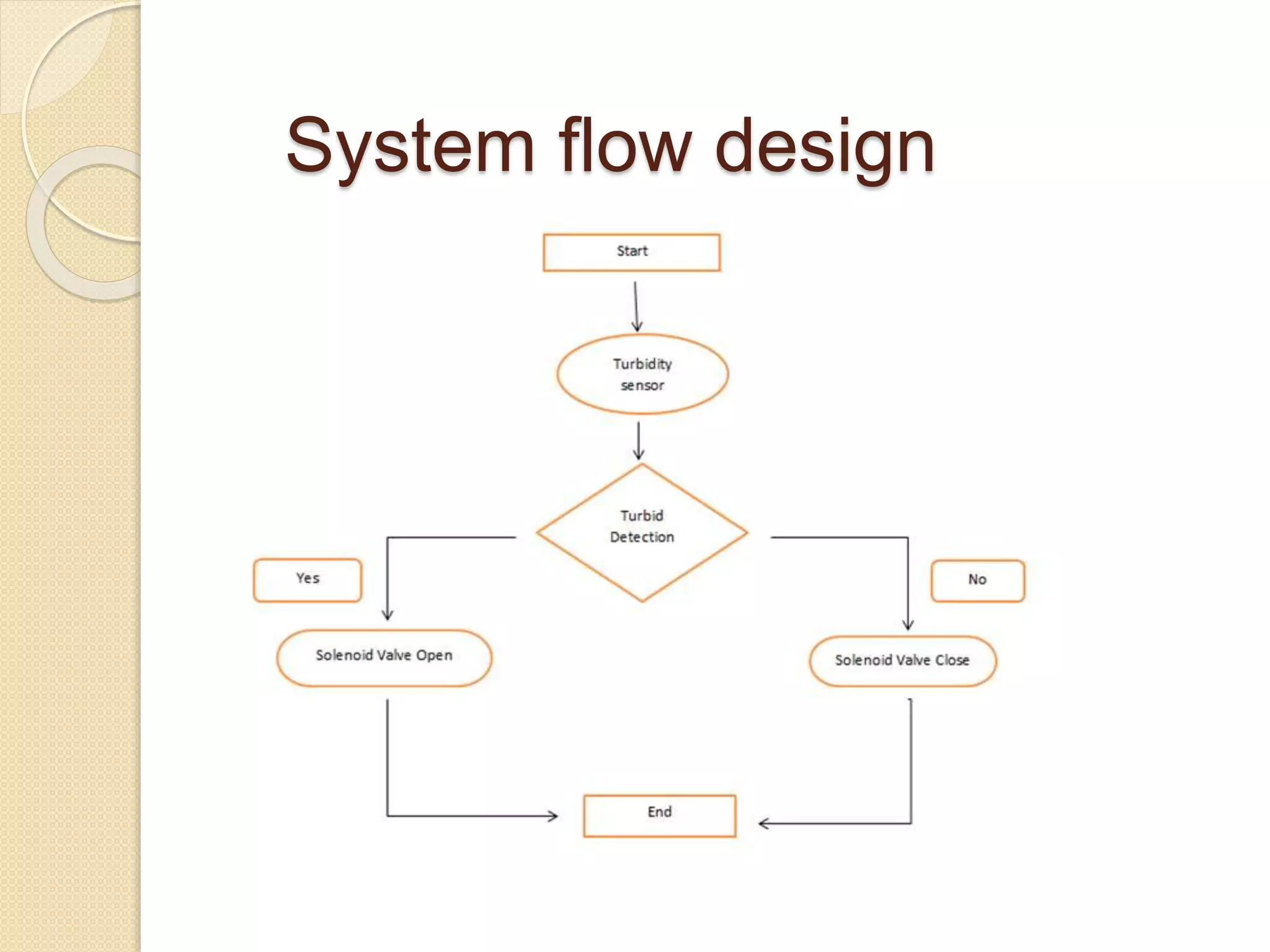
This document discusses the development of a system to monitor and control water quality in a rainwater harvesting tank used for agricultural irrigation. The system uses a turbidity sensor connected to a solenoid valve to automatically open the valve when turbidity levels are high, reducing the farmer's burden to manually monitor water quality. The objectives are to develop this system and test that it can accurately detect turbidity levels and open/close the valve as required. The results show the system was successfully developed and tested to meet these objectives.