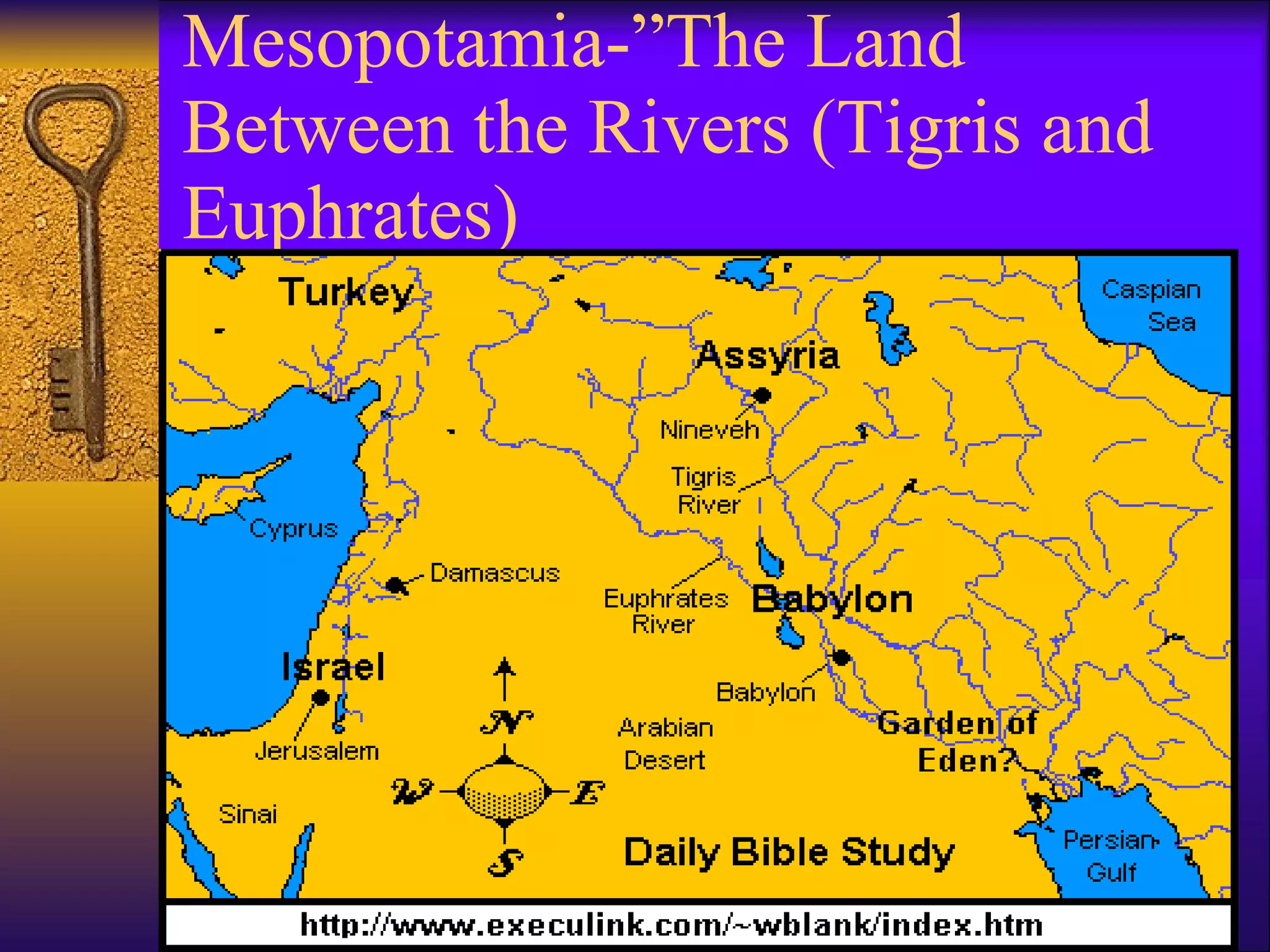
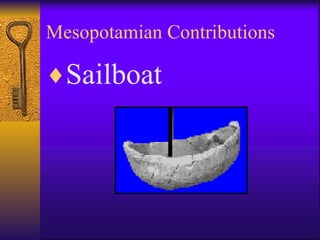
Mesopotamia, located in present-day Iraq, was the site of one of the earliest known civilizations. Its settlers were herders who began controlling their environment through irrigation canals and growing crops like barley. They lived in city-states like Ur, with mud brick walls for protection, temples as the center of community life, and developed legal systems as populations grew. Mesopotamian achievements included some of the first written laws, use of the wheel, plow, sailboat, and a 12-month calendar based on astronomy.