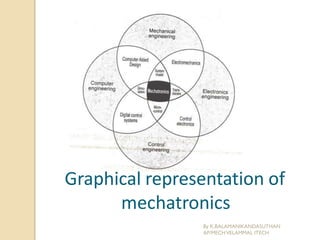
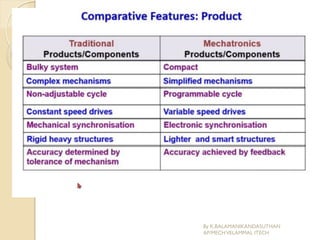
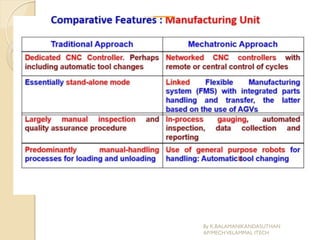
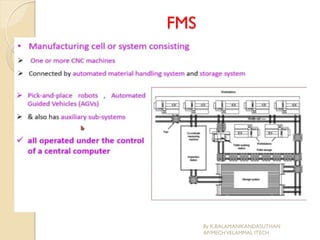
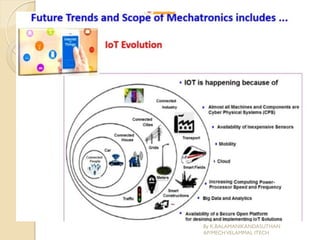
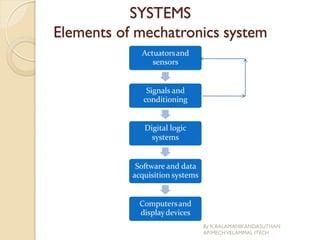
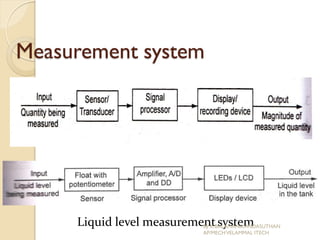
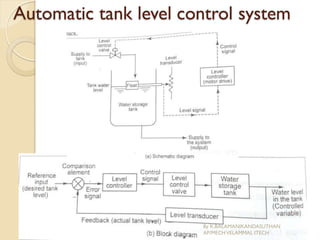
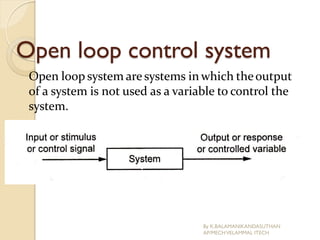
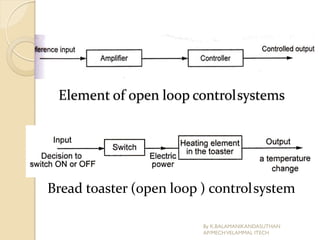
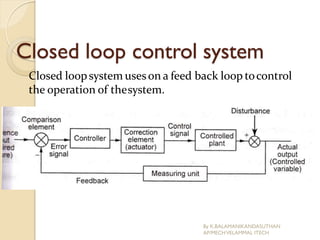
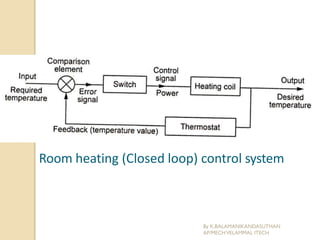
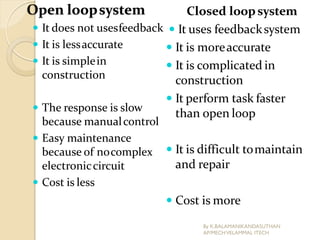
The document presents an overview of mechatronics, which integrates mechanics, electronics, and computer technology to enhance products and systems. It discusses the historical development of mechatronics from its introduction in 1969, including various technologies and applications in fields such as aerospace and automotive engineering. Additionally, it covers elements of mechatronic systems, control systems, and emerging areas like unmanned vehicles and medical imaging.