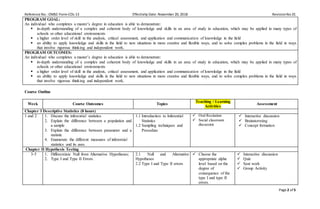
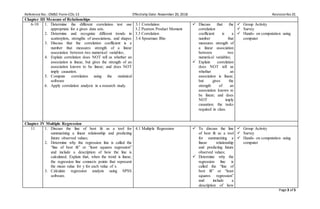
This document provides information about a Master of Arts in Education course on Statistics in Education offered by Occidental Mindoro State College. It includes the college's vision and mission, the graduate school's goal, and details about the course including its description, code, credit units, prerequisite, outline, requirements, grading system, and approvals. The course aims to provide students with knowledge of fundamental statistical areas, tools, and analyses that can be applied to educational research.