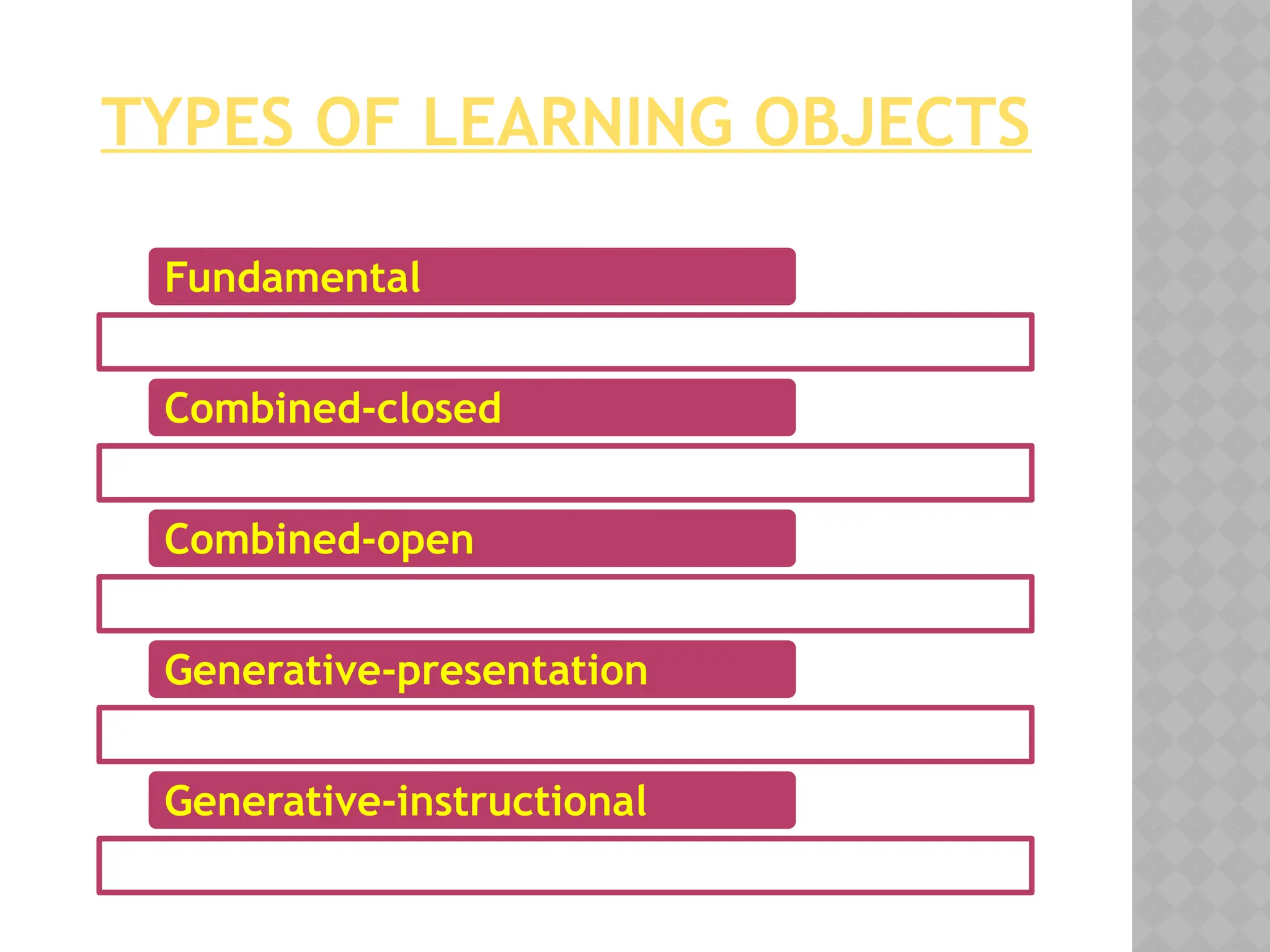
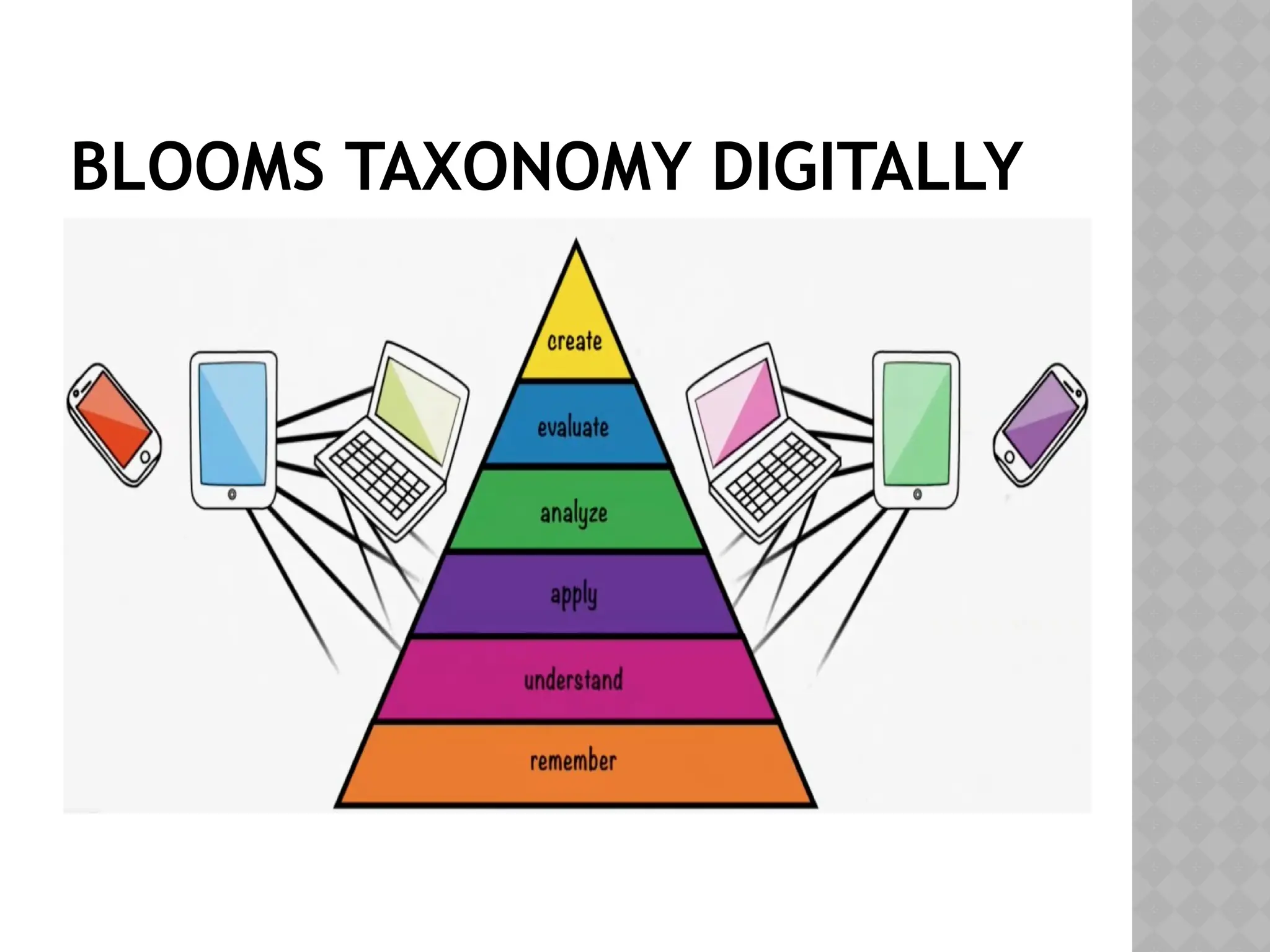
The document discusses digital learning objects and their role in modern education, highlighting their ability to enhance learning by providing reusable and accessible resources through the internet. It categorizes various types of learning objects, including fundamental, combined-closed, combined-open, generative-presentation, and generative-instructional. Additionally, it touches on web-based and web-enhanced instruction, as well as definitions related to information, instruction, and learning.