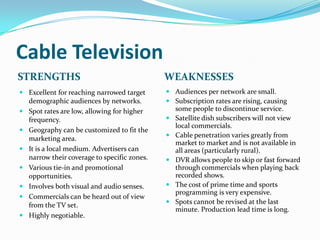
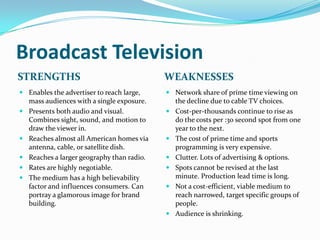
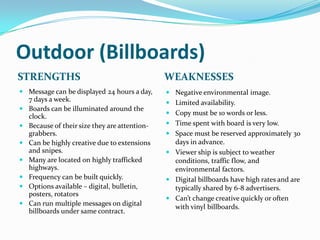
The document provides guidance on developing an effective media plan, including evaluating advertising objectives and options, setting a budget, creating schedules, and defining key terms related to advertising mediums such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, and online. It discusses strengths and weaknesses of different advertising channels and how to calculate costs per thousand impressions. The overall goal is to help advertisers select the right mix of media to accomplish their objectives within budget constraints.