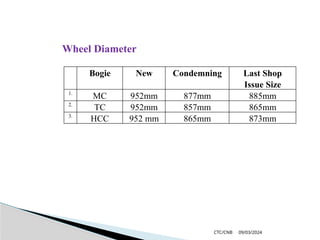
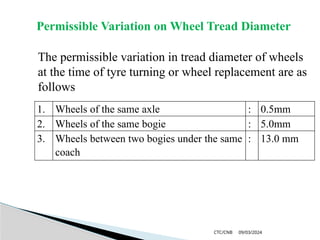
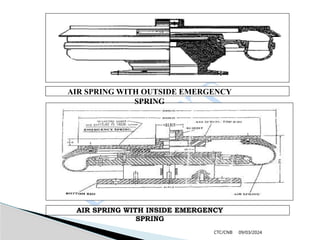
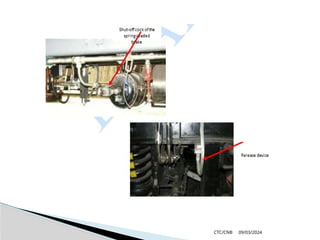
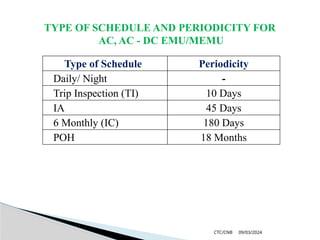
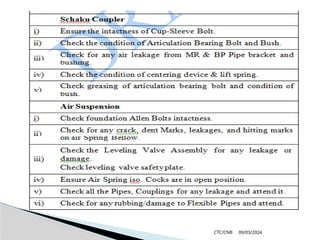
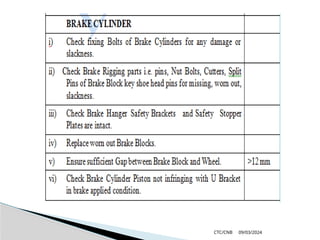
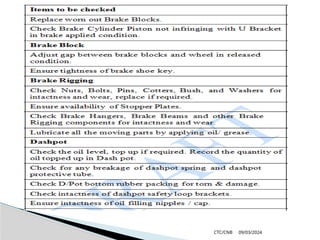
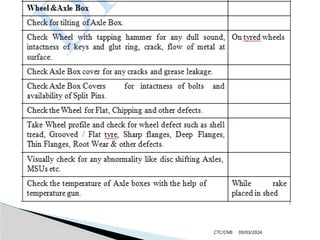
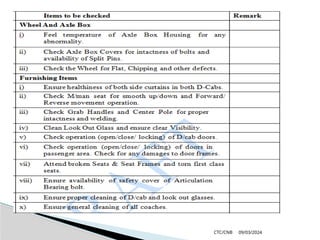
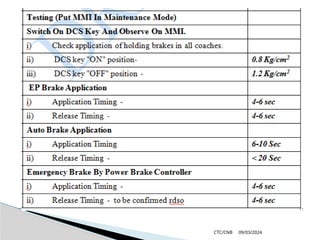
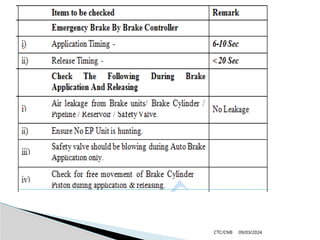
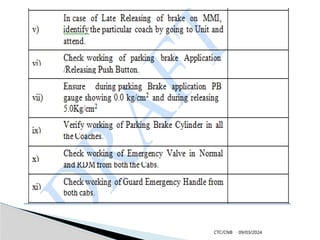
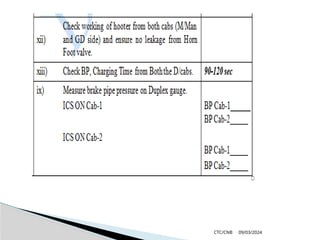
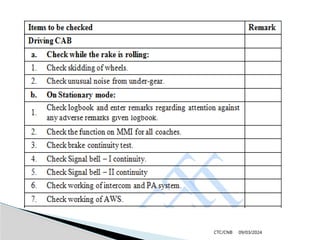
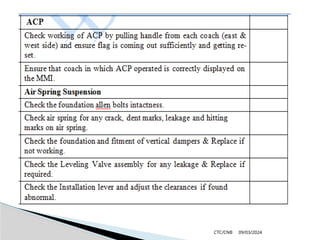
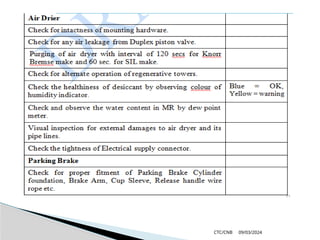
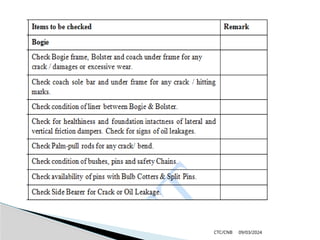
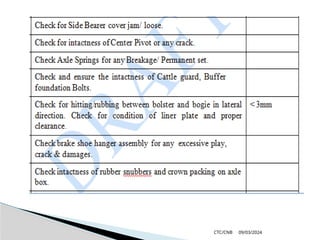
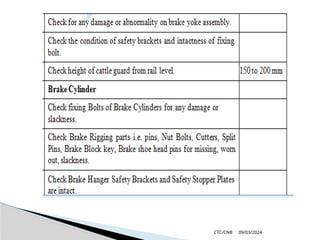
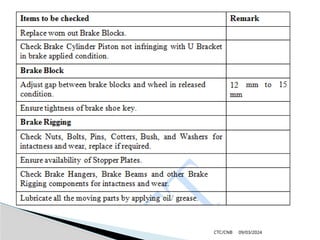
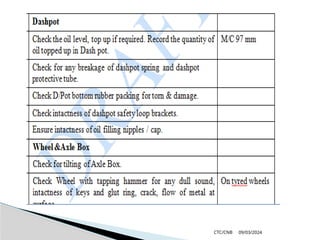
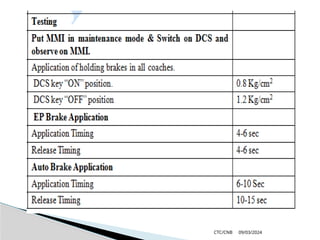
