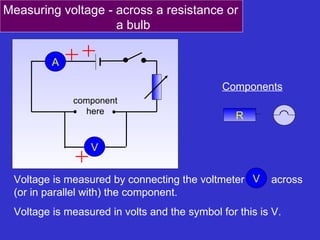
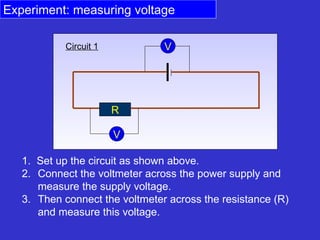
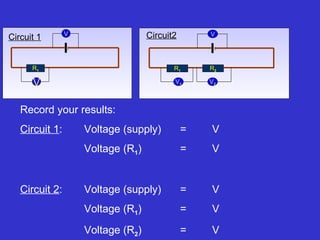
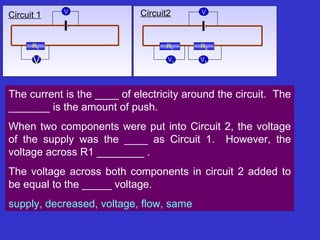
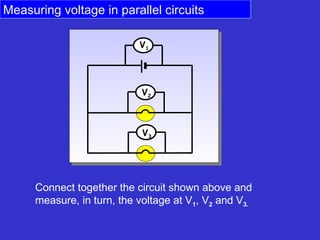
The document discusses measuring voltage in electrical circuits. It explains that voltage is measured using a voltmeter connected across or in parallel with a circuit component. It provides instructions for setting up simple circuits and measuring the supply voltage and voltages across individual resistors. It finds that in a parallel circuit, the total voltage across all components equals the supply voltage, but the voltage across each individual component decreases compared to a single component circuit.