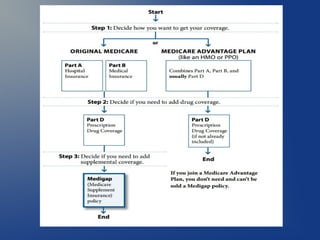
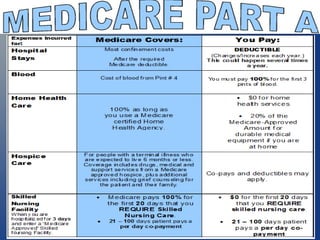
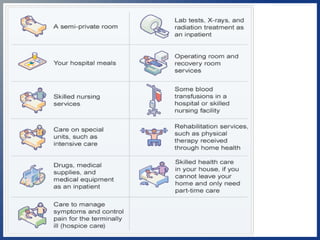
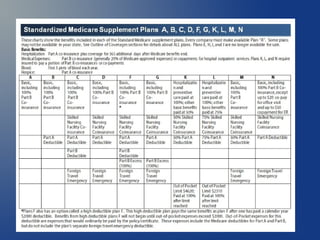
This document provides an overview of the different parts of Medicare (Parts A, B, C, D) and Medicare supplements (Medigap). It explains that Medicare Part A covers hospital insurance, Part B covers medical insurance, Part C are Medicare Advantage plans offered by private insurers that include benefits from Parts A, B and often Part D. Part D is prescription drug coverage. Medicare supplements help cover costs that original Medicare does not. The document provides details on the benefits and requirements of each part/program.