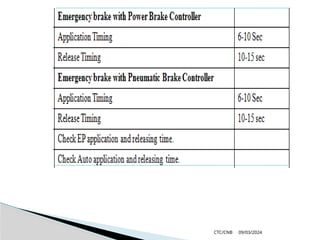
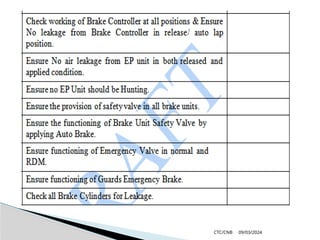
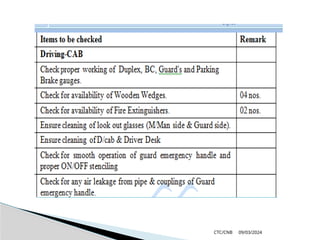
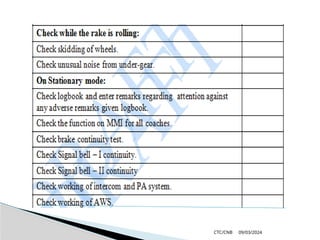
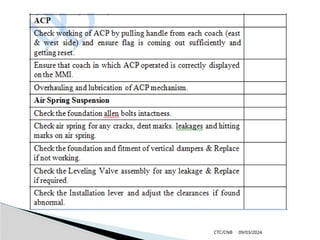
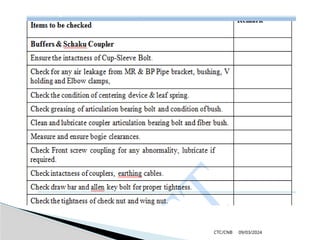
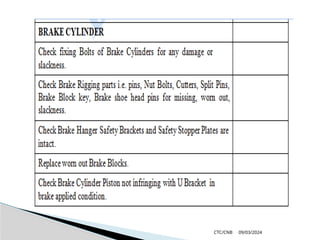
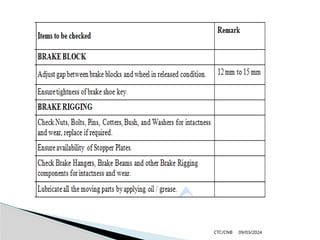
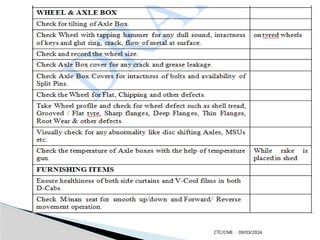
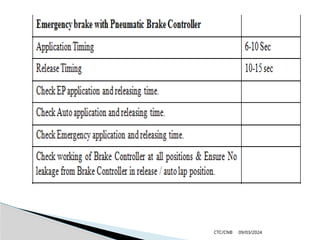
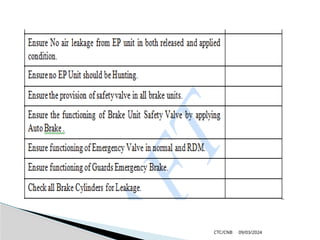
The document details the construction, components, and maintenance of bogies and wheel systems in EMU coaches, highlighting their design features such as welded construction, roller bearings, and air suspension. It outlines technical specifications, permissible variations for wheel diameters, and the functioning of a multi-system braking system, including electric and pneumatic brakes. Additionally, it provides schedules for routine inspections and maintenance, emphasizing safety and reliability standards.