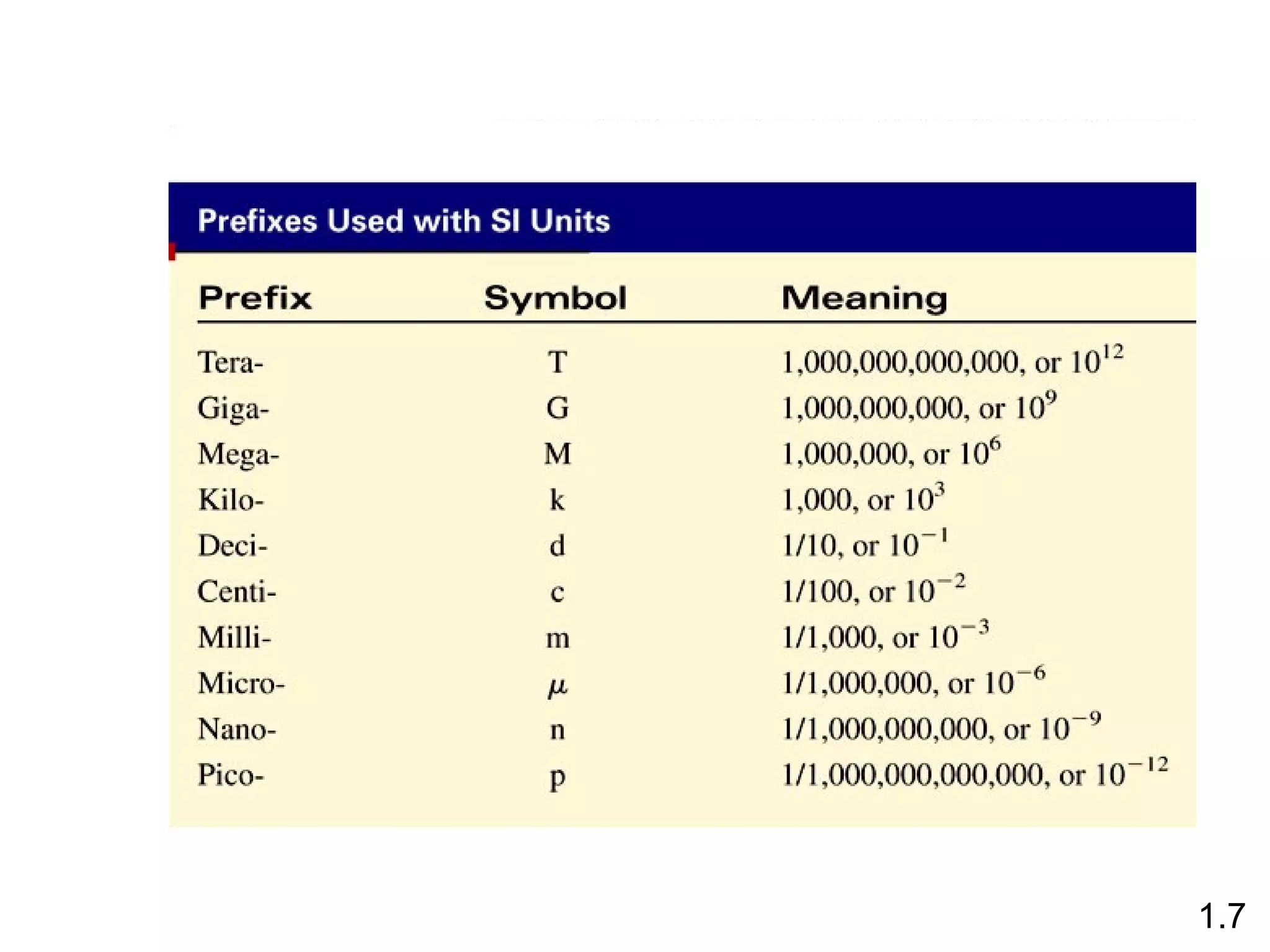
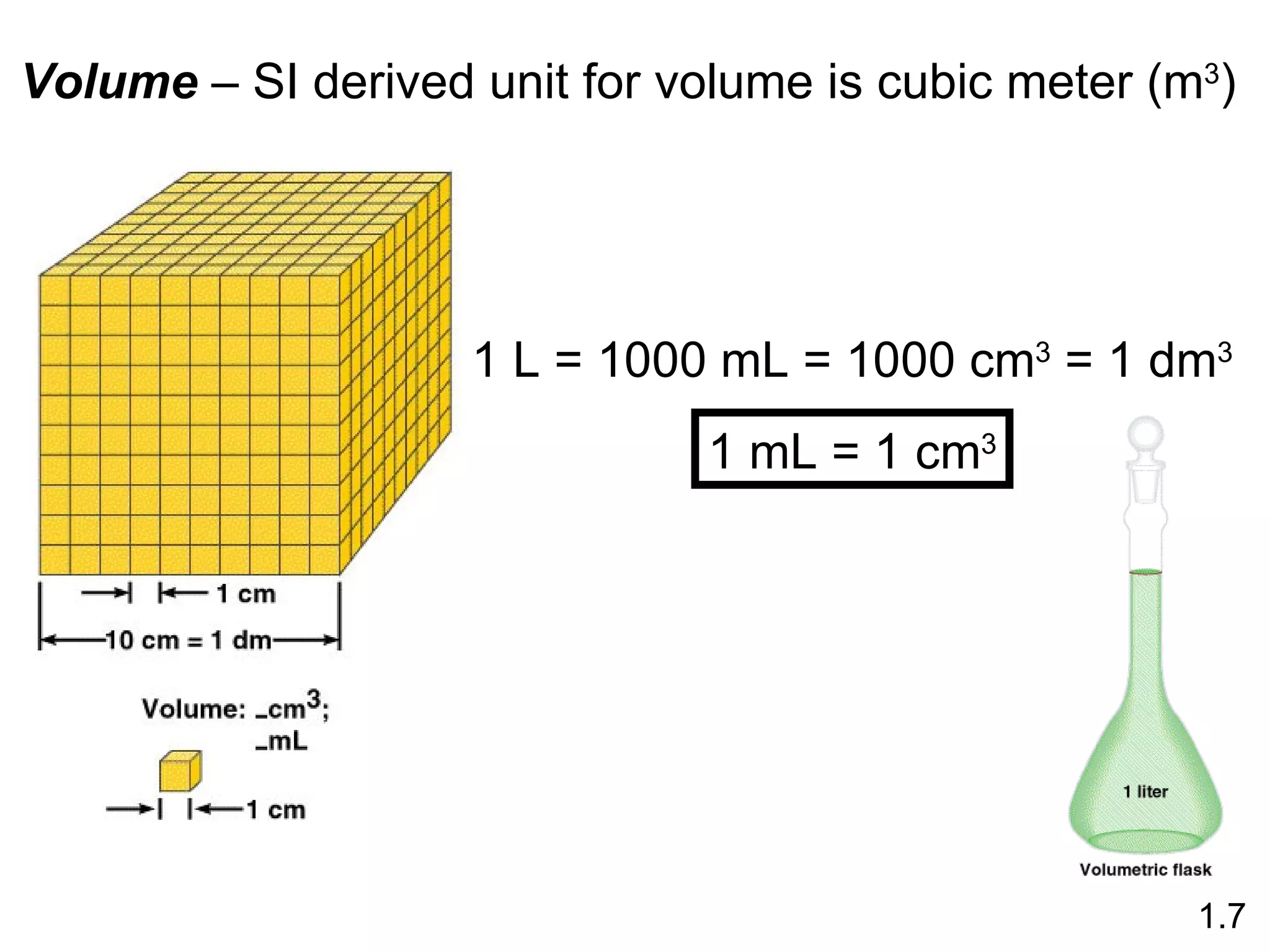
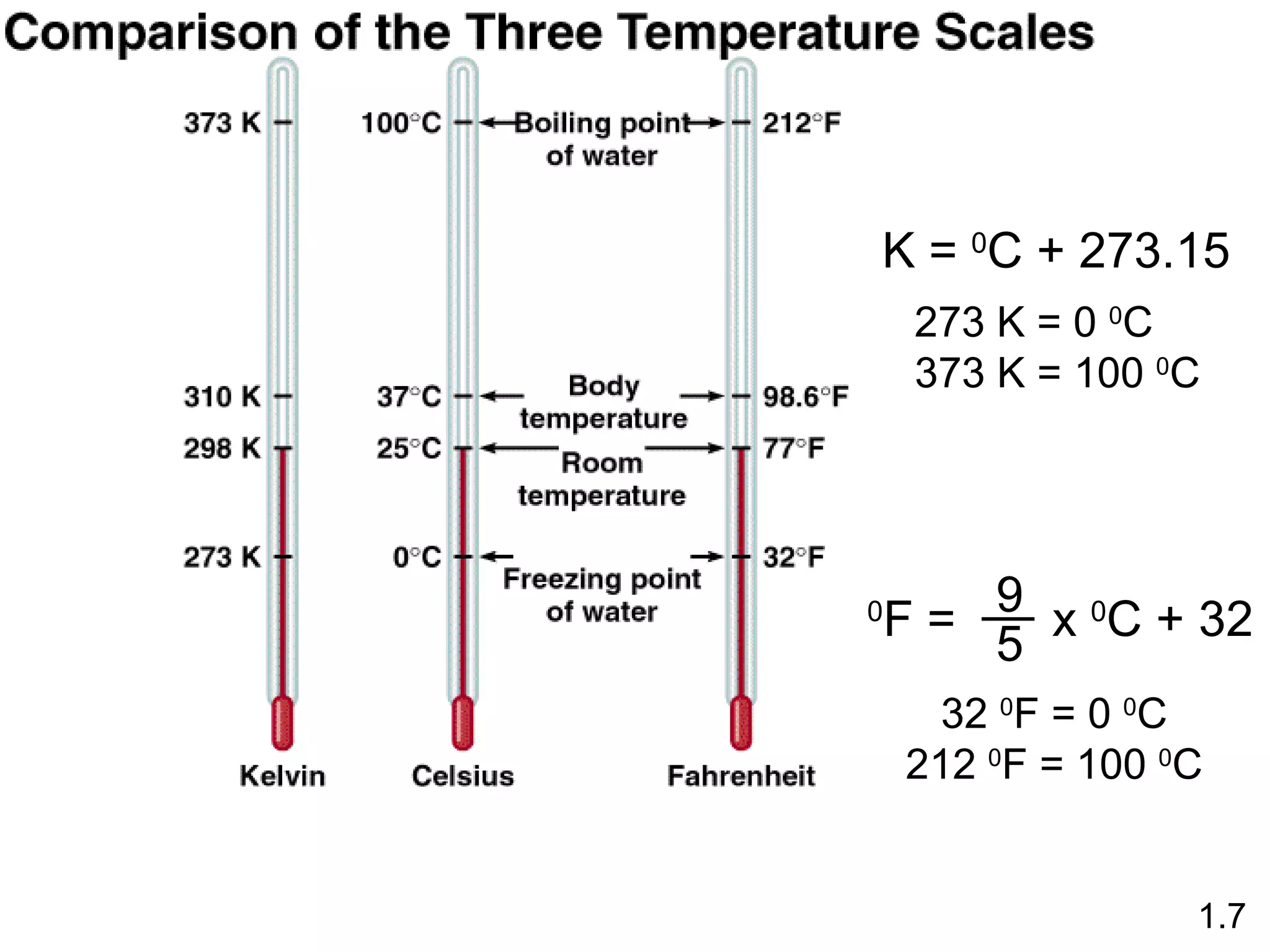
