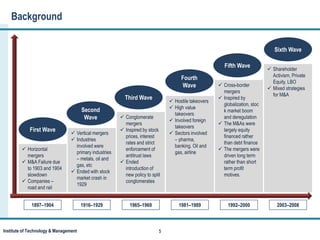
This document provides an overview and agenda for a presentation on mergers and acquisitions (M&A). It discusses the definitions of mergers and acquisitions. It also outlines the classification of M&A into horizontal mergers, vertical mergers, conglomerate mergers, and acquisitions and takeovers. The document describes the six waves of M&A activity historically. It then details the generic process of M&A in six stages: pre-merger planning, planning for M&A, execution, delivering on targets, and unlocking value. Finally, it lists some of the key Indian regulatory acts that govern M&A activity.