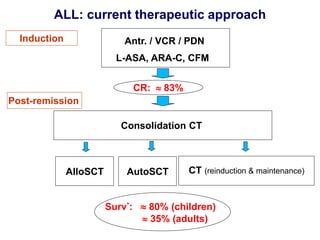
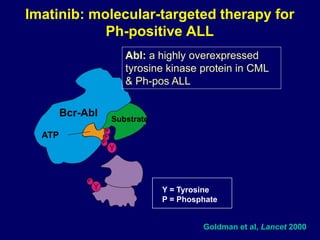
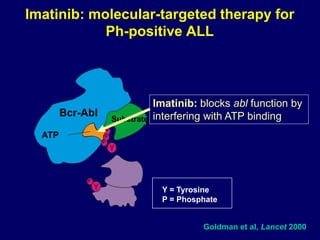
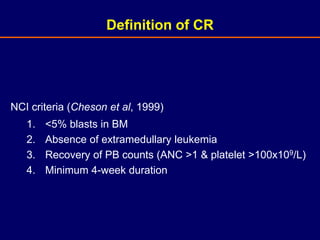
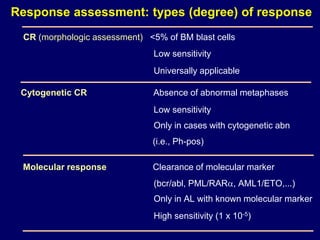
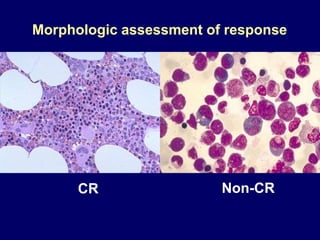
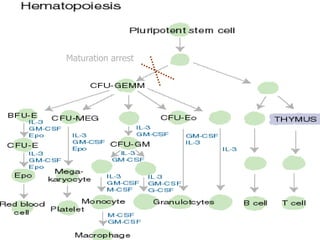
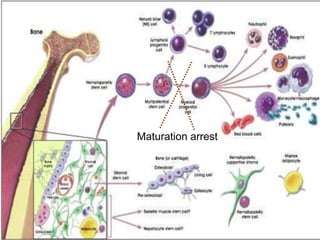
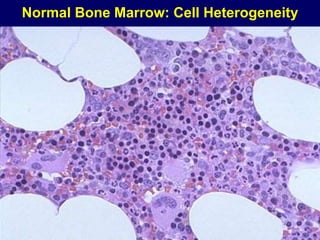
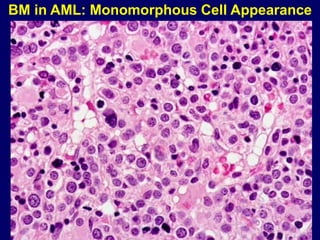
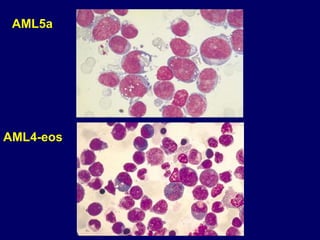
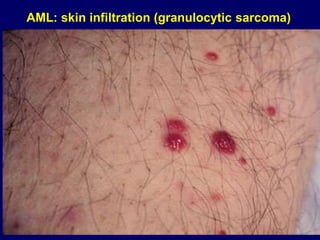
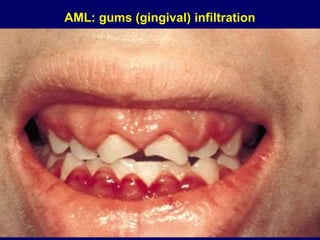
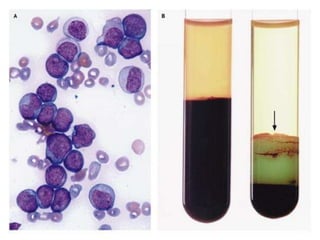
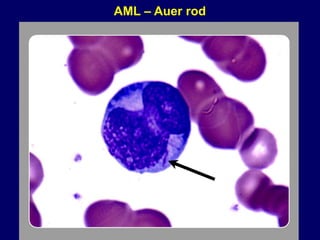
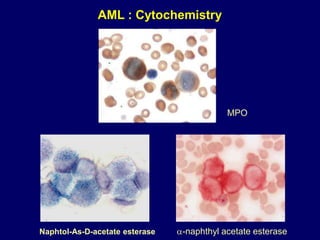
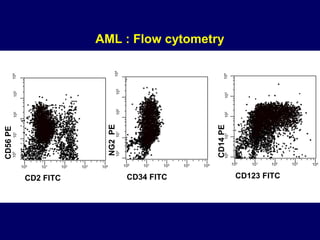
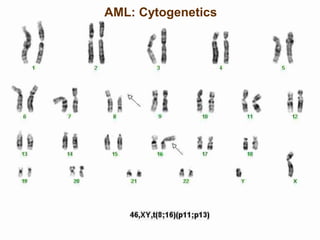
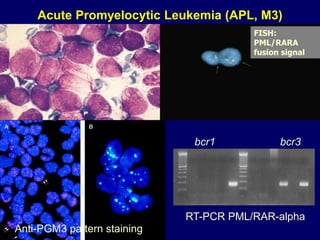
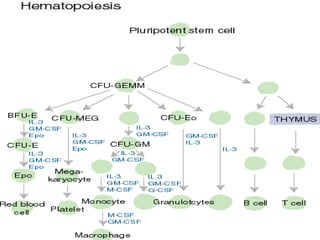
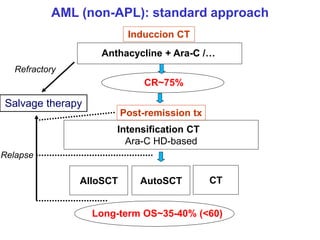
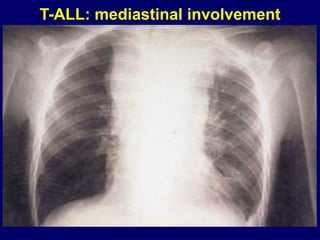
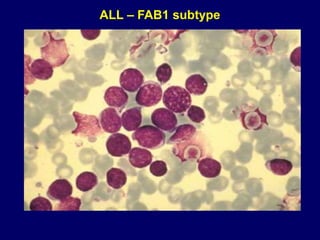
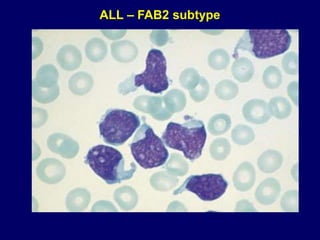
Acute leukaemia refers to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). AML is defined by a clonal expansion of myeloid blasts in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, or other tissues. ALL is defined by a clonal expansion of lymphoid precursor cells in the same areas. Both result from a proliferation and differentiation block. AML is diagnosed through cytology, cytochemistry, immunophenotyping, cytogenetics, and molecular biology tests. Response to treatment is assessed by degree of response including complete response, cytogenetic response, and molecular response.

















![– Favorable: t(12;21),
– Intermediate risk: normal karyotype, t(1;19)
– Unfavorable: t(9;22), 11q23 abn [t(4;11) & other],
hypoploid
ALL: main cytogenetic abnormalities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/med341-220906052221-d44ea90b/85/MED-341-Acute-Leukemia-March-2011-ppt-36-320.jpg)