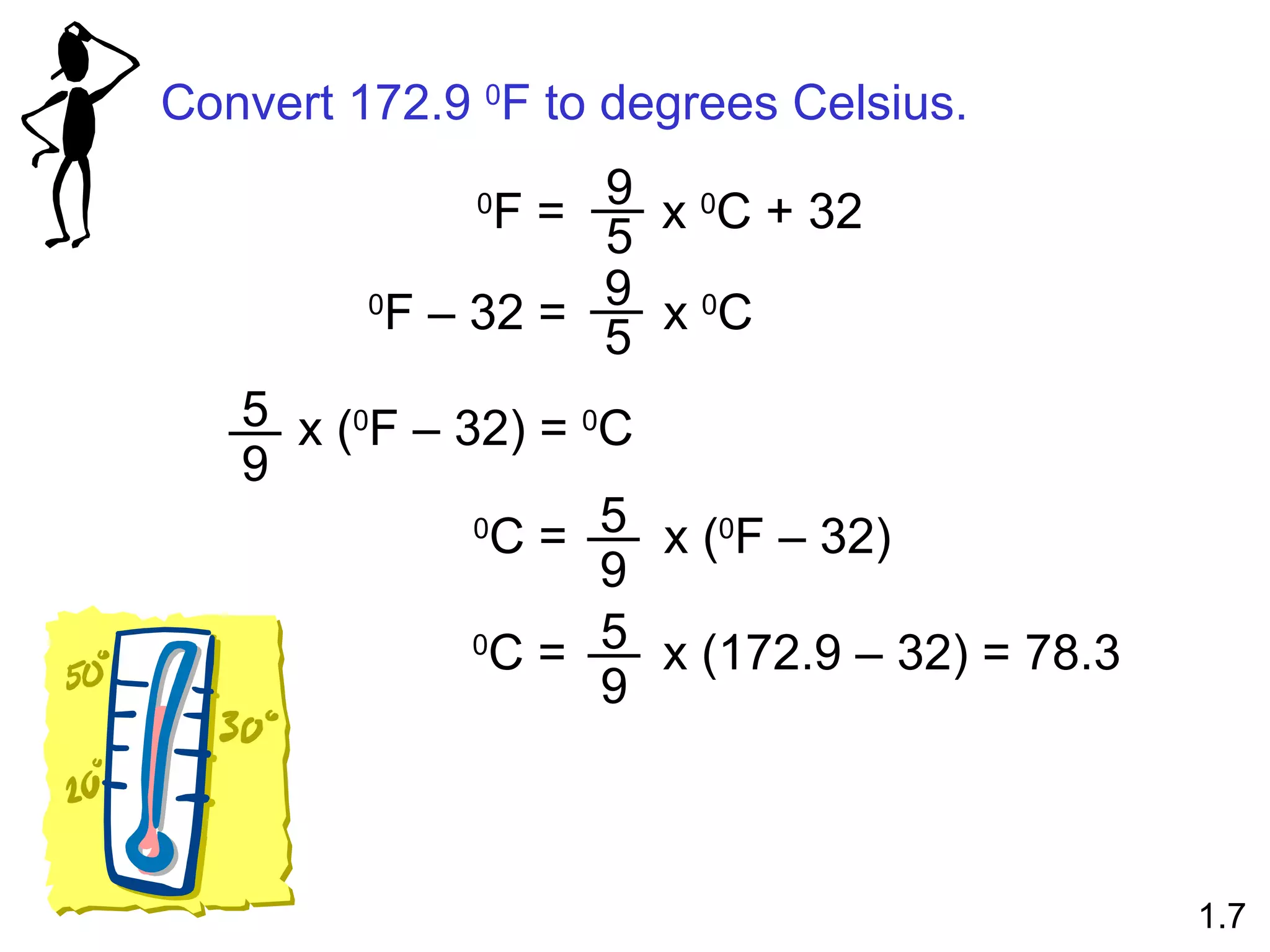
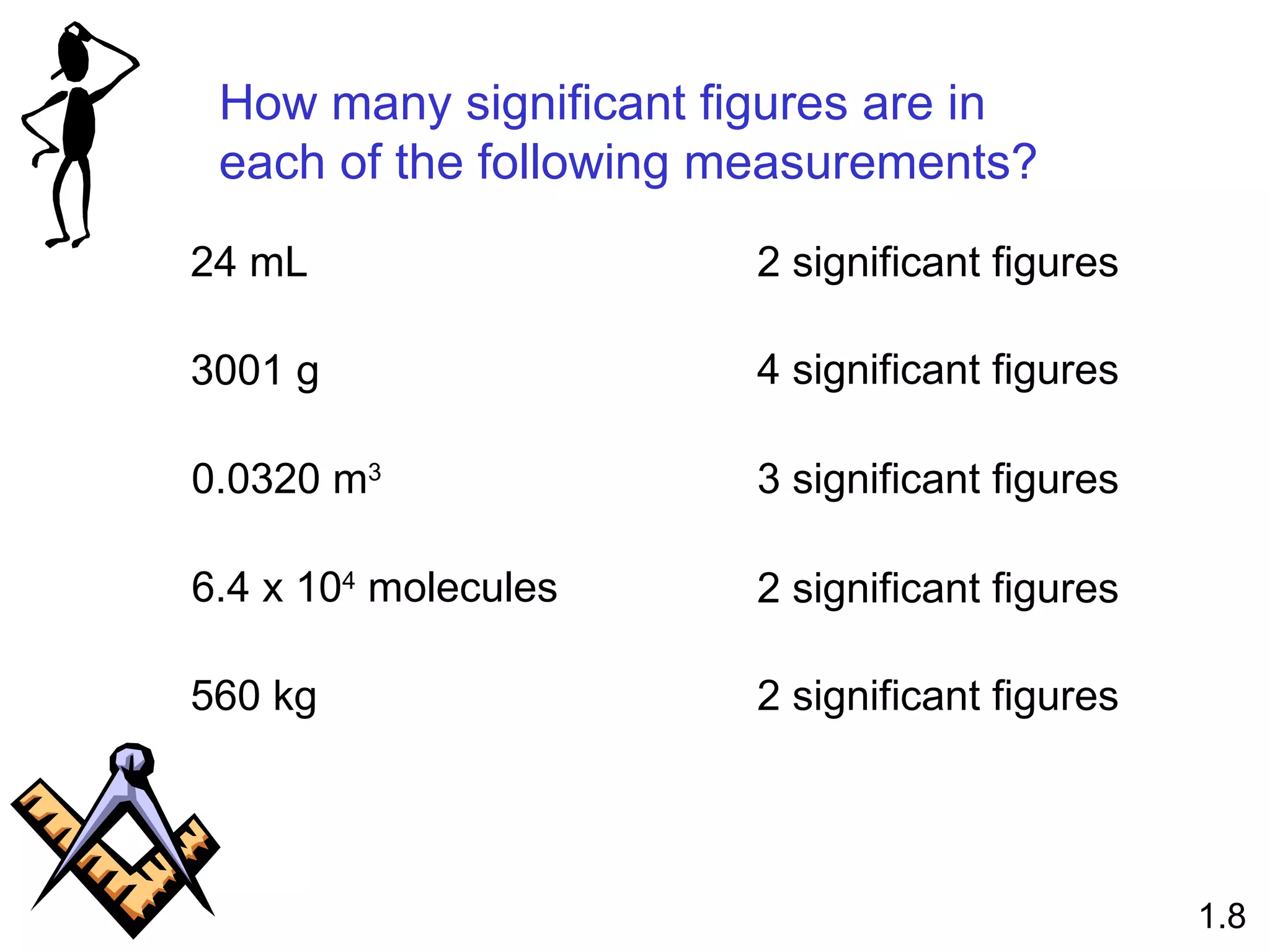
