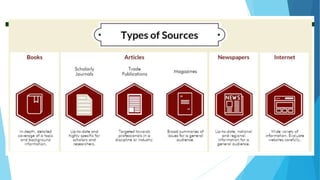
This document discusses different sources of information and how to evaluate their reliability and accuracy. It identifies libraries, the internet, and mass media as key sources. Libraries are often considered highly reliable due to processes like peer review and ISBN registration. Information online can vary greatly in quality and requires validation of sources. Mass media provides speed but information may be biased. Some tips for evaluating sources include checking the author, date, citations, domain or owner, and writing style to assess reliability, and looking for facts, consistency with other sources, and objectivity to determine accuracy. Developing these evaluation skills benefits information literacy.