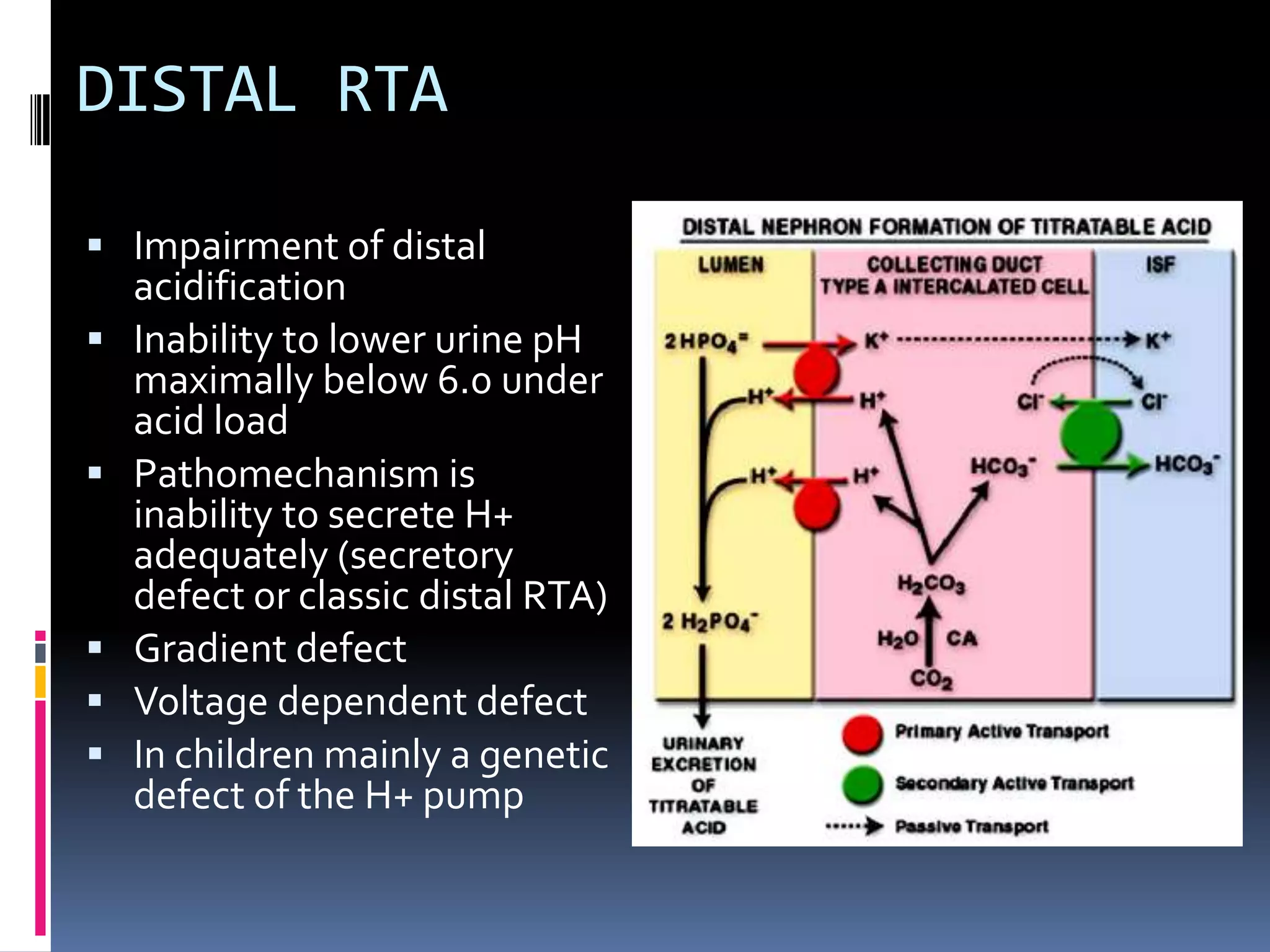
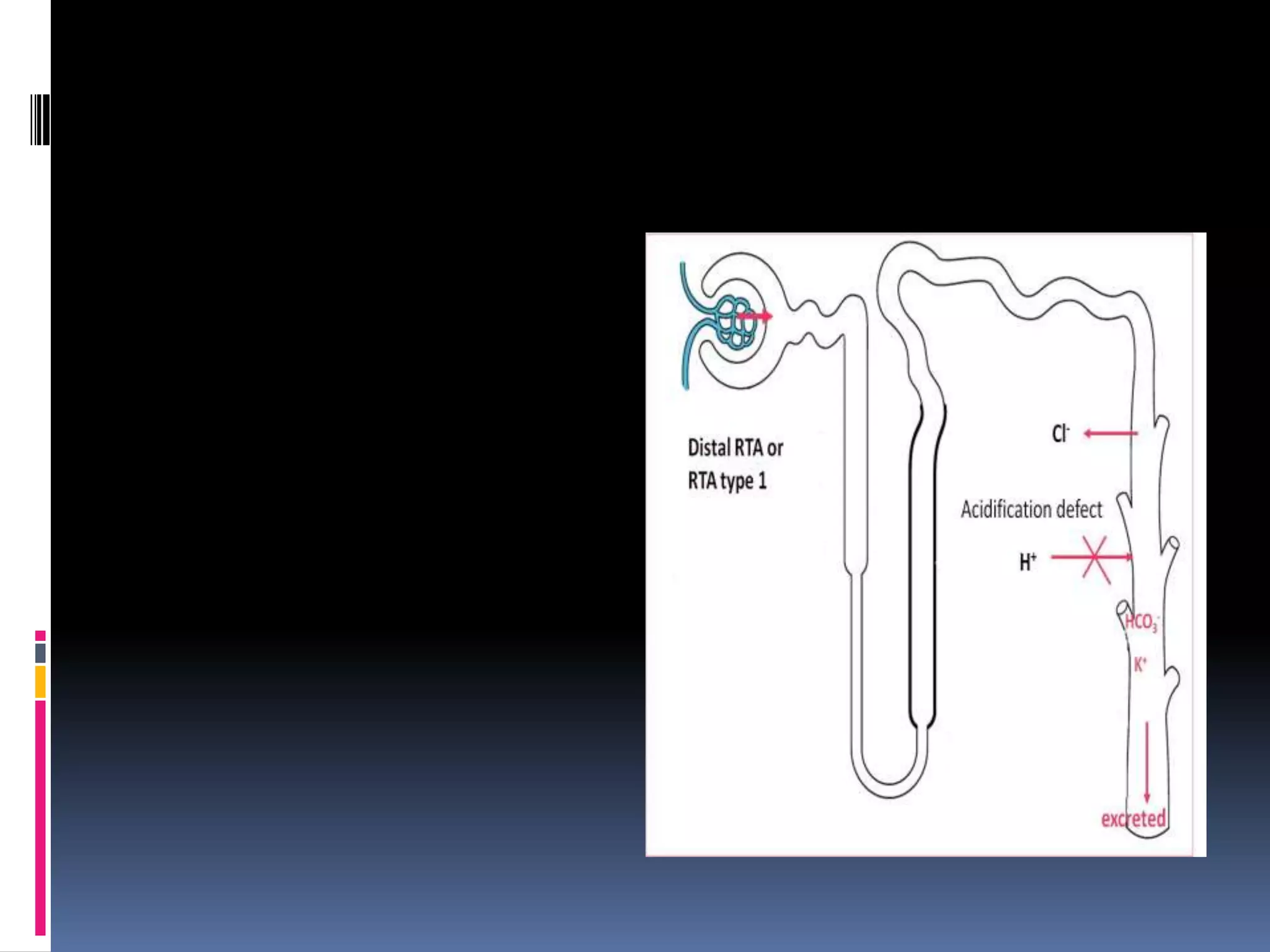
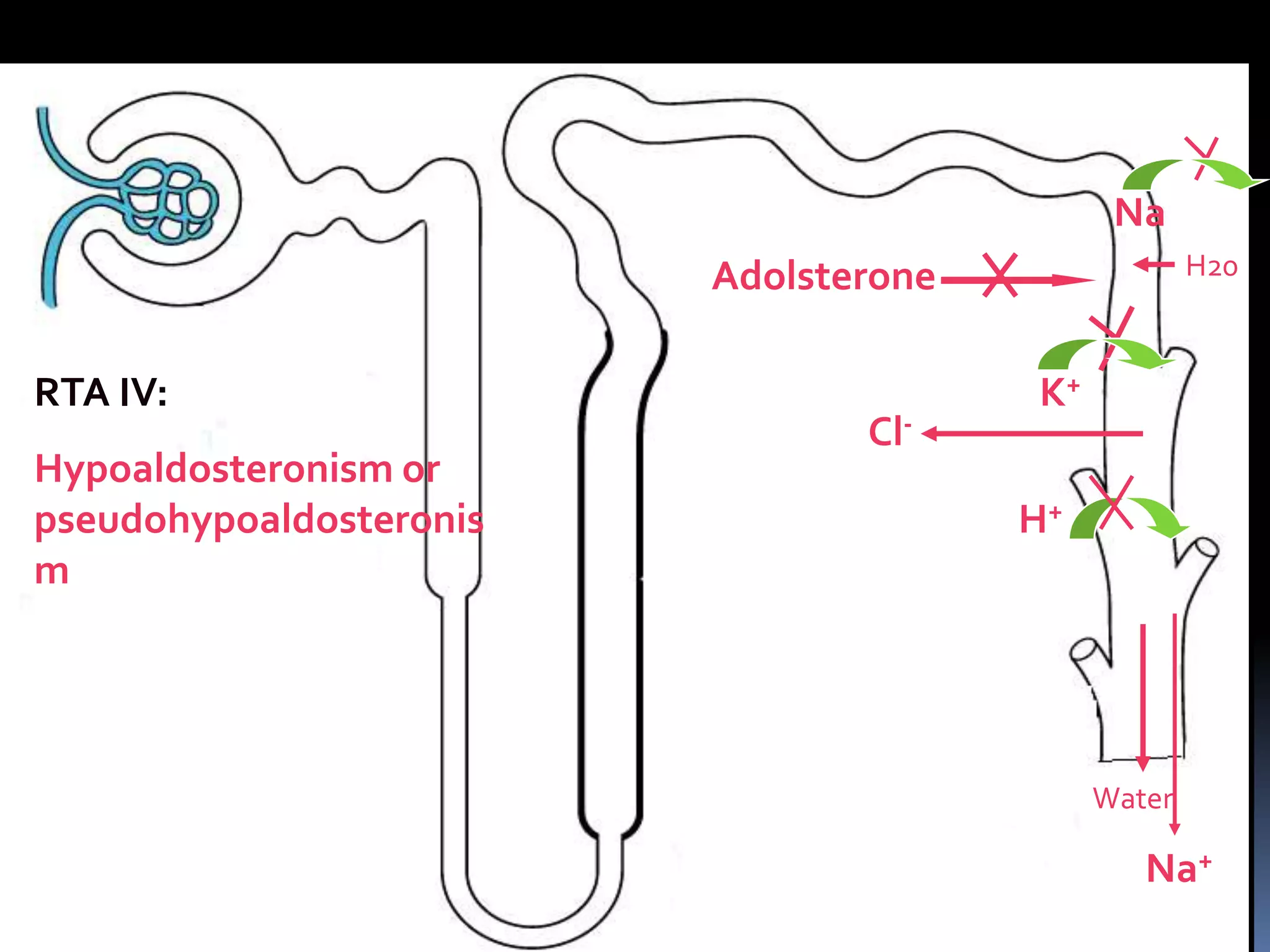
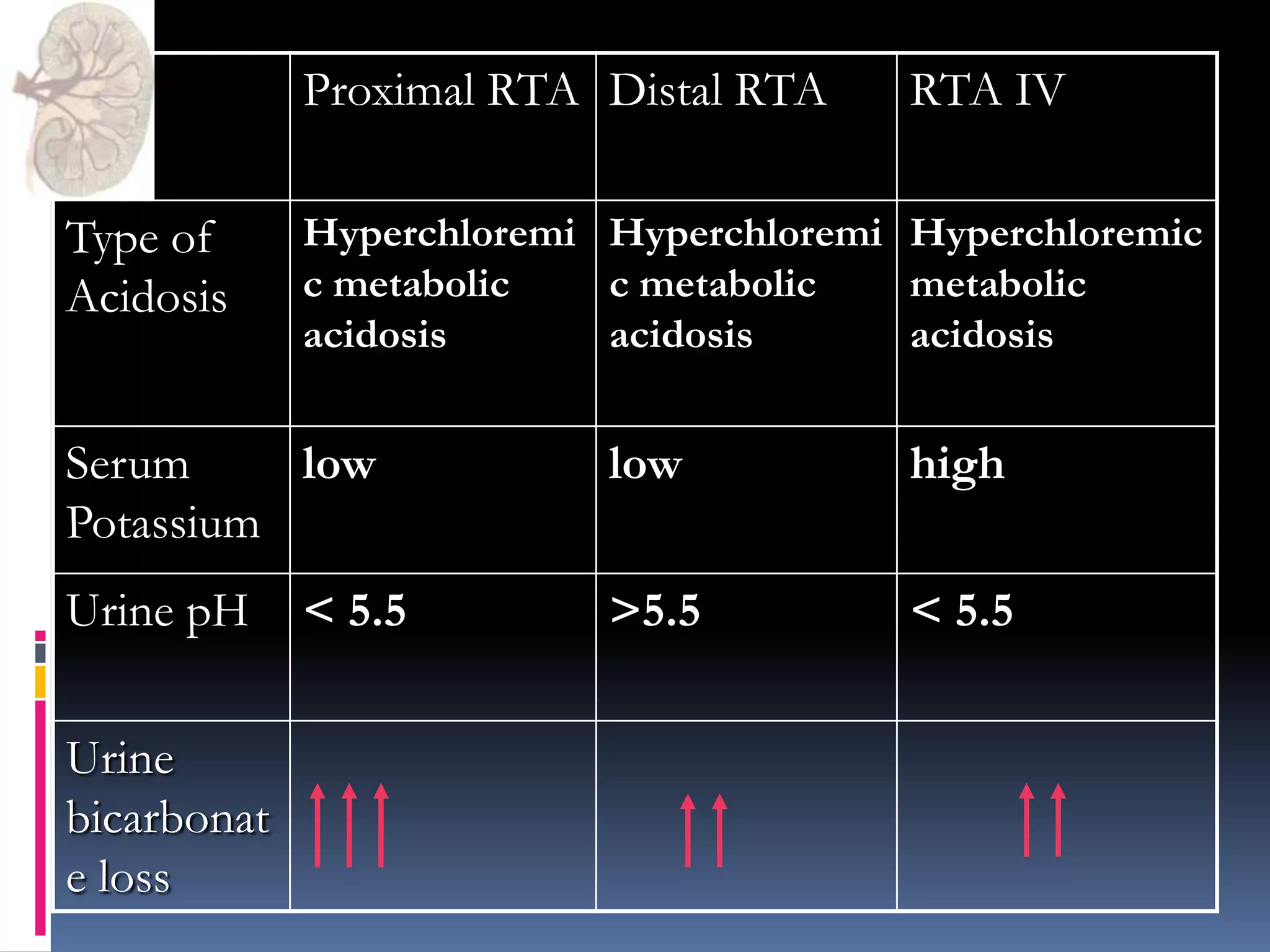
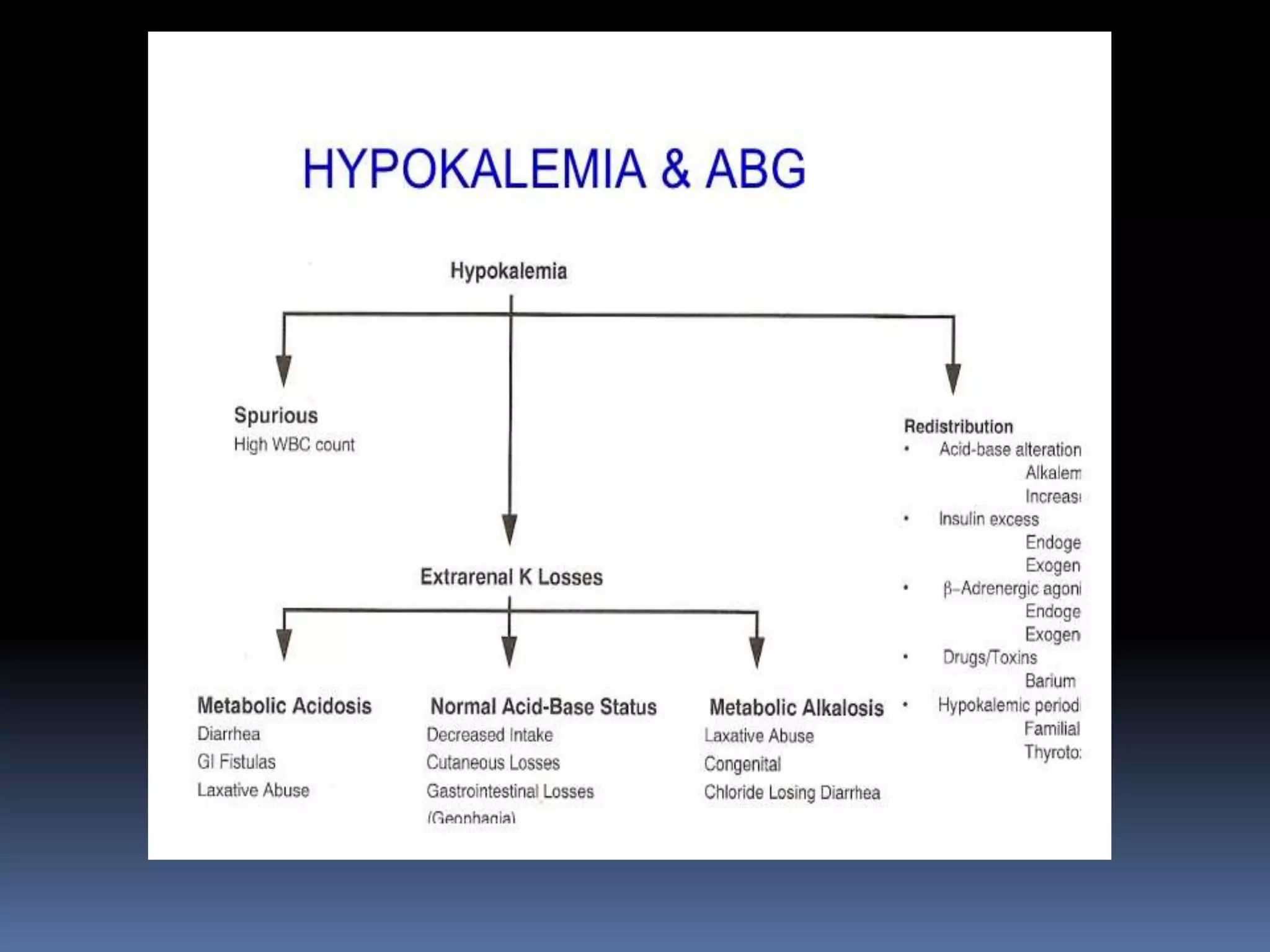
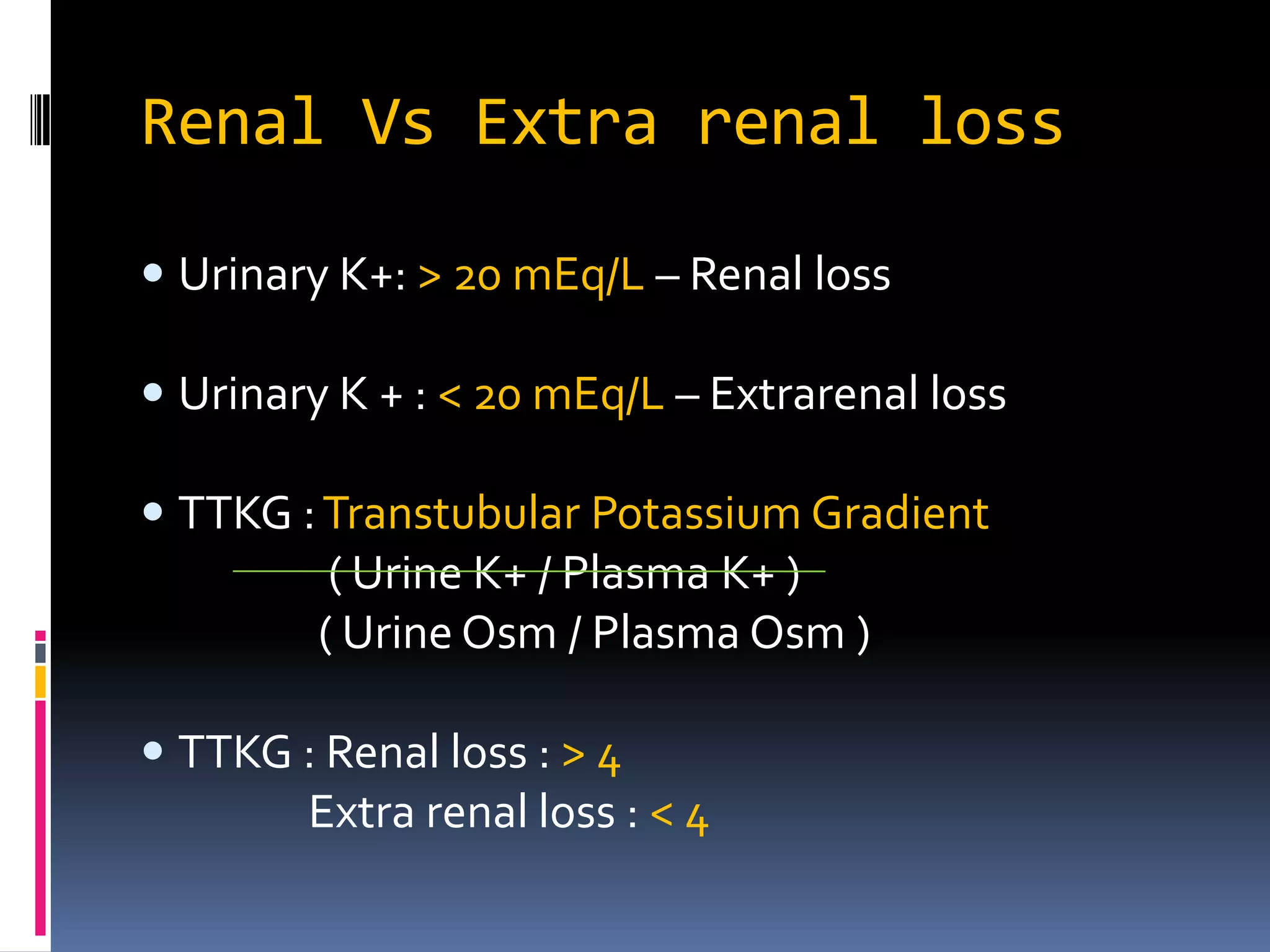
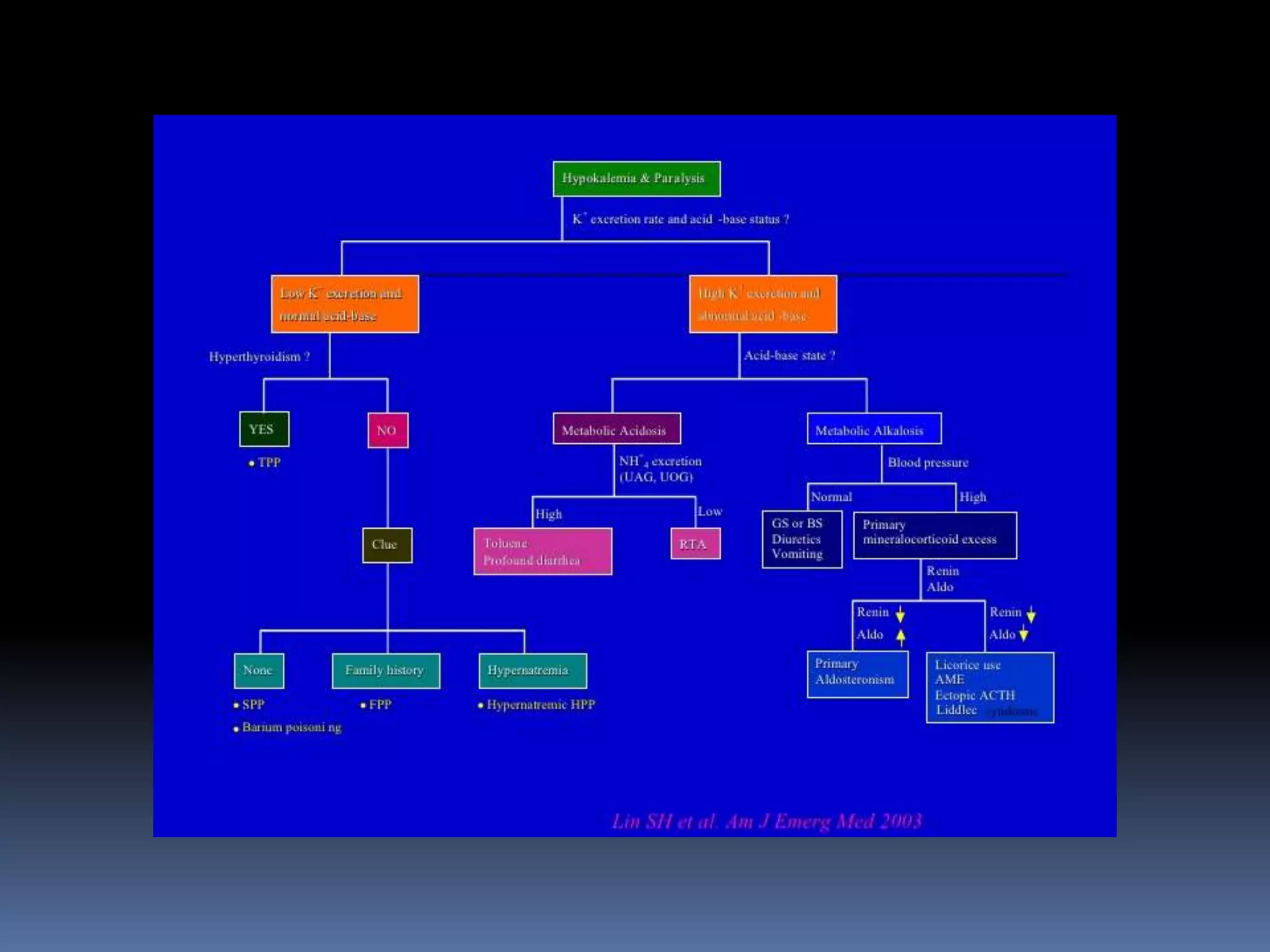
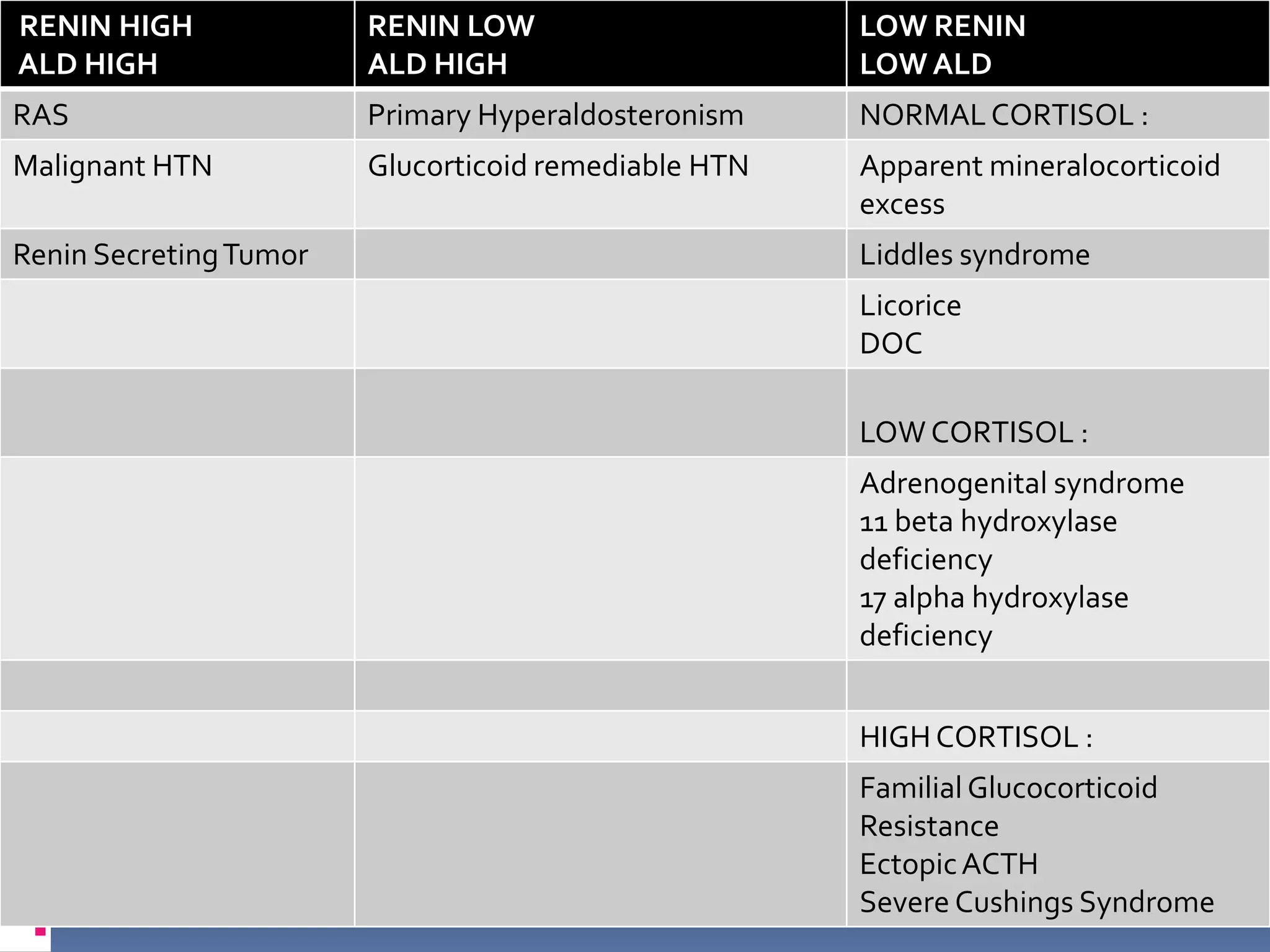
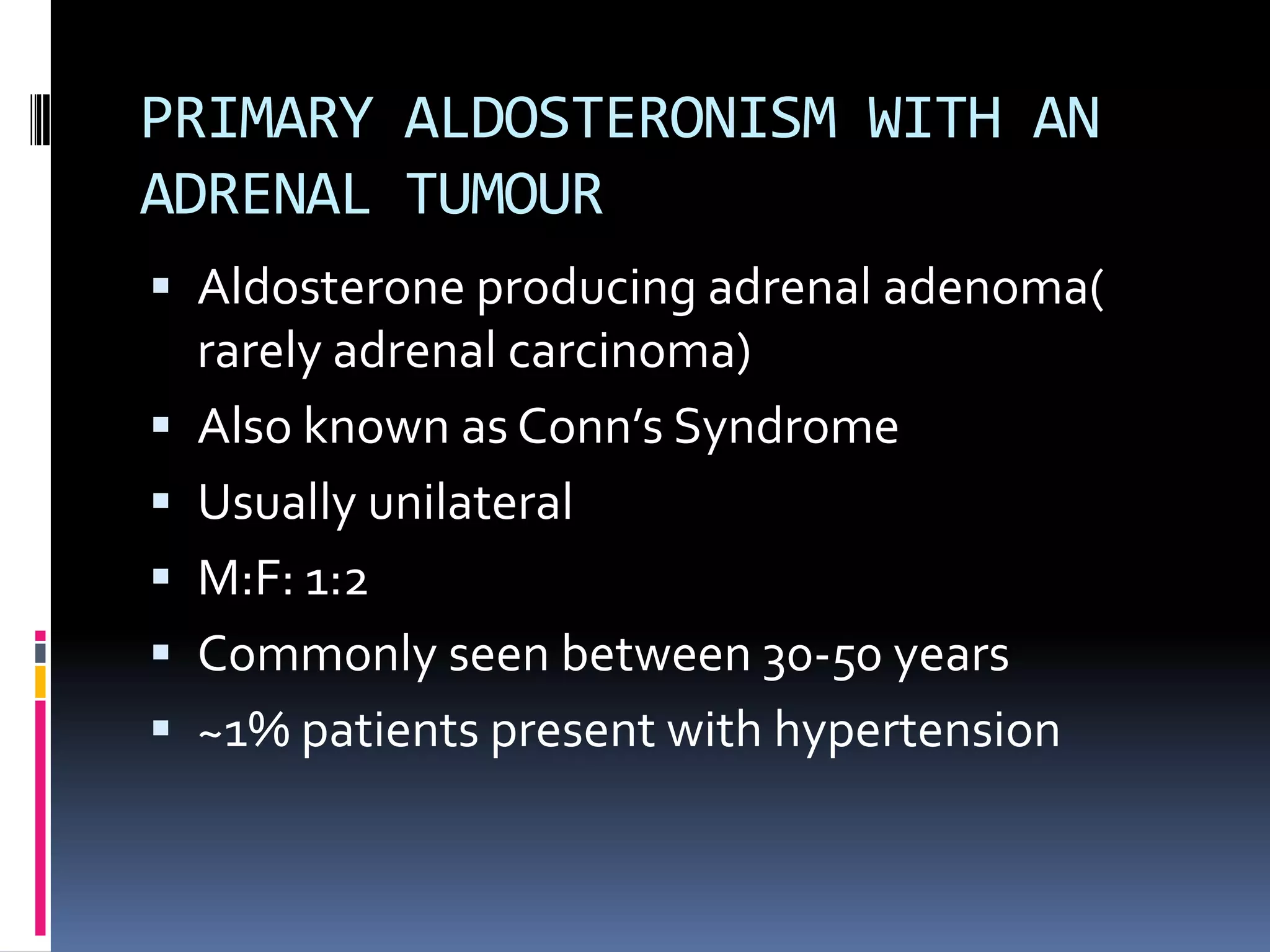
