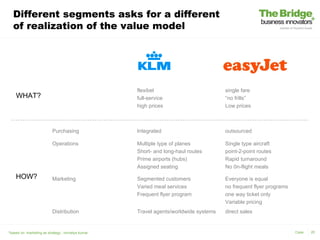
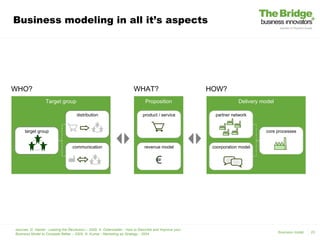
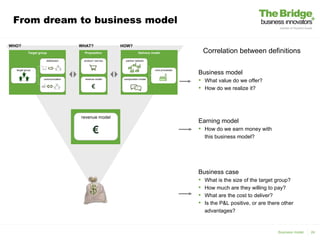
This document discusses business modeling and its importance. It contains the following key points in 3 sentences:
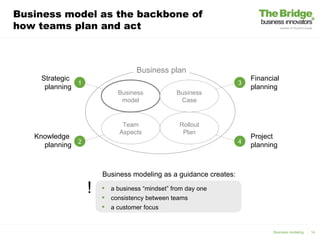
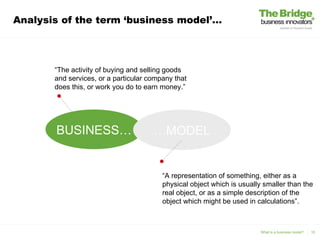
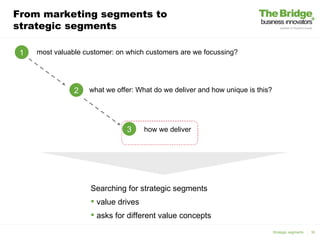
1) Business modeling creates a business "mindset" from the start, ensures consistency across teams, and keeps a customer focus. 2) The document analyzes the terms "business" and "model" and provides definitions. 3) It discusses identifying the most valuable customers to organize around, determining what unique value is offered to customers, and how that value is delivered.