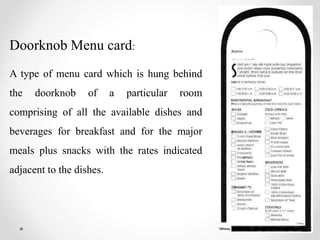
Menu planning involves considering several factors like the competition, establishment policies, customers, operations, nutrition, and regulations. The key types of menus are a la carte, which allows customers to order individually priced items, and table d'hote, which provides a fixed price multi-course meal. Menus originated in China during the Song Dynasty when paper became widely available and were used to list food options for merchants. They later spread to Europe in the 18th century and were standardized into courses by Escoffier. Effective menu planning balances customer choice and needs with a business's resources and goals.