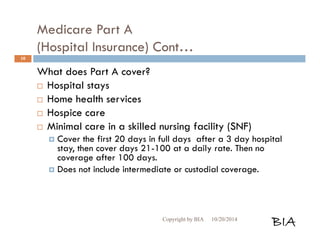
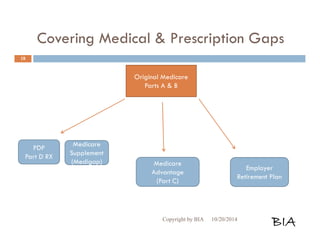
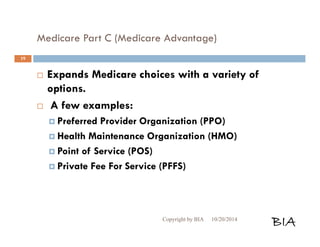
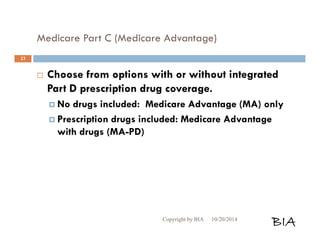
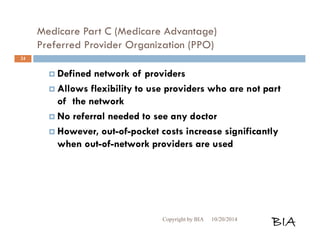
This document provides an overview and summary of Medicare and supplemental insurance options. It begins with introducing Boone Insurance Associates, which provides various health and life insurance products. The bulk of the document then summarizes Medicare Parts A, B, C, and D - including what they cover, who qualifies, premium and cost-sharing details. It also discusses options for covering gaps in Medicare like Medicare Advantage plans, Medigap plans, and Part D prescription drug plans. Specific plan types like HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans are defined.




![Medicare Part A
(Hospital Insurance) Cont…
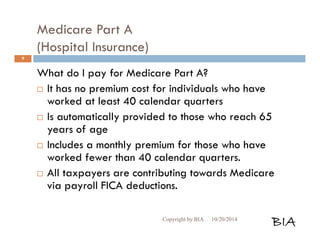
Part A Deductibles
[2013] Hospital stay per benefit period:
Days 1-60 [$1184] per benefit period
Days 61-90 [$296] per day
Days 91-150 [$592] per day
[2013] Skilled Nursing Facility:
Days 1-20 [$0] per day
Days 21-100 [$148] per day
Copyright by BIA 10/20/2014 BIA
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biamedicare101presentationnew-141021091220-conversion-gate01/85/BIA-Medicare-101-Presentation-Long-Form-11-320.jpg)
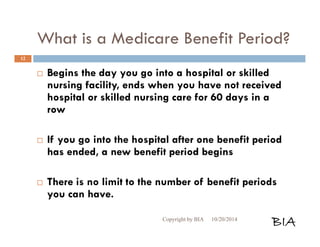
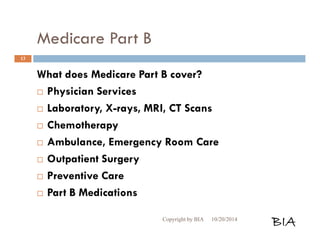
![Medicare Part B Cont…
What do I pay for Medicare Part B?
Part B premium is based on Part B medical costs and annual income level per
individual
[2013] Part B Premium Annual Income per Individual
$104.90 [$85,000 or less]
$146.00 [$85,001 to $107,000]
$209.80 [$107,001 to $160,000]
$272.70 [$160,000 to $214,000]
$335.70 More than [$214,000]
Double amounts listed above for married couples filing jointly
Premiums are deducted from the Social Security benefits, or billed quarterly
Copyright by BIA 10/20/2014 BIA
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biamedicare101presentationnew-141021091220-conversion-gate01/85/BIA-Medicare-101-Presentation-Long-Form-14-320.jpg)
![Medicare Part B Cont…
Deductibles & Coinsurance for
Deductible:
2013 [$147] per year
Other Services:
Patient pays [20%] of approved amount, after
deductible. {Medicare pays 80%}
[50%] for most Outpatient mental healthcare
services.
There is no OOP maximum, risk is unlimited
Copyright by BIA 10/20/2014 BIA
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biamedicare101presentationnew-141021091220-conversion-gate01/85/BIA-Medicare-101-Presentation-Long-Form-15-320.jpg)






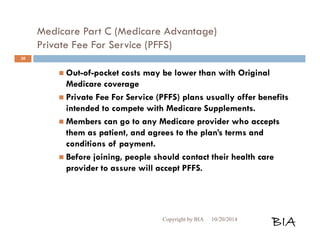






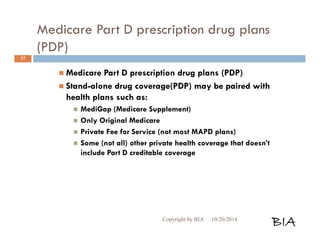
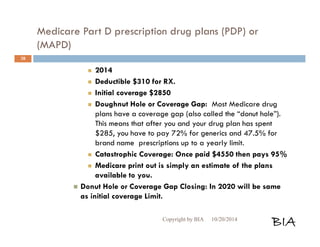


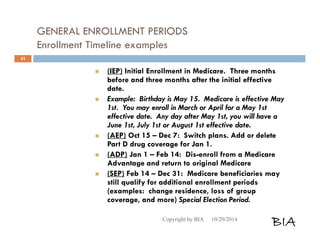

![Enrolling in a Medicare Plan
When entitled to Medicare and enrolling Cont…
Submit it during the appropriate enrollment
period.
You may not combine an MA-only PPO or HMO
with a stand-alone PDP. Choose one or the other.
If you did not have creditable coverage in [2006],
your monthly plan premium may be slightly
higher when you enroll in Part D coverage plan
(MAPD, PDP).
Copyright by BIA 10/20/2014 BIA
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biamedicare101presentationnew-141021091220-conversion-gate01/85/BIA-Medicare-101-Presentation-Long-Form-43-320.jpg)


