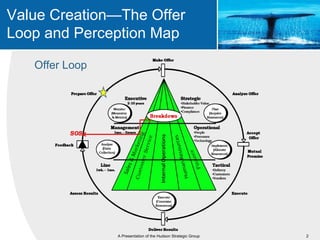
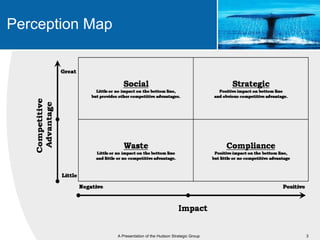
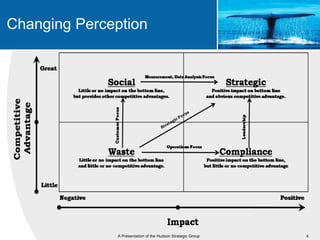
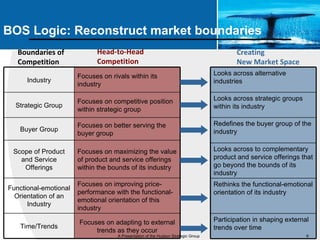
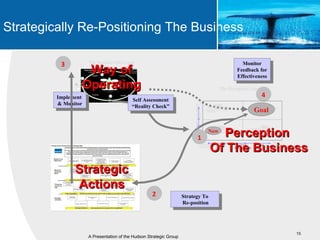
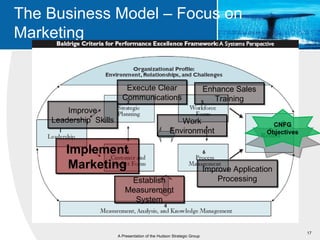
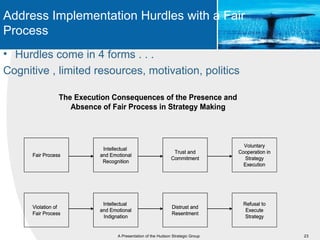
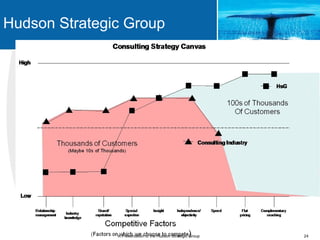
This document provides an overview of blue ocean strategy (BOS) and how to develop a BOS. It discusses key principles of BOS including reconstructing market boundaries, focusing on value innovation rather than competition, and getting the strategic sequence right. The document outlines tools for analyzing the current market situation, identifying new opportunities, and addressing barriers to implementing a new strategy. The overall goal of BOS is to create new demand by shifting focus from competitors to value creation for customers.