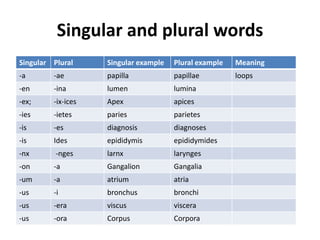
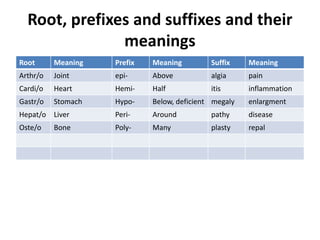
The document outlines the basics of medical terminology, focusing on the structure of medical terms through roots, prefixes, and suffixes. It explains the significance of these components in constructing terms and emphasizes the importance of understanding their meanings for effective communication in healthcare. Additionally, it provides rules for combining these elements and guidelines for pronunciation and pluralization of medical terms.