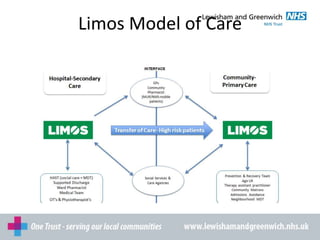
LIMOS provides in-home support to patients managing long-term conditions and medicines. They target patients with hospital admissions or readmissions related to medicines, adherence problems, mental health issues, or who are housebound. LIMOS pharmacists visit patients at home or in the hospital to support medicines management, improve adherence, address barriers, and communicate with other healthcare providers. They assess patients' needs and create individualized care plans. LIMOS offers three levels of community support services depending on a patient's needs for assistance with ordering, collecting, opening containers, or total medication management. Common barriers to adherence include mobility, dexterity, cognition, literacy, and ability to manage daily tasks that LIMOS works to overcome through