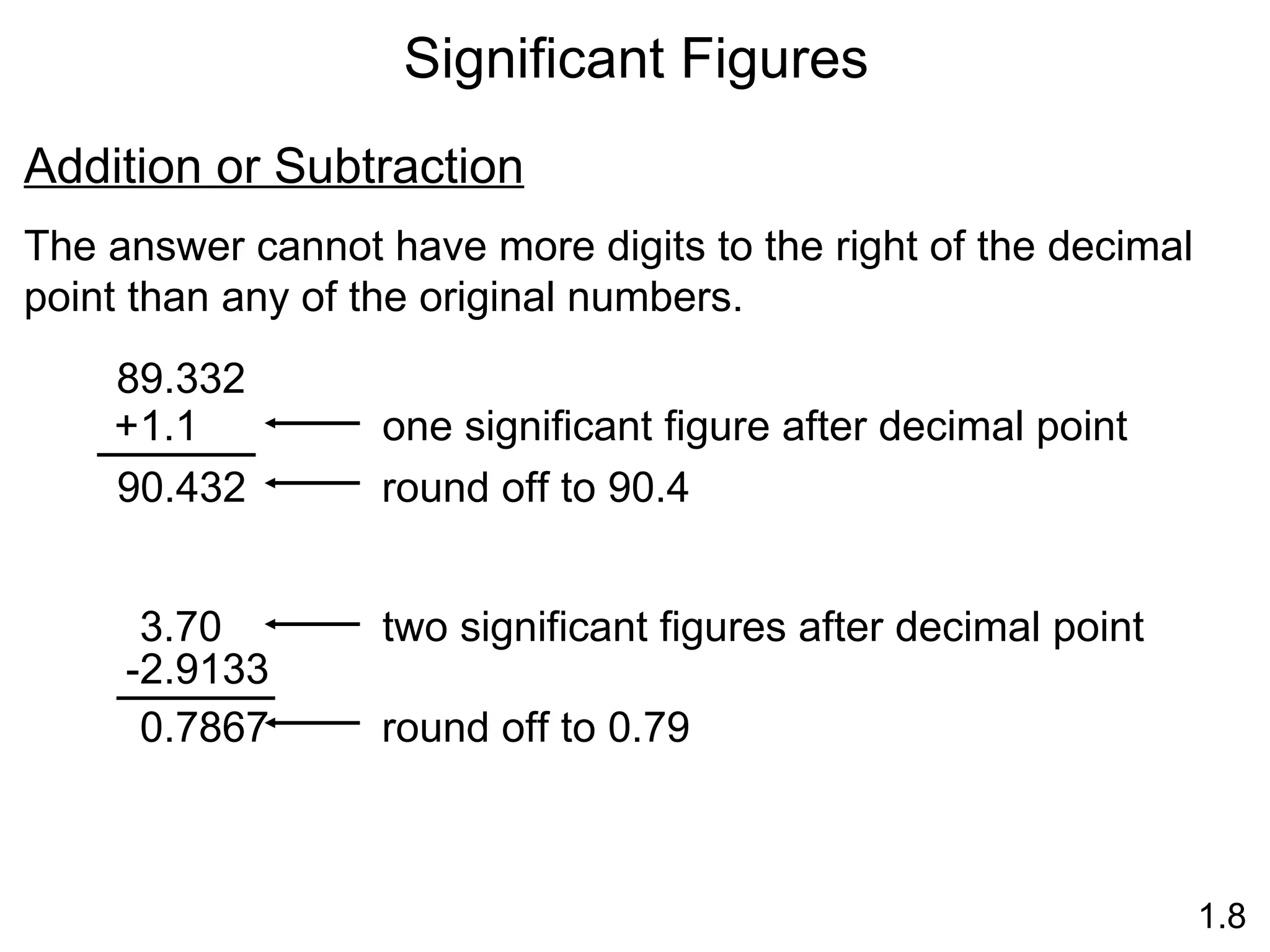
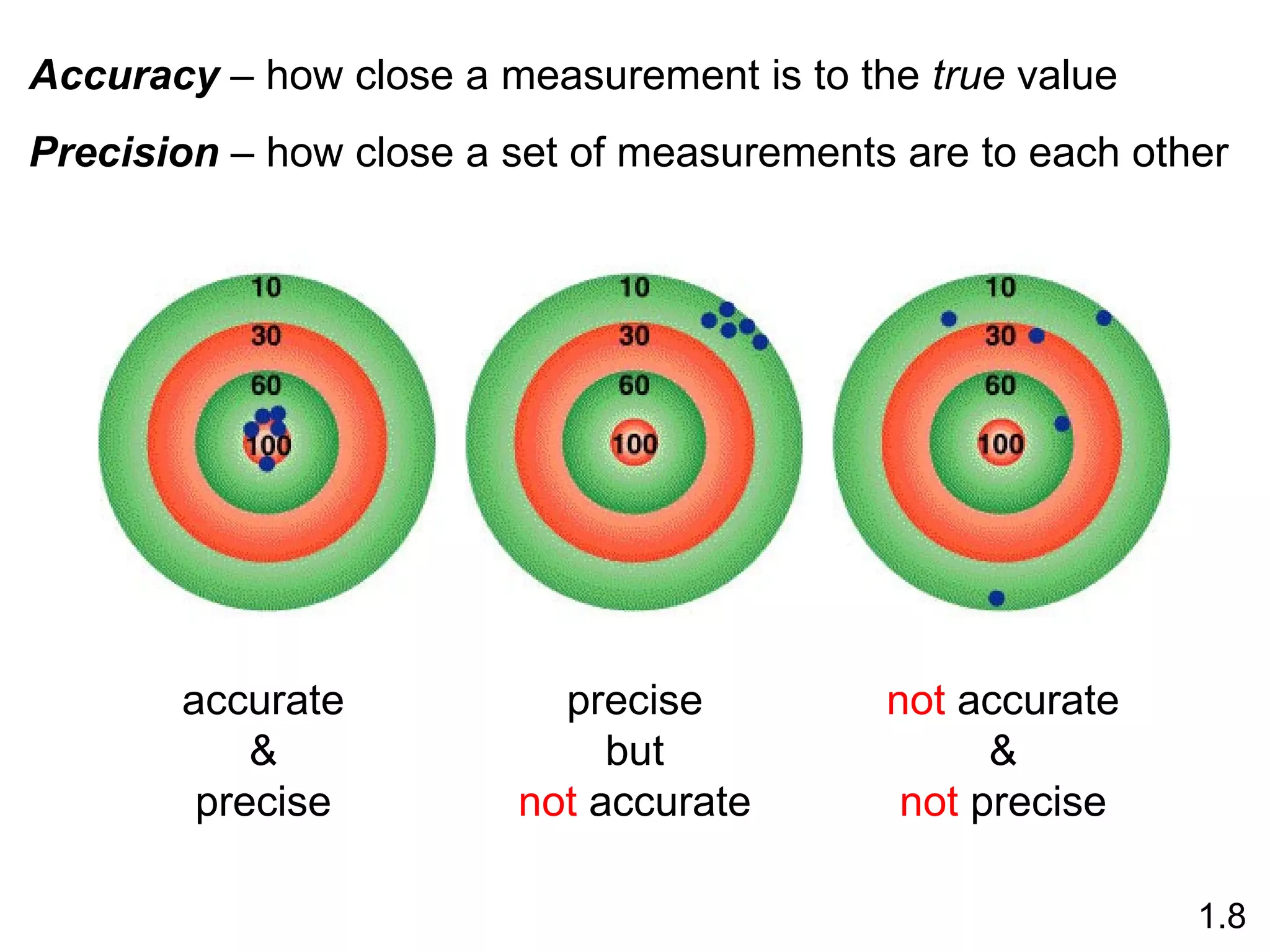
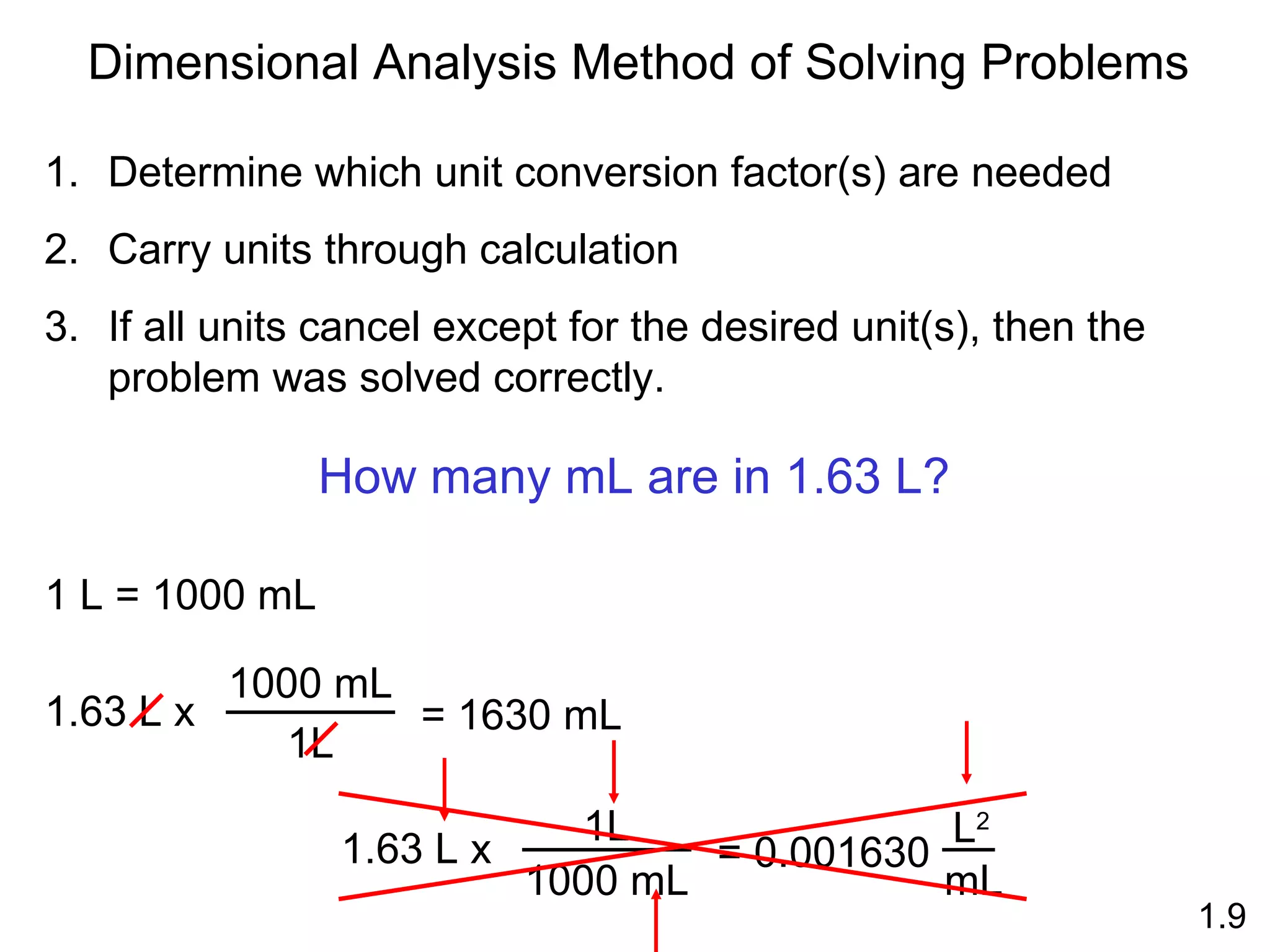
