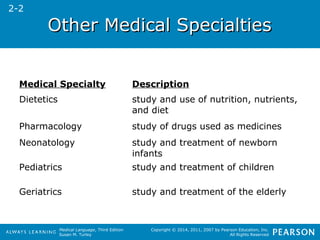
The document discusses the structure of medical language. It covers the origins of medical terminology from Latin and Greek, how medical words are formed using combining forms, suffixes, and prefixes, and provides examples of common word parts. The objectives are to learn the basics of medical terminology including word structures, meanings, spellings, and pronunciations.

























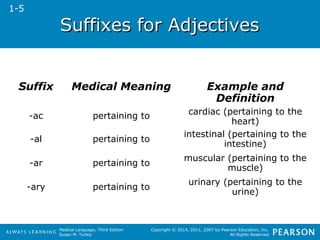
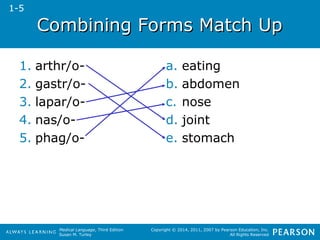
![SSuuffffiixxeess ffoorr AAddjjeeccttiivveess
Suffix Medical Meaning Example and
-ic pertaining to pelvic (pertaining to the
-ine pertaining to uterine (pertaining to the
-ive pertaining to digestive (pertaining to
-ous pertaining to venous (pertaining to a
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Definition
pelvis)
uterus)
break[ing] down food)
vein)
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-31-320.jpg)
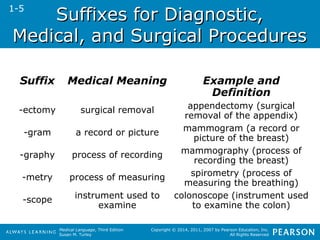
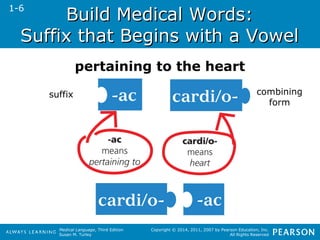
![SSuuffffiixxeess ffoorr PPrroocceesssseess
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Suffix Medical
Meaning
Example and Definition
-ation a process; being or
having
urination (a process [of making] urine)
-ion action; condition digestion (action of break[ing] down
food)
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-32-320.jpg)
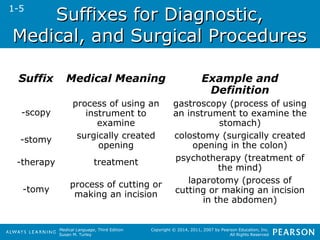
![SSuuffffiixxeess ffoorr DDiisseeaasseess
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
1-5
Suffix Medical
Meaning
Example and Definition
-ia condition; state;
thing
pneumonia (condition of the lung)
-ism process; disease
from a specific cause
hypothyroidism (disease from a
specific cause of deficient thyroid gland
[hormone])
-itis inflammation of;
infection of
tonsillitis (infection of the tonsil)
-megaly enlargement cardiomegaly (enlargement of the
heart)
-oma tumor; mass neuroma (tumor on a nerve)
-osis condition; abnormal
condition; process
psychosis (abnormal condition of the
mind)
-pathy disease arthropathy (disease of a joint)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-33-320.jpg)



