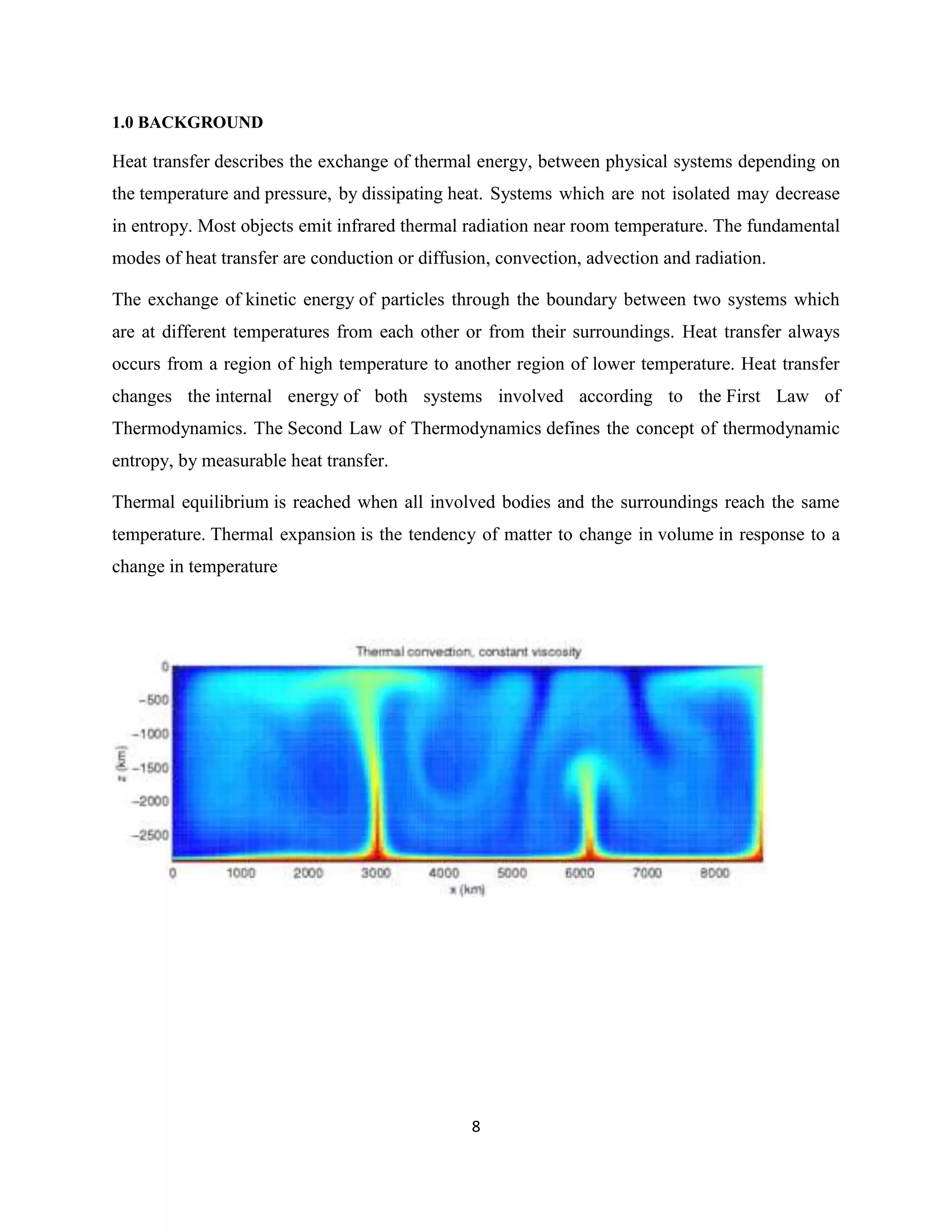
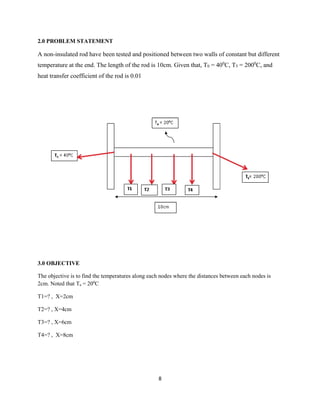
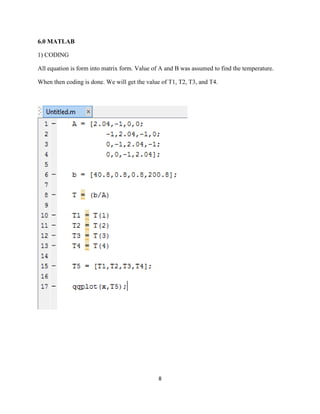
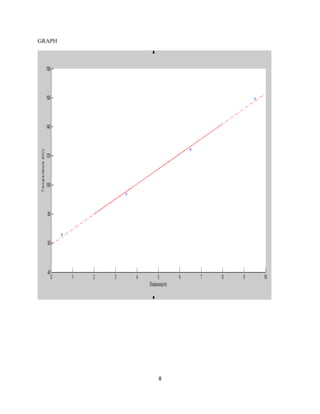
The document discusses heat transfer between systems at different temperatures. It provides background on the fundamental modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, radiation, advection). It then presents a problem statement involving the temperature at different points along a rod with varying temperatures at its ends. Both analytical and numerical solutions are developed to calculate the temperatures at each point. The numerical solution uses a finite difference method and matrix equations in MATLAB to calculate temperatures with higher accuracy than the analytical solution.