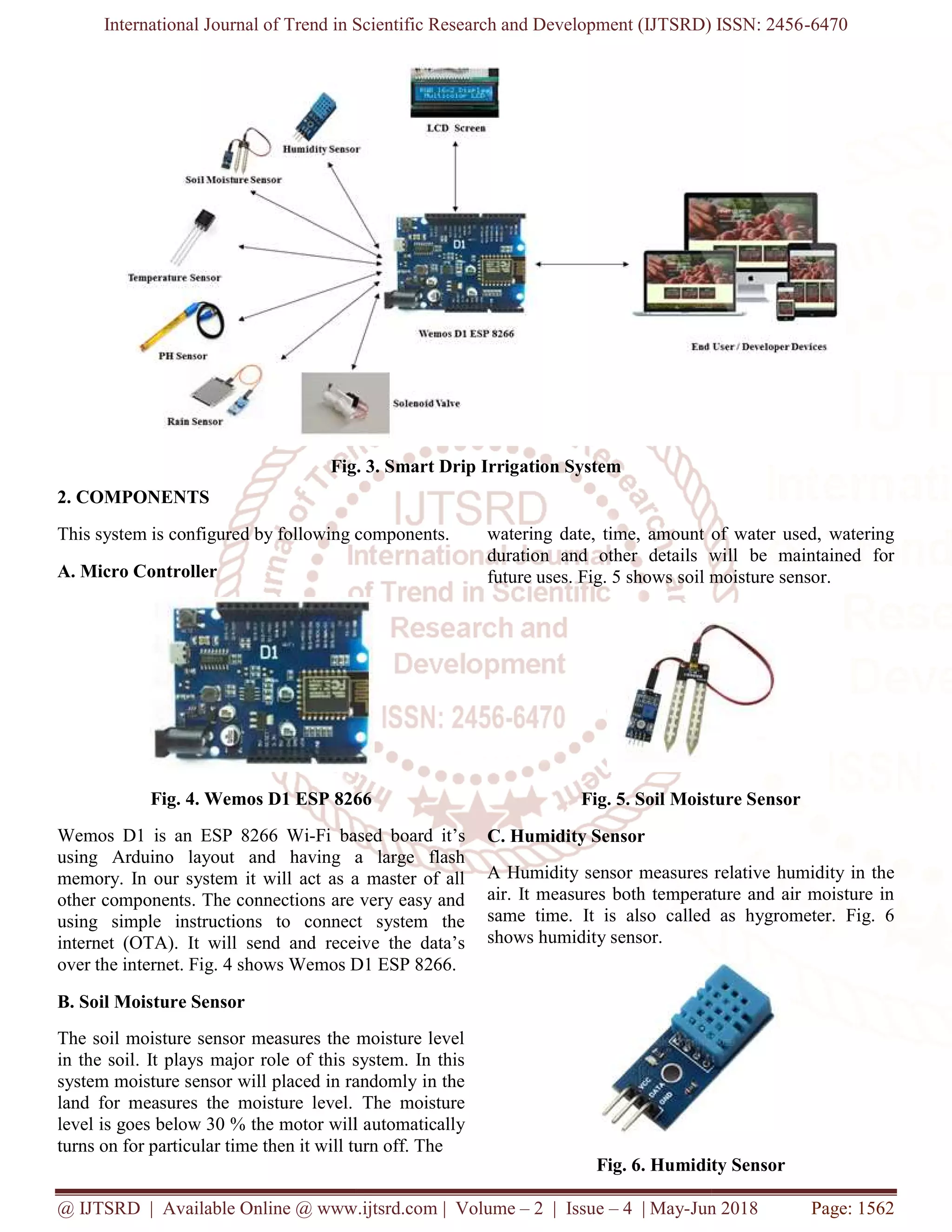
The document discusses an IoT-based smart drip irrigation system designed to improve traditional agricultural practices by reducing water wastage and optimizing crop water management through automated monitoring. Utilizing the Wemos D1 ESP8266, the system integrates various sensors to monitor soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors, allowing farmers to manage irrigation more efficiently. The proposed system enhances crop yield while minimizing manual labor and resource consumption.