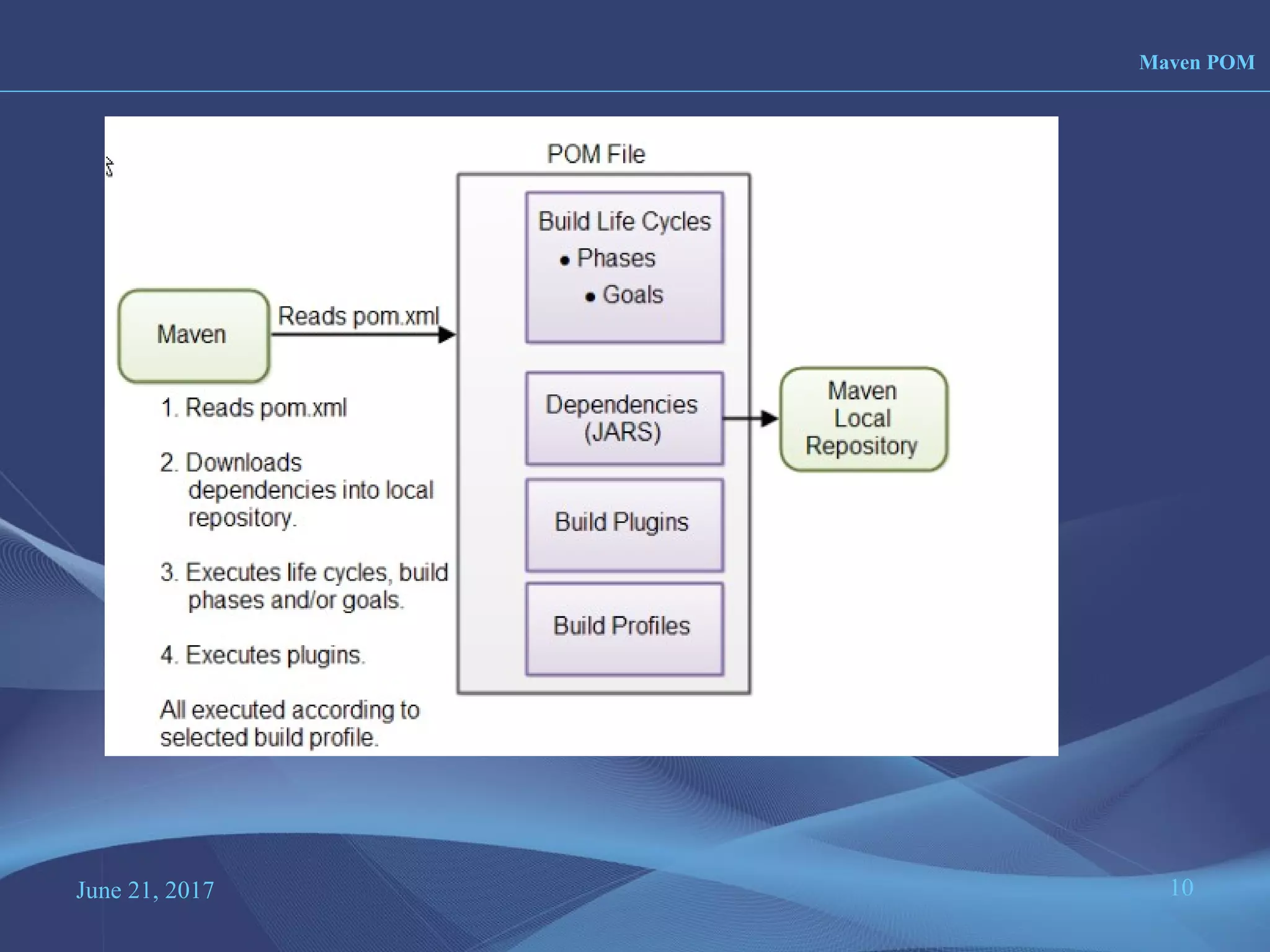
