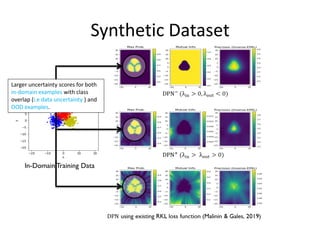
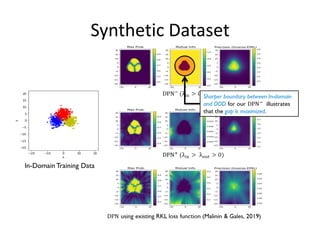
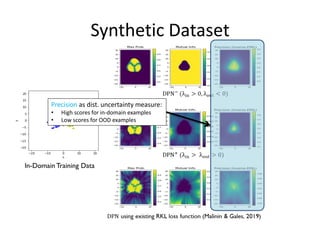
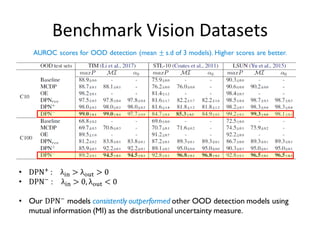
The paper addresses the limitations of existing out-of-distribution (ood) detection models, particularly under high data uncertainty, by proposing a novel loss function that maximizes the representation gap between in-domain and ood examples. It introduces a multi-modal Dirichlet distribution to model distributional uncertainty more effectively, leading to improved performance in ood detection. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing approaches.

![Predictive Uncertainty of DNNs
Data or Aleatoric uncertainty:
Arises from the natural complexities of the
underlying distribution, such as class
overlap, label noise, homoscedastic and
heteroscedastic noise
Distributional Uncertainty:
Distributional mismatch between the
training and test examples during inference
Model or Epistemic uncertainty
Uncertainty to estimating the network parameters, given training data
Reducible given enough training data
In-domain example with Data
or Aleatoric uncertainty
Out-of-distribution (OOD)
example, that leads to
distributional uncertainty
[Gal, 2016; Candela et al., 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-2-320.jpg)

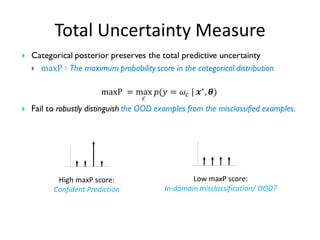
![Existing Approaches: Non-Bayesian
• Representation of predictive uncertainty:
• Sharp categorical posterior for in-domain examples
• Flat categorical posterior for out-of-domain (OOD) examples
• Limitations:
• Cannot robustly determine the source of uncertainty
• In particular, high data uncertainty among multiple class leads to the same
representation for both in-domain and OOD examples.
In-Domain
Misclassification
Out-of-Domain (OOD)
Examples
In-Domain
Confident Prediction
[Hendrycks et al., 2019b, Lee et al., 2018]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-4-320.jpg)
![Existing Approaches: Bayesian
• Bayesian neural networks assumes a prior distribution over the network parameters
• Approximation requires to estimate the true posterior of the model parameters
• Sample model parameters using MCMC or Deep Ensemble etc.
• Limitations:
• Computationally expensive to produce the ensemble
• Difficult to control this desired behavior
In-Domain Confident pred.
• Ensemble of prediction in one
corner of the simplex.
In-Domain Misclassification:
• Ensemble of prediction in the
middle of the simplex.
OOD Examples:
• Ensemble of prediction are
scattered over the simplex.
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
[Gal and Ghahramani, 2016; Lakshminarayanan et al., 2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-5-320.jpg)
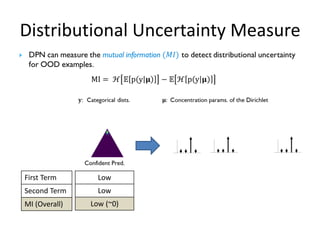
![Dirichlet Prior Network (Existing)
• Parameterize a prior Dirichlet distribution to the categorical posteriors over a
simplex
• Objective: Efficiently emulating the behavior of Bayesian (ensemble) approaches
Sharp Dirichlet in one corner
Uni-modal categorical.
Sharp Dirichlet in the middle
Multi-modal categorical
Flat Dirichlet
Uniform categorical
over all class labels.
Confident prediction
(In-Domain Examples)
Misclassification
(In-Domain Examples)
OOD Examples
[Malinin & Gales, 2018; 2019]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-6-320.jpg)
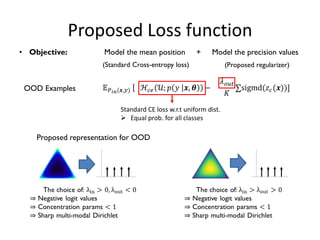
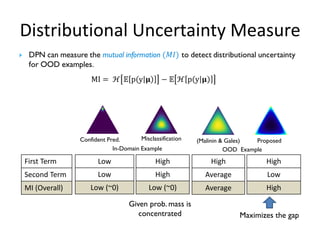
![Proposed Representation for OOD
• Limitation (high Data uncertainty)
• In-domain examples with high data-uncertainty, among multiple classes, leads to
producing flatter Dirichlet distribution
• Can be observed for classification task with large number of classes
• This often leads to indistinguishable representation from OOD examples.
• Compromise the OOD detection performance
Confident prediction
(In-Domain Examples)
Misclassification
(In-Domain Examples)
OOD Examples
Desired Actual
[see detailed analysis in our paper]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-7-320.jpg)

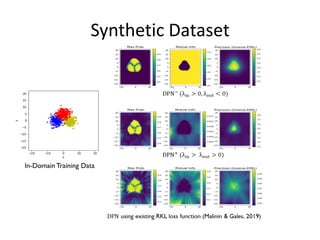
![Proposed Loss function
Confident prediction
(In-Domain Examples)
Misclassification
(In-Domain Examples)
OOD Examples
Desired Actual Existing Proposed
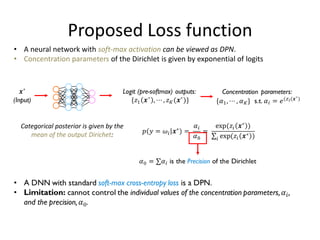
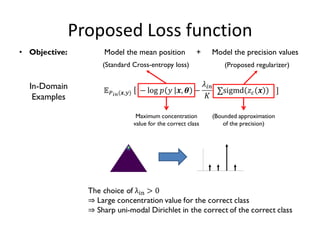
We propose a novel loss function to separately model the mean and precision of the
output Dirichlet distribution:
• Mean: Cross entropy loss with soft-max activation
• Precision:A novel explicit precision regularization function
Provides a better control on the desired representation.
We show that the existing RKL loss cannot produce this representation
[see more detailed analysis in our paper]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingtherepresentationgapbetweenin-domainood-200716163413/85/Maximizing-the-Representation-Gap-between-In-domain-OOD-examples-9-320.jpg)