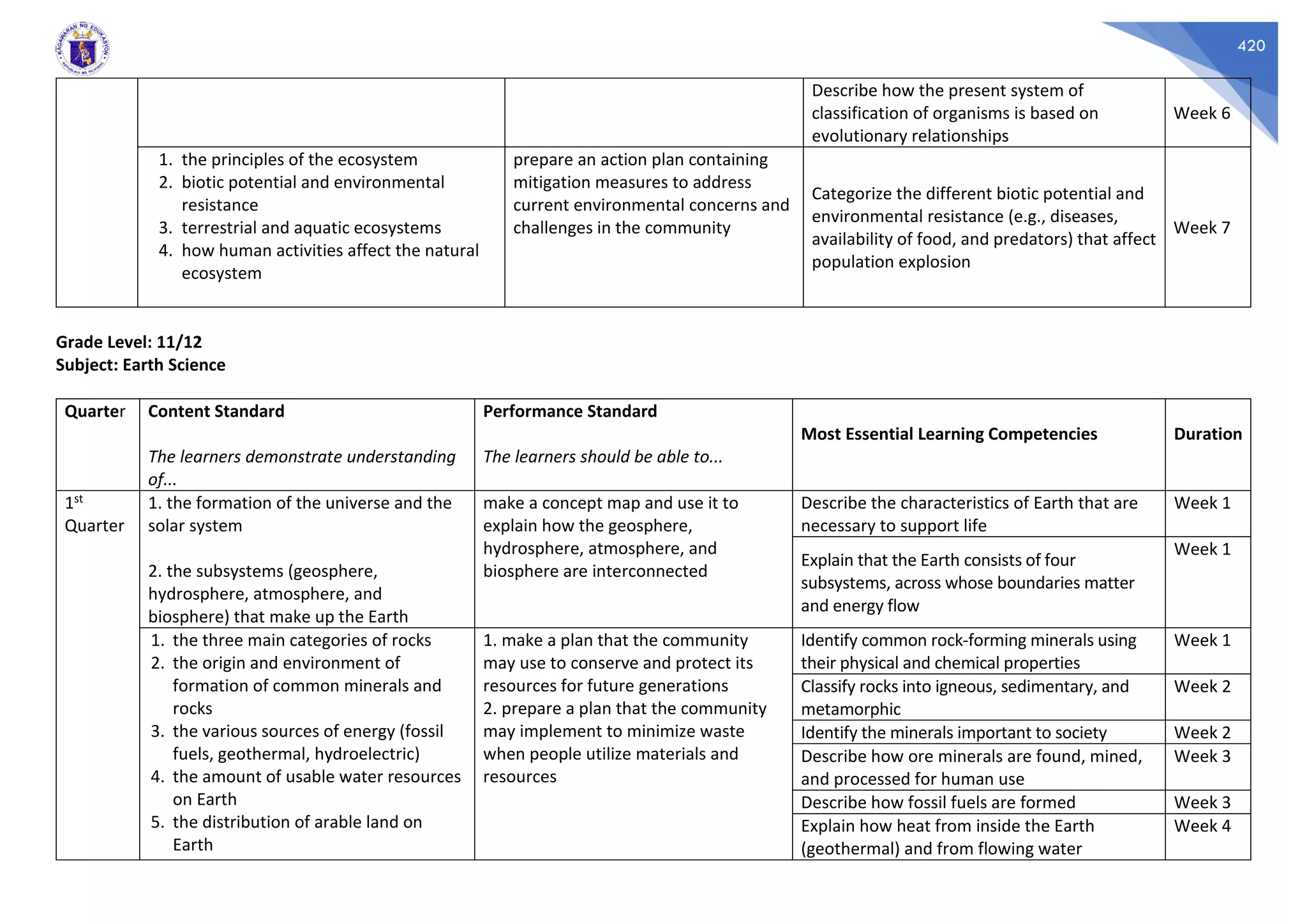
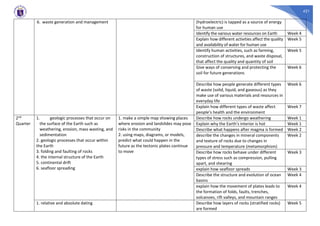
This document contains a sample quarterly lesson plan for an Earth Science class for grades 11-12. It includes 4 content standards, 4 performance standards, and outlines 7 weekly topics to be covered in the 1st quarter, including the formation of the universe and solar system, Earth's subsystems, rocks and minerals, and natural resources. It also provides 6 weekly topics to be covered in the 2nd quarter, such as geologic surface and internal processes, continental drift, and methods of dating geological events. The lesson plan identifies the essential learning competencies and expected duration for students to meet each topic.