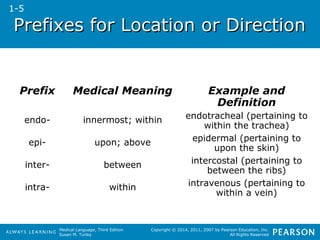
![PPrreeffiixxeess ffoorr AAmmoouunntt,,
NNuummbbeerr,, oorr SSppeeeedd
Prefix Medical Meaning Example and
bi- two bilateral (pertaining to two
brady- slow bradycardia (condition of a
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Definition
sides)
slow heart)
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
hemi- one half
hemiplegia (condition of one
half [of the body with]
paralysis)
hyper- above; more than
normal
hypertension (condition of
more than normal pressure)
hypo- below; deficient
hypothyroidism (disease
from a specific cause of
deficient thyroid gland
[hormone])
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-41-320.jpg)
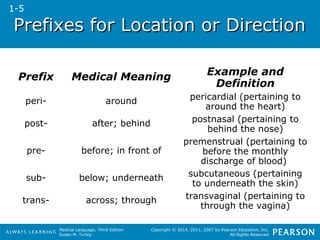
![PPrreeffiixxeess ffoorr AAmmoouunntt,,
NNuummbbeerr,, oorr SSppeeeedd
Prefix Medical Meaning Example and
poly- many; much polyneuritis (inflammation
quadri- four quadriplegia (condition of
tachy- fast tachycardia (condition of a
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Definition
of many nerves)
four [limbs with] paralysis)
fast heart)
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
tri- three
trigeminal (pertaining to
three [nerve branches in a]
group)
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-42-320.jpg)
![Prefixes ffoorr DDeeggrreeee oorr QQuuaalliittyy
Prefix Medical Meaning Example and
a- away from; without aspermia (condition [of
an- without; not anesthesia (condition [of
anti- against antibiotic (pertaining to
de- reversal of; without dementia (condition [of
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Definition
being] without sperm)
being] without sensation)
against living organisms)
being] without a mind)
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-43-320.jpg)
![Prefixes ffoorr DDeeggrreeee oorr QQuuaalliittyy
Prefix Medical Meaning Example and
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Definition
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
dys- painful; difficult;
abnormal
dysphagia (condition of
painful or difficult eating
and swallowing)
eu- normal; good
euthyroidism (process of
normal thyroid gland
[function])
mal- bad; inadequate
malnutrition (being or
having inadequate
nourishment)
re- again and again respiration (a process of
again and again breathing)
1-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-44-320.jpg)

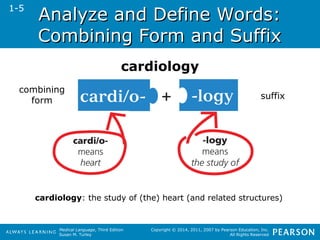



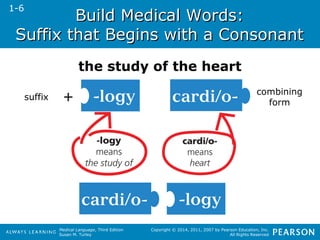












































































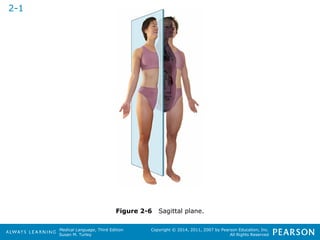
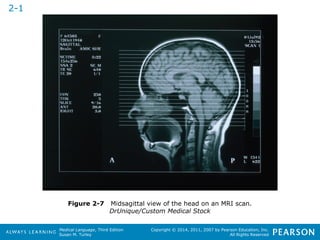

