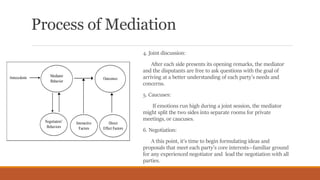
Private Court offers a cloud-based mediation service that ensures privacy and confidentiality while facilitating dispute resolution outside of traditional court settings. The mediation process involves a neutral third-party mediator guiding parties through five stages to reach a mutually acceptable agreement, with minimal lawyer involvement and flexible scheduling. Although the process may lack immediate binding authority, it empowers the parties to collaboratively resolve their disputes efficiently.