- Physical changes do not alter the composition or identity of a substance, while chemical changes do alter the composition or identity of one or more substances.
- Extensive properties depend on amount, while intensive properties do not.
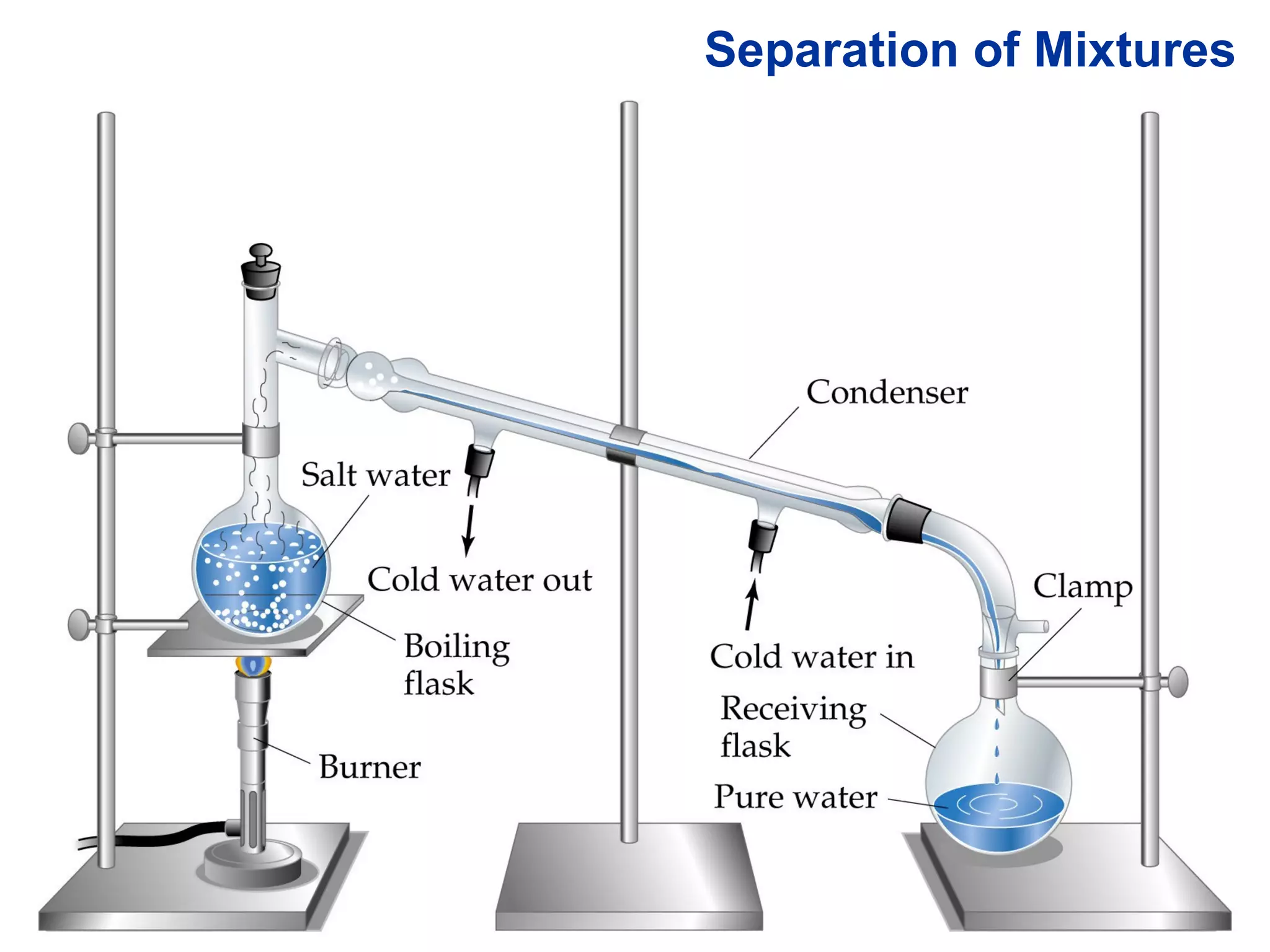
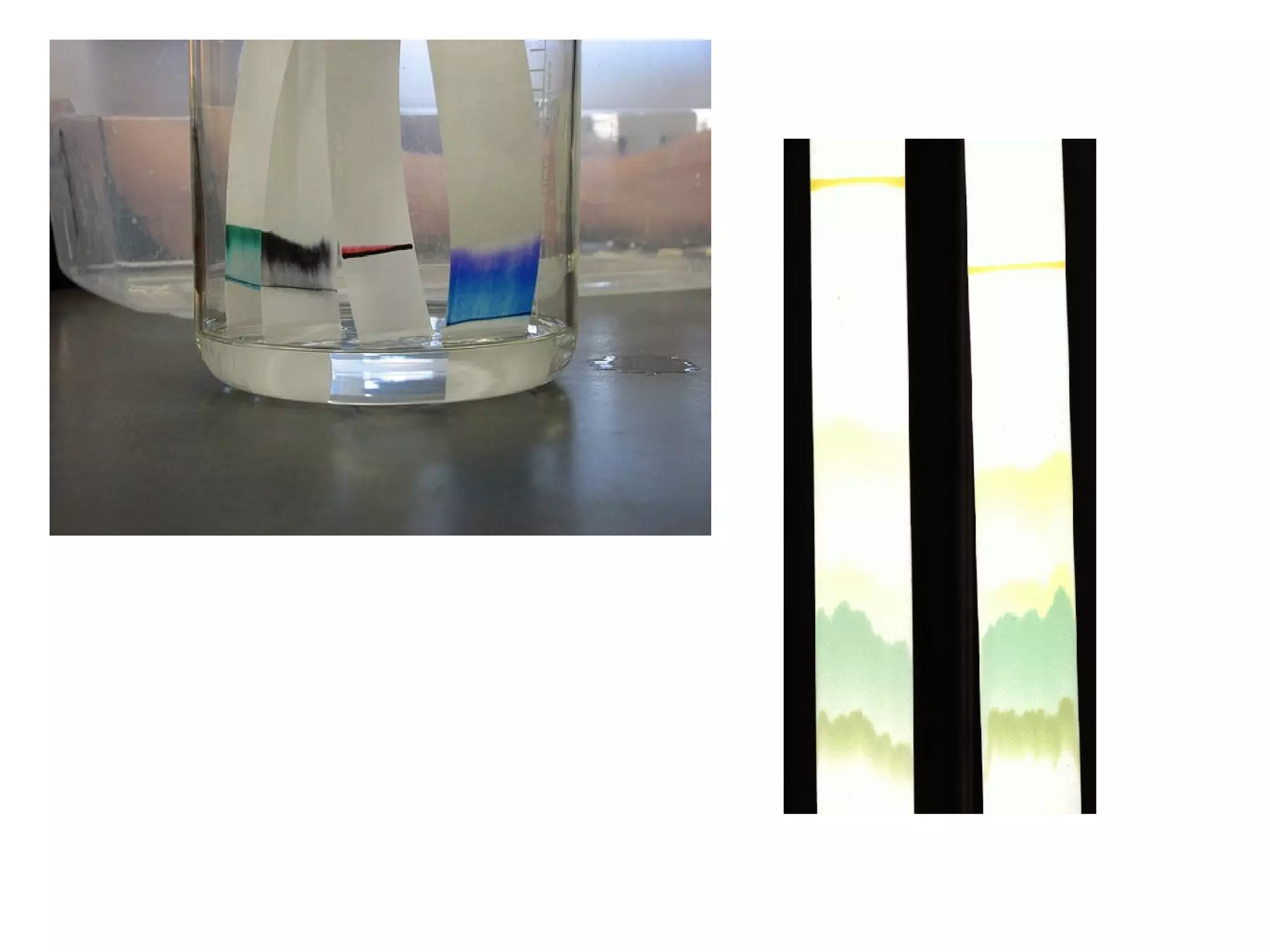
- Mixtures can be separated based on differences in their physical properties, such as filtering solids from liquids, distilling liquids based on differing boiling points, and chromatography.