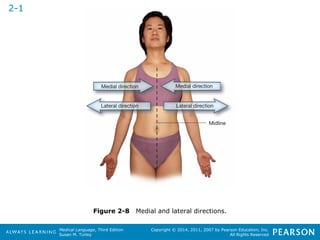

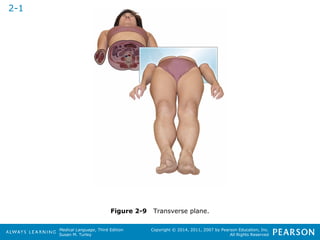






















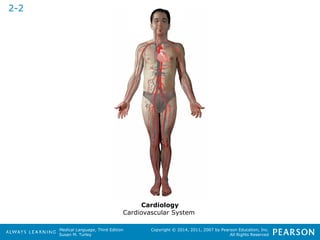


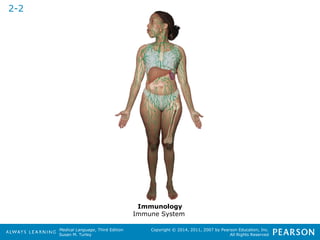

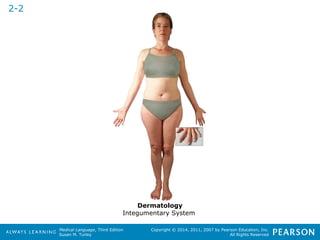

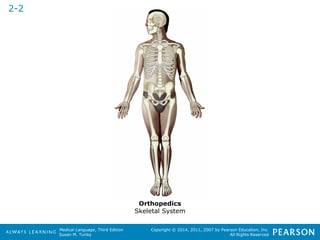

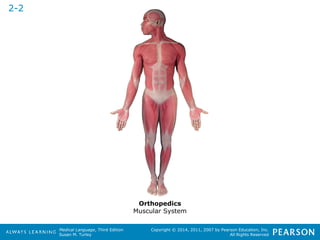

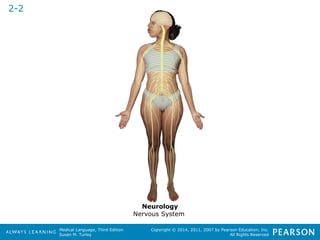

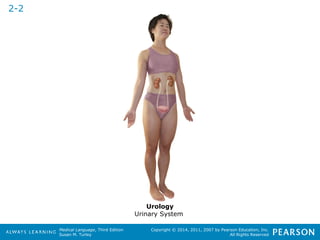

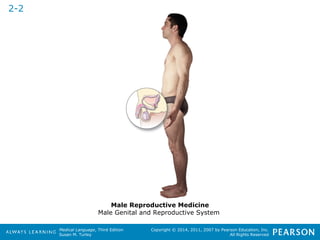

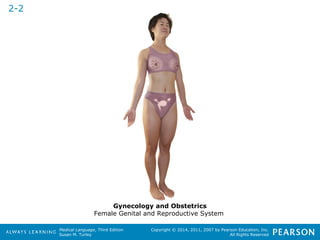

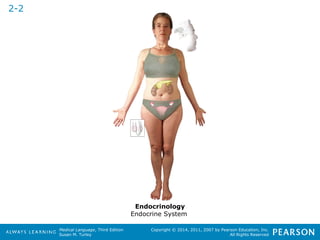

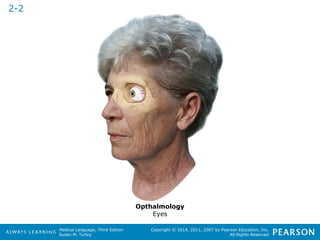

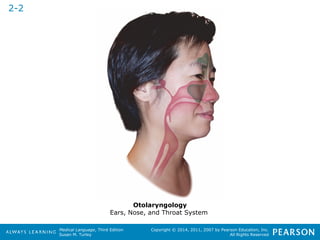










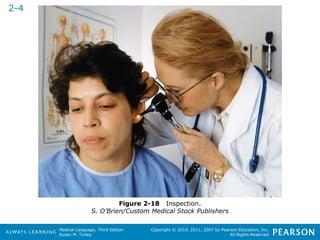
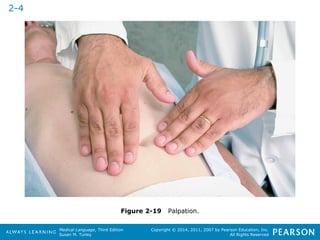

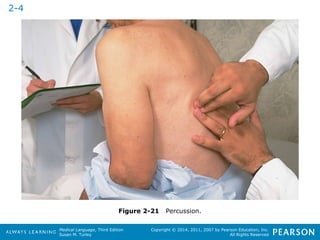













![HHeeaalltthhccaarree PPrrooffeessssiioonnaallss
Medical Language, Third Edition
Susan M. Turley
Copyright © 2014, 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
• Allied Health Professionals
Nurses (registered nurse [RN], licensed
practical nurse [LPN], or licensed
vocational nurse [LVN]) examines
patients, makes nursing diagnoses, and
administers treatments or drugs ordered
by the physician.
Nurses give hands-on care and focus on
the physical and emotional needs of the
patient and the family.
2-5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medtermch1andch2-140903192740-phpapp01/85/Med-Term-Ch-1-and-Ch-2-228-320.jpg)