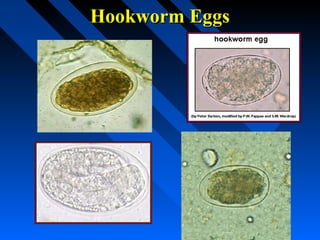
The document discusses several nematode parasites including Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm), the hookworms Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus, and Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm). It provides details on the life cycles, diagnostic stages, geographic distribution, and distinguishing morphological features of these parasites. Comparative information is given on the rhabditiform and filariform larvae and eggs of hookworms and Strongyloides stercoralis.