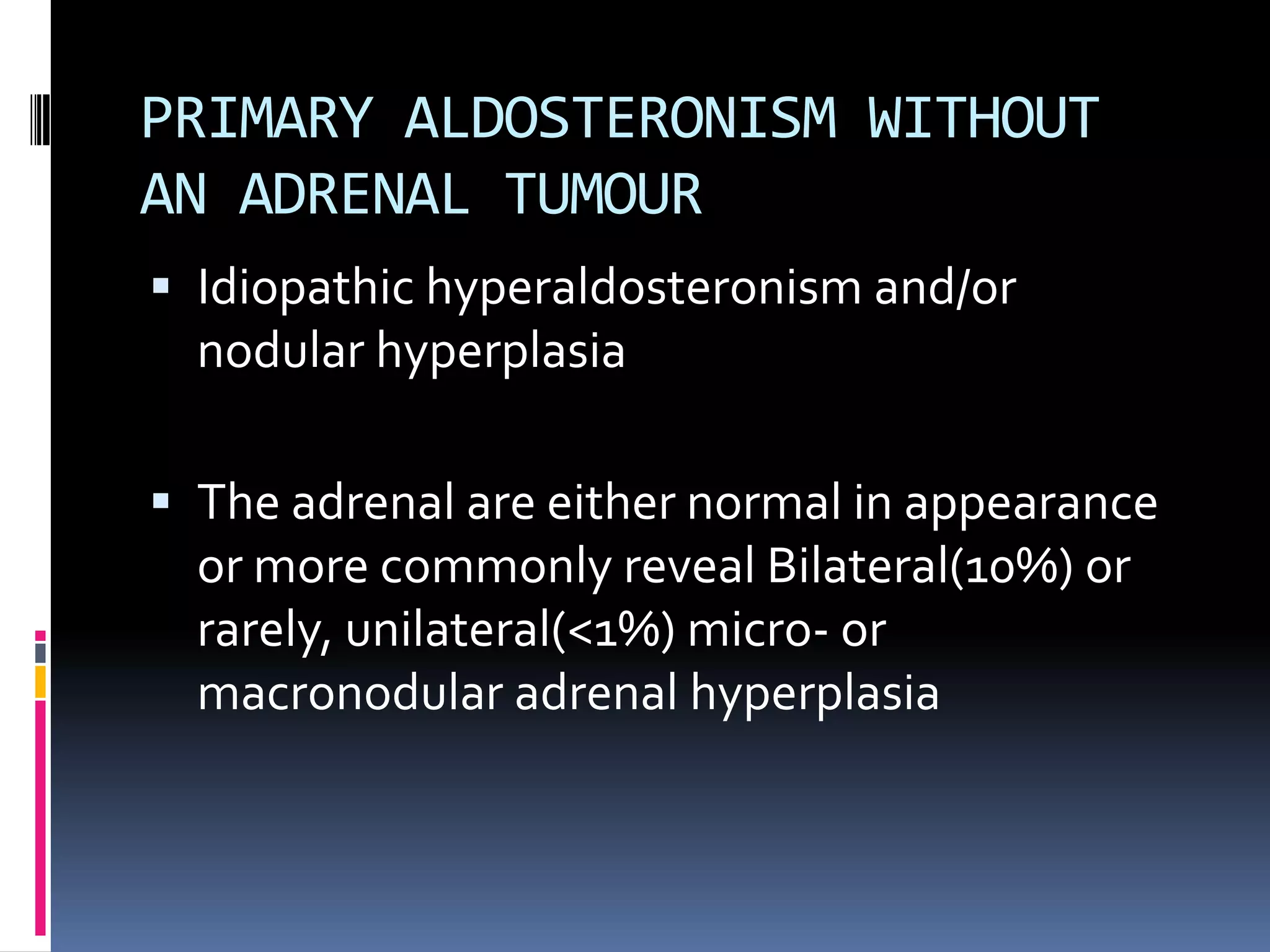
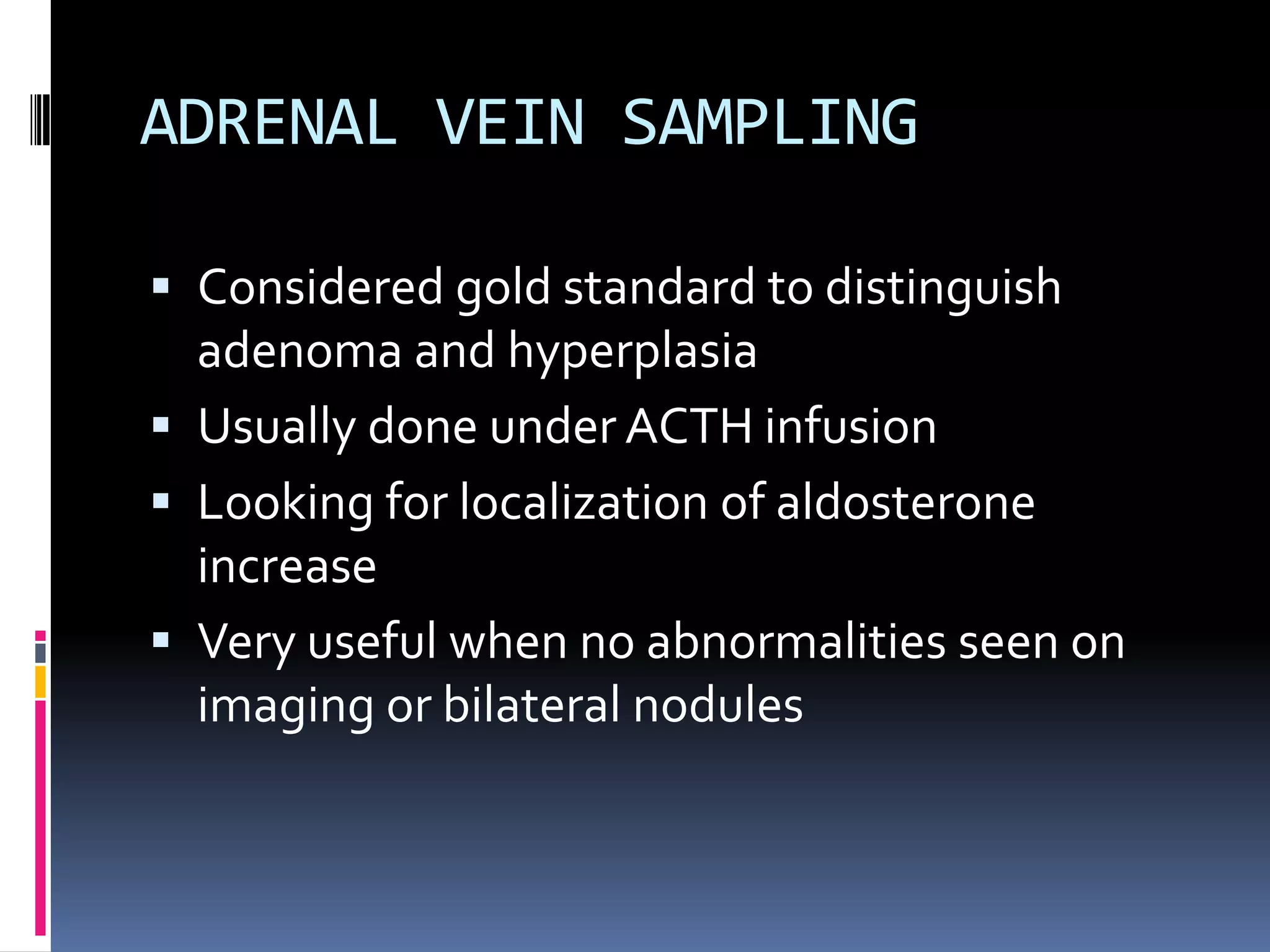
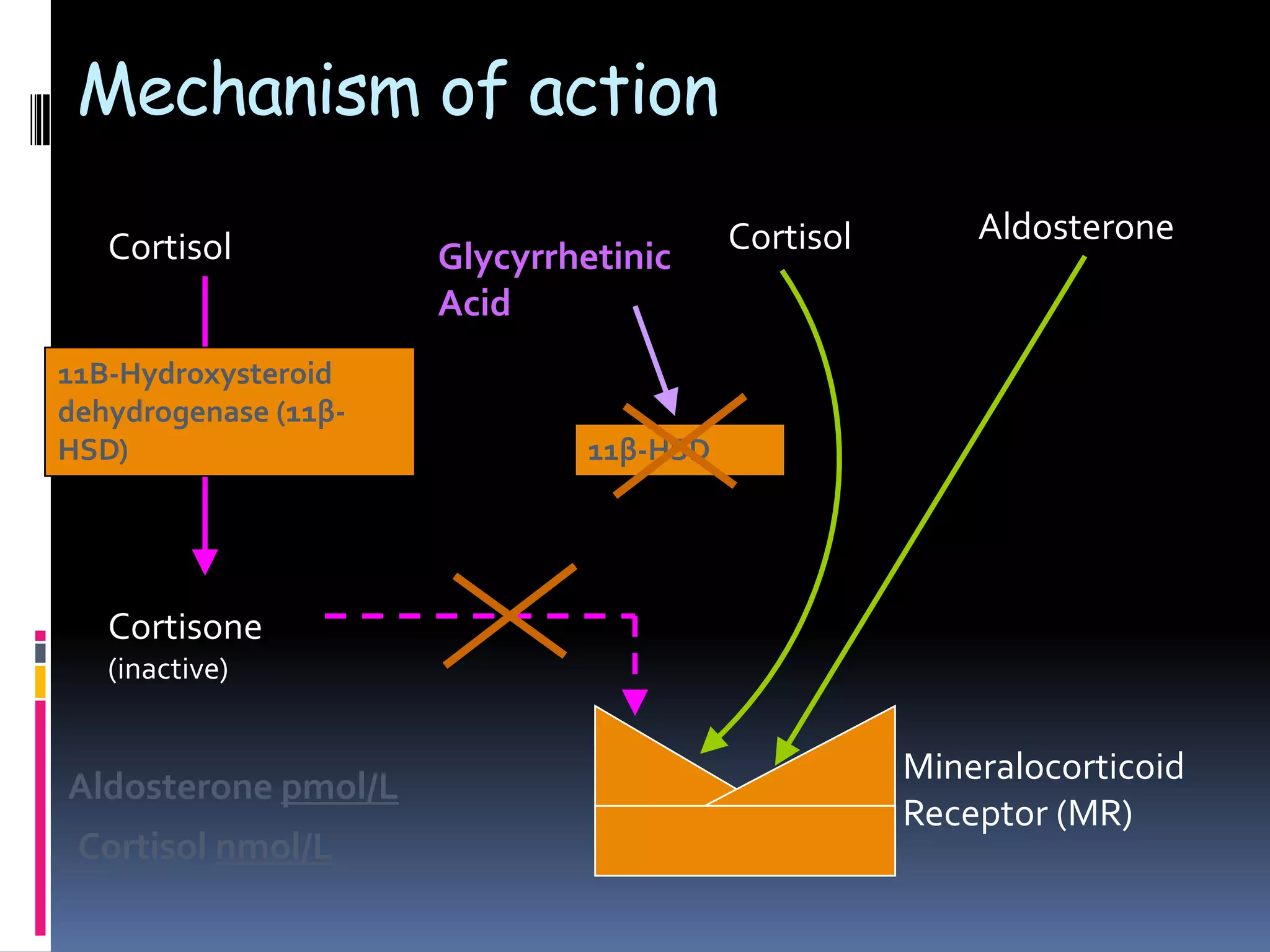
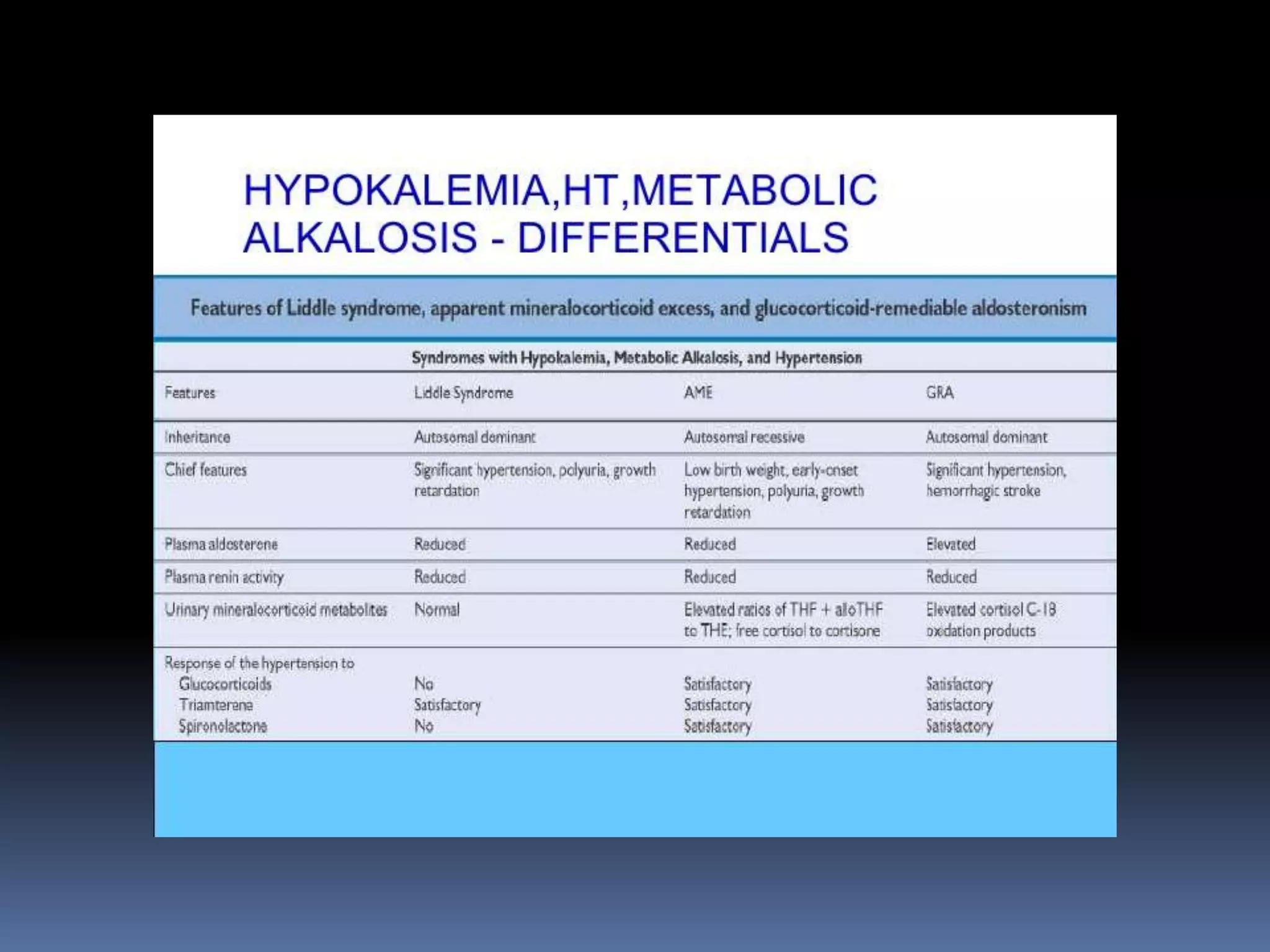
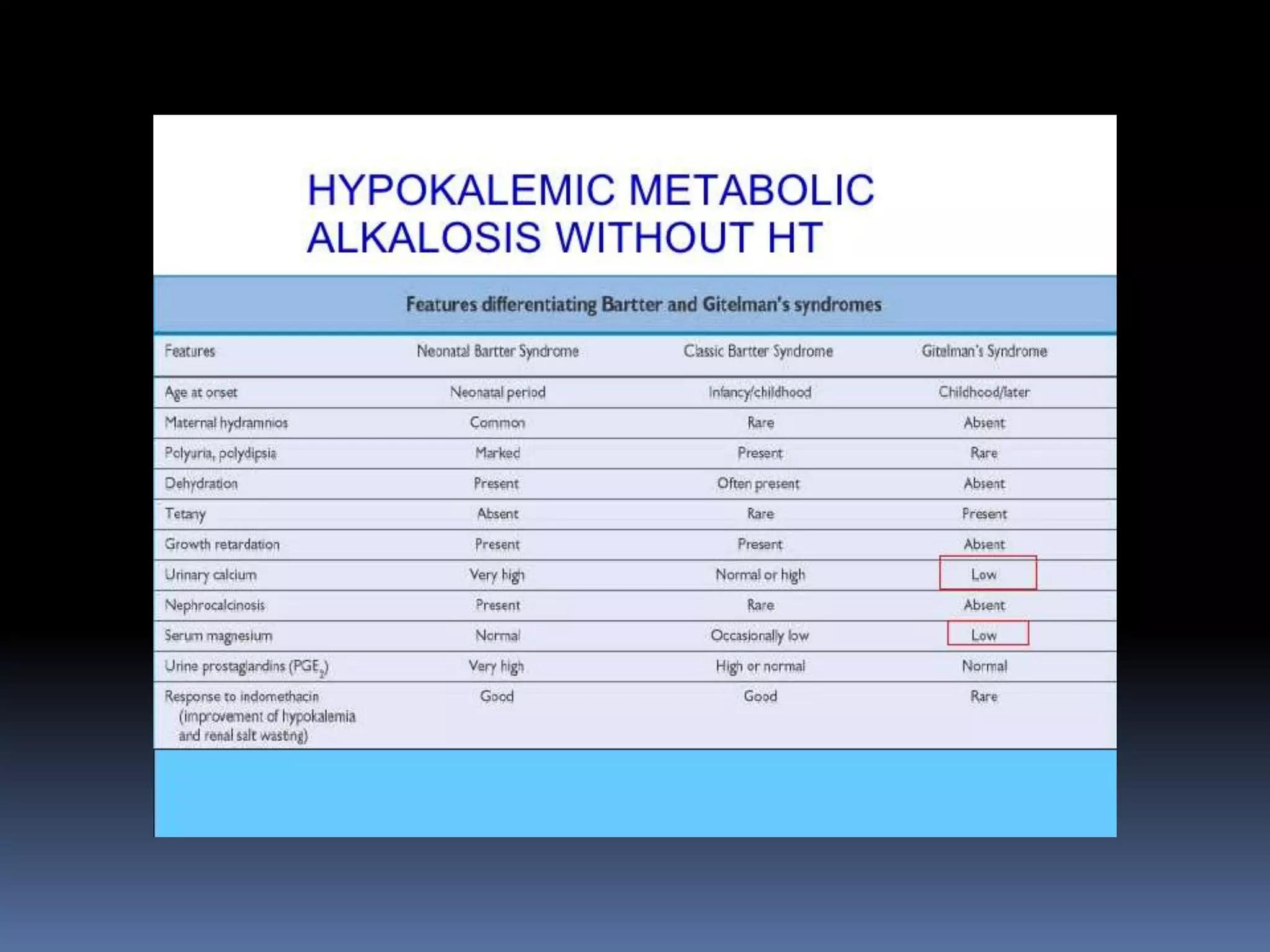
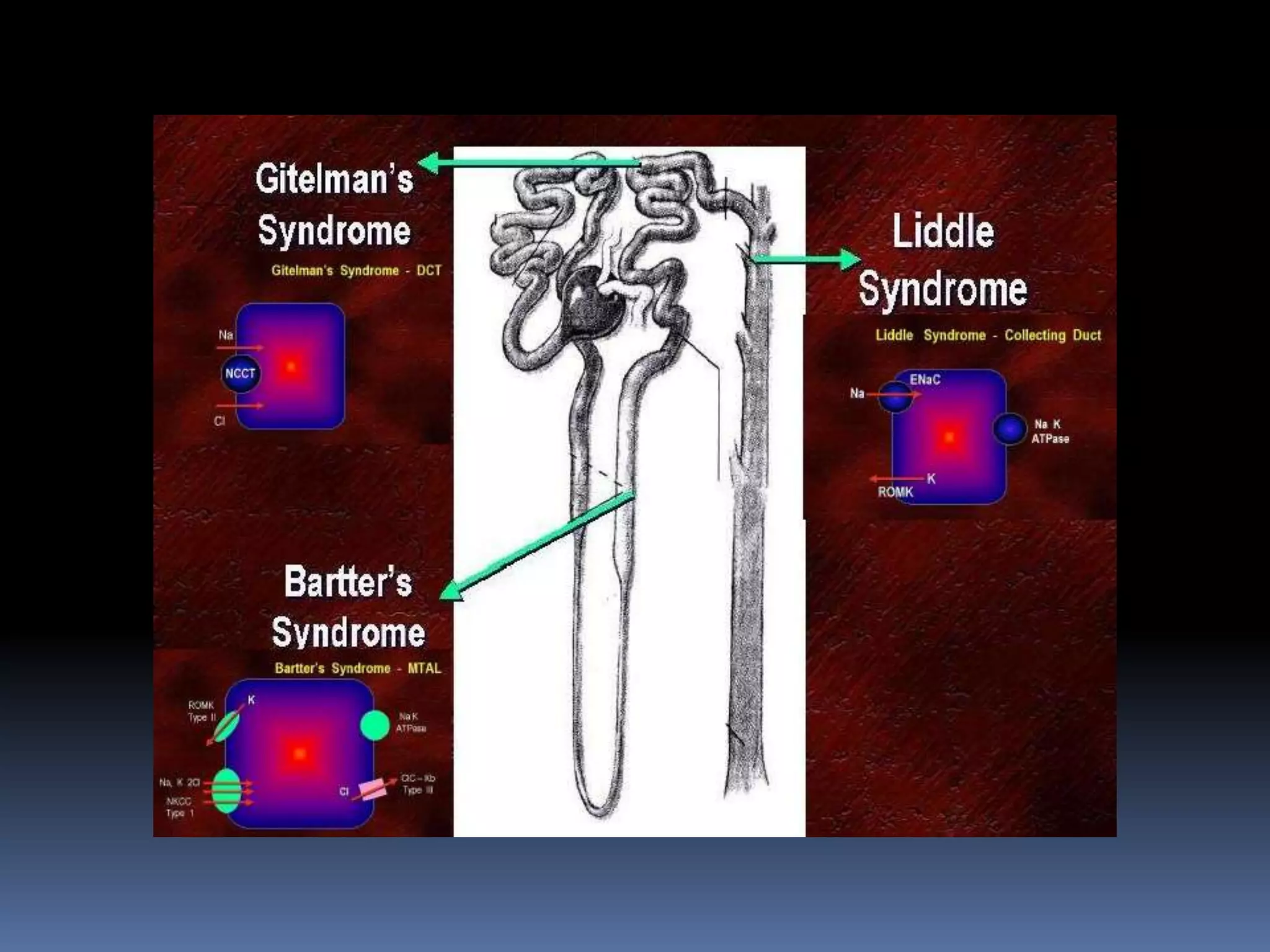
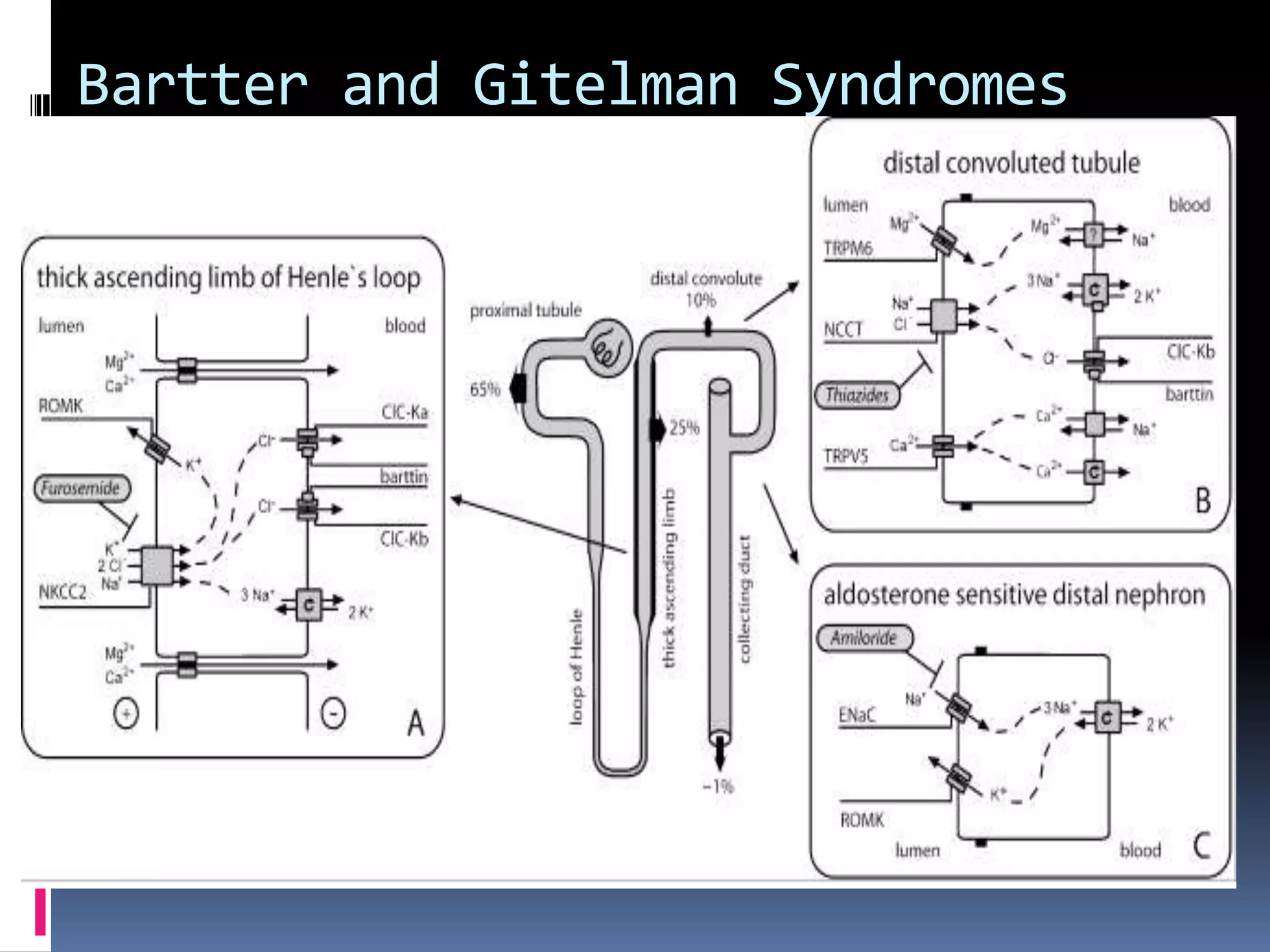
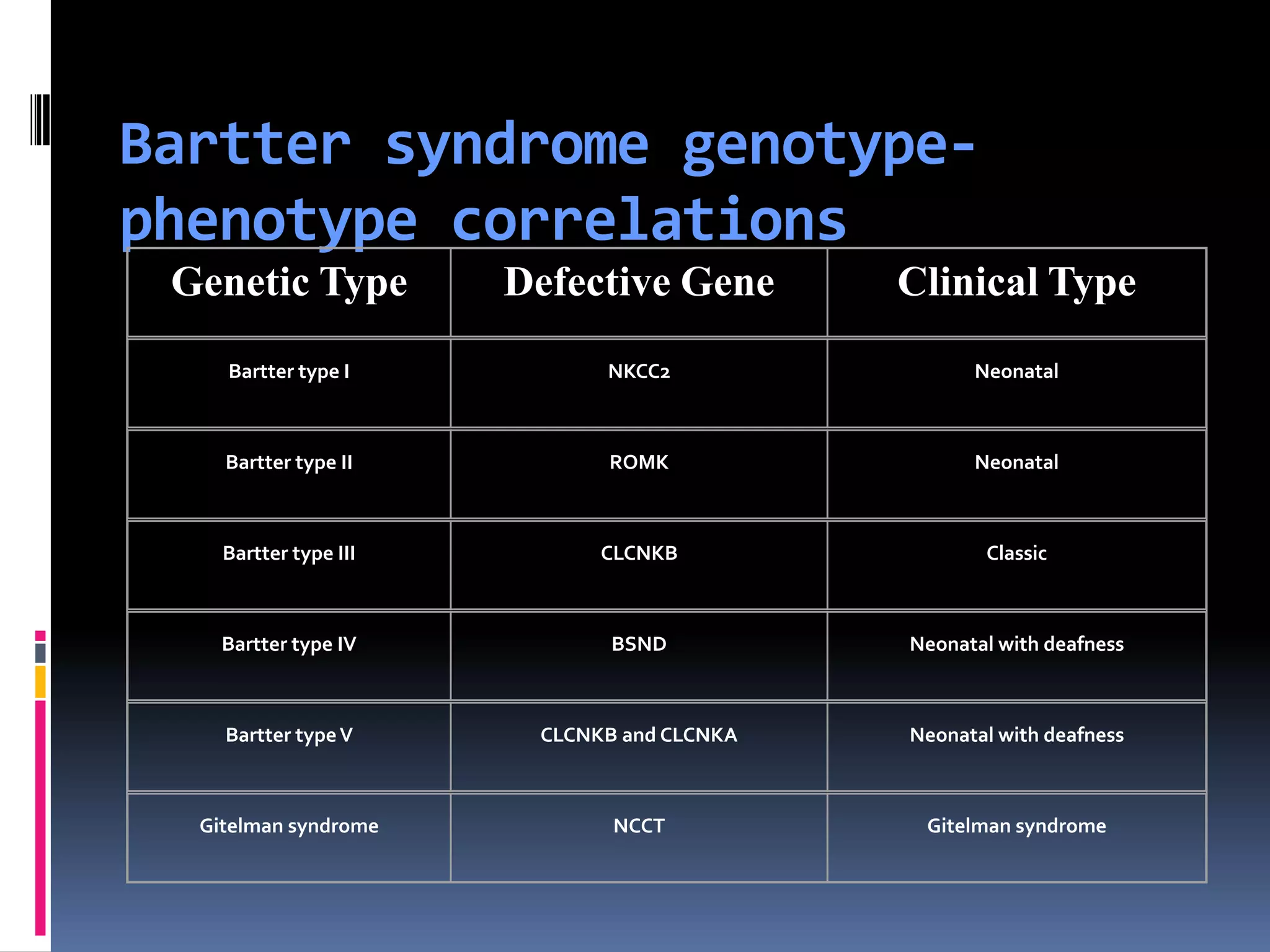
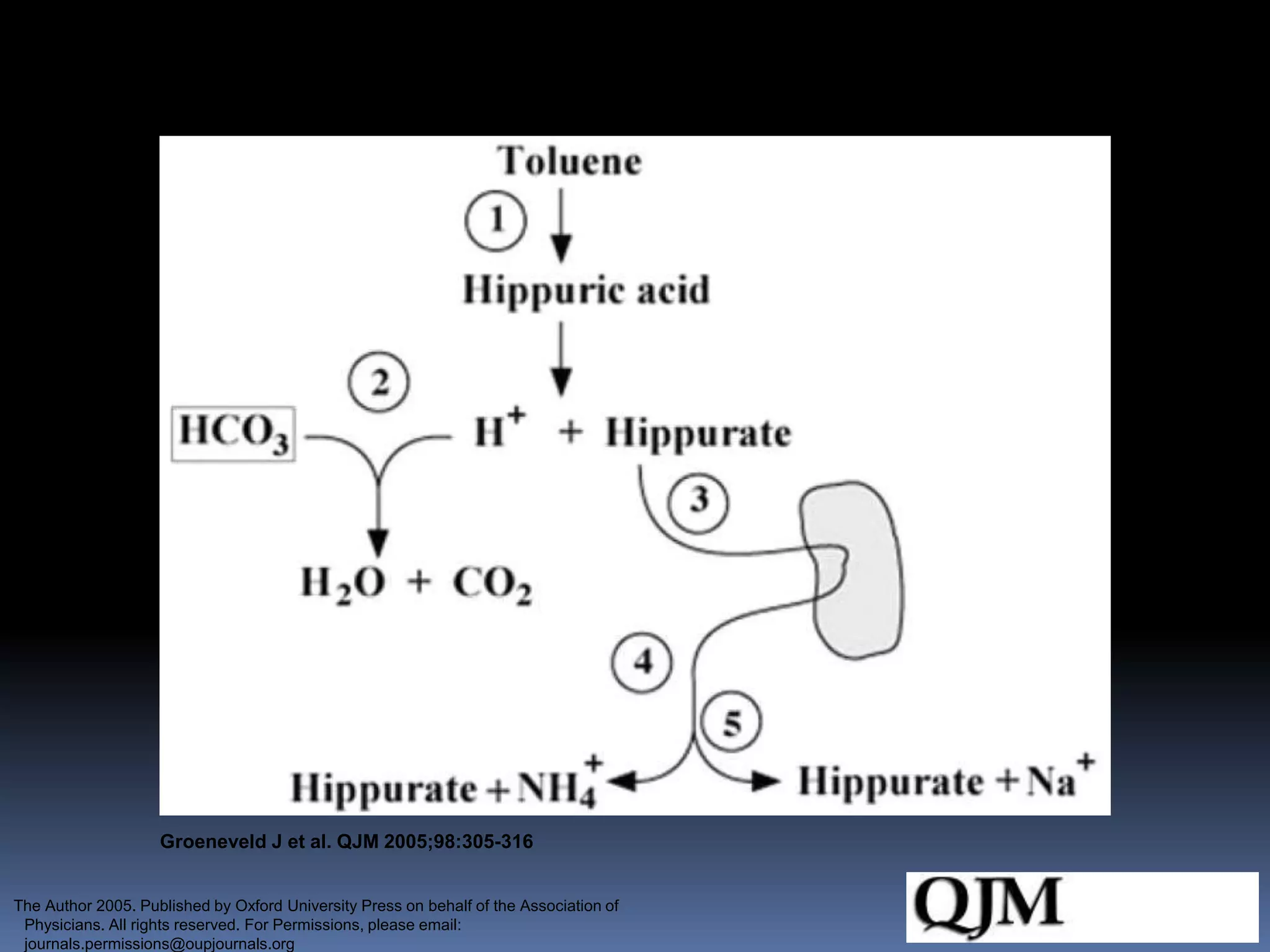
