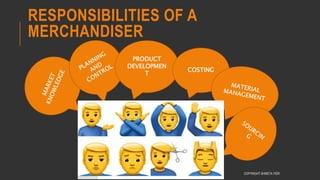
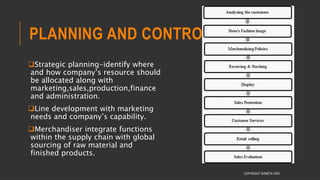
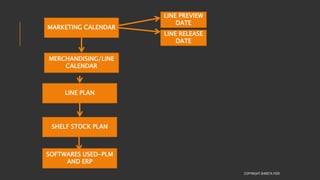
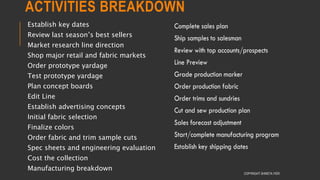
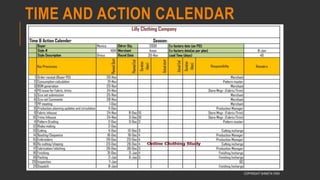
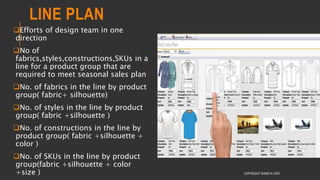
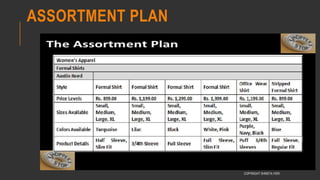
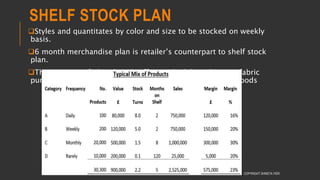
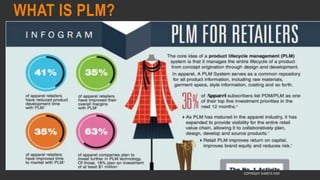
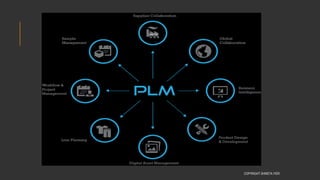
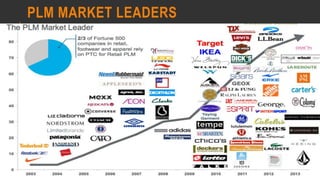
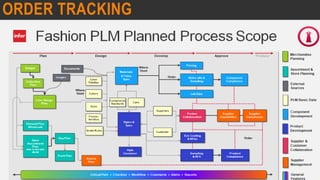
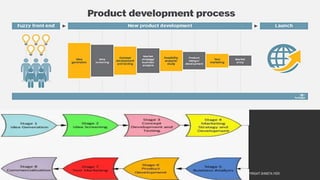
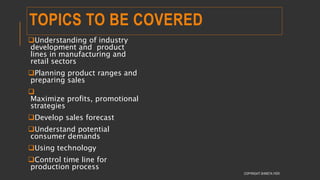
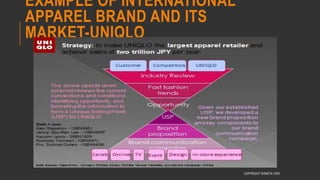
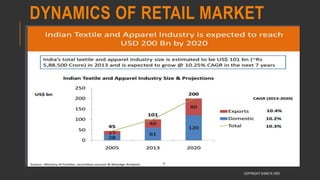
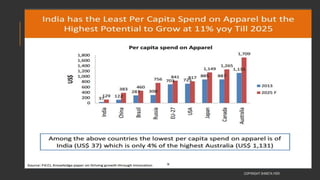
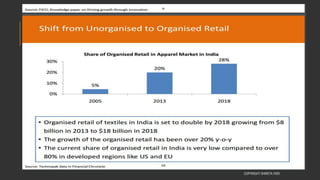
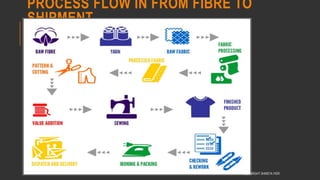
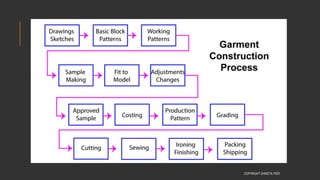
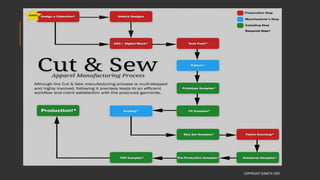
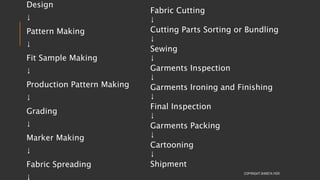
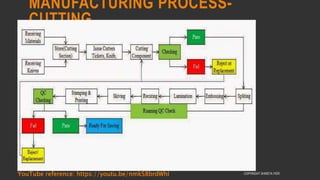
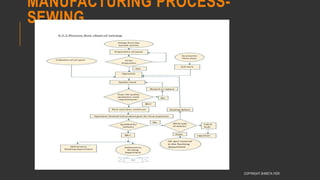
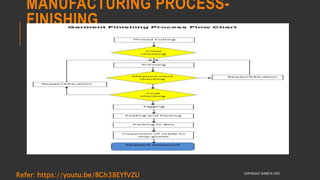
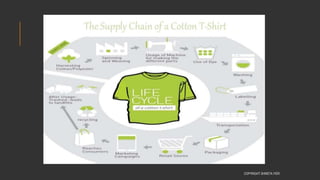
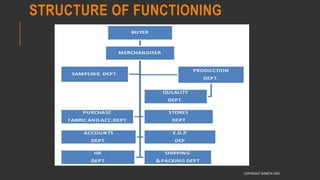
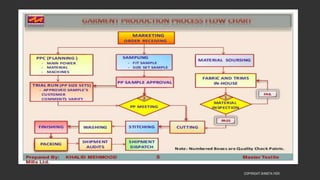
This document provides information about the roles and responsibilities of merchandisers in the fashion industry. It covers topics like understanding industry development, planning product ranges, maximizing profits, developing sales forecasts, understanding consumer demands, and using technology. It also discusses merchandiser roles in different departments like sampling, purchasing, stores, and production process coordination. The document aims to educate about the merchandising function in apparel manufacturing and retail sectors.






















![ROLE OF MERCHANDISER WITH
