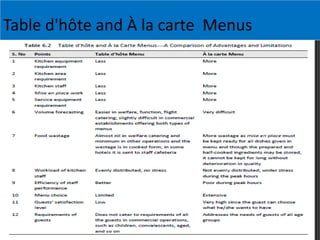
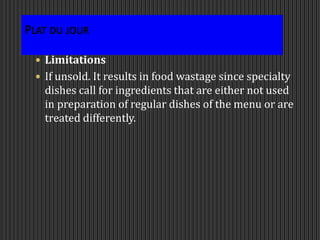
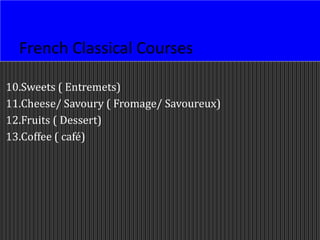
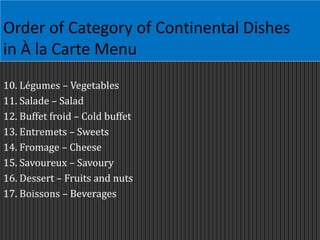
This document discusses menus used in food service establishments. It describes the main types of menus including table d'hôte, à la carte, plat du jour, and cyclic menus. It outlines the key characteristics and order of each type. The document also details the standard sequence of French classical courses in an à la carte menu as well as categories in an Indian à la carte menu. Finally, it emphasizes that understanding menus is essential for managerial and operational decisions in food service.