This document discusses the approach to hypokalemia. It begins by distinguishing between renal and extrarenal causes of hypokalemia based on urinary potassium levels and the transtubular potassium gradient. It then reviews various endocrine causes of hypokalemia related to the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Primary aldosteronism is discussed in more detail, including criteria for diagnosis, screening methods such as the aldosterone-renin ratio, and distinctions between forms with and without an adrenal tumor. Tests for evaluating renal tubular function like the urine anion gap and methods for diagnosing renal tubular acidosis are also summarized.











![Urine anion gap (UAG)
Urine anion gap = [Na+] + [K+] – [Cl-]
Normal: zero or positive
Metabolic acidosis: NH4+ excretion increases (which is excreted with
Cl-) if renal acidification is intact
GI causes: “neGUTive” UAG
Impaired renal acid excretion (RTA): positive or zero
Often not necessary b/c clinically obvious (diarrhea)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtohypokalemia-140429090209-phpapp02/75/Approach-to-Hypokalemia-27-2048.jpg)

![Urine osmolal gap
When the urine AG is positive and it is unclear
whether increased excretion of unmeasured
anions is responsible, the urine ammonium
concentration can be estimated from
calculation of the urine osmolal gap.
UOG=Uosm - 2 x ([Na + K]) + [urea
nitrogen]/2.8 + [glucose]/18.
UOG of >100 represents intact NH4 secretion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtohypokalemia-140429090209-phpapp02/75/Approach-to-Hypokalemia-29-2048.jpg)

![TTKG
TTKG is a concentration gradient between the
tubular fluid at the end of the cortical collecting
tubule and the plasma.
TTKG = [Urine K ÷ (Urine osmolality / Plasma
osmolality)] ÷ Plasma K.
Normal value is 8 and above.
Value <7 in a hyperkalemic patient indicates
hypoaldosteronism.
This formula is relatively accurate as long as the
urine osmolality exceeds that of the plasma urine
sodium concentration is above 25 meq/L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtohypokalemia-140429090209-phpapp02/75/Approach-to-Hypokalemia-31-2048.jpg)