DIFFERENT DEPARTMENTS
Role of Merchandiser with Buyer and Sampling Department:
The merchandise in the initial stages of order receipt and
conformation coordinates with the buyer and sampling
department for various approvals.
Role of Merchandiser with Buyer:
A garment merchandiser receives the techpack from the
buyer [enquiry].
He has to work with various departments and prepare a
validity report and a feasible quote.
The quote will be intimated to the buyer, price is negotiated
and confirmed.
The purchaser order is then sent by the buyer along with the
LC.
At the various stages of samples, prints embroideries and
accessories are sent to the buyer for approval. Once the
entire approval phase is over goods are produced and
COPYRIGHT SHWETA IYER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/merchandisingrolesandresponsibilities-170730171914/85/Merchandising-roles-and-responsibilities-42-320.jpg)
![ROLE OF MERCHANDISING IN
SAMPLINGRole of Merchandiser with Sampling
department:
1. Here garments merchandiser arranges for
approval of the first sample it may be in
just one size, pre-production sample may
be in jumping size or entire size set,
embroidery, print approval and placement
approvals are also finalized in the
sampling stage.
2. The measurement chart is also checked
and confirmed upon any increase in
measurement will lead to an up charge.
3. The paper pattern is also completed with
all revisions asked by the Buyer. The
fabric [Knit downs, bit looms and first
taka] and accessories are approved at this COPYRIGHT SHWETA IYER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/merchandisingrolesandresponsibilities-170730171914/85/Merchandising-roles-and-responsibilities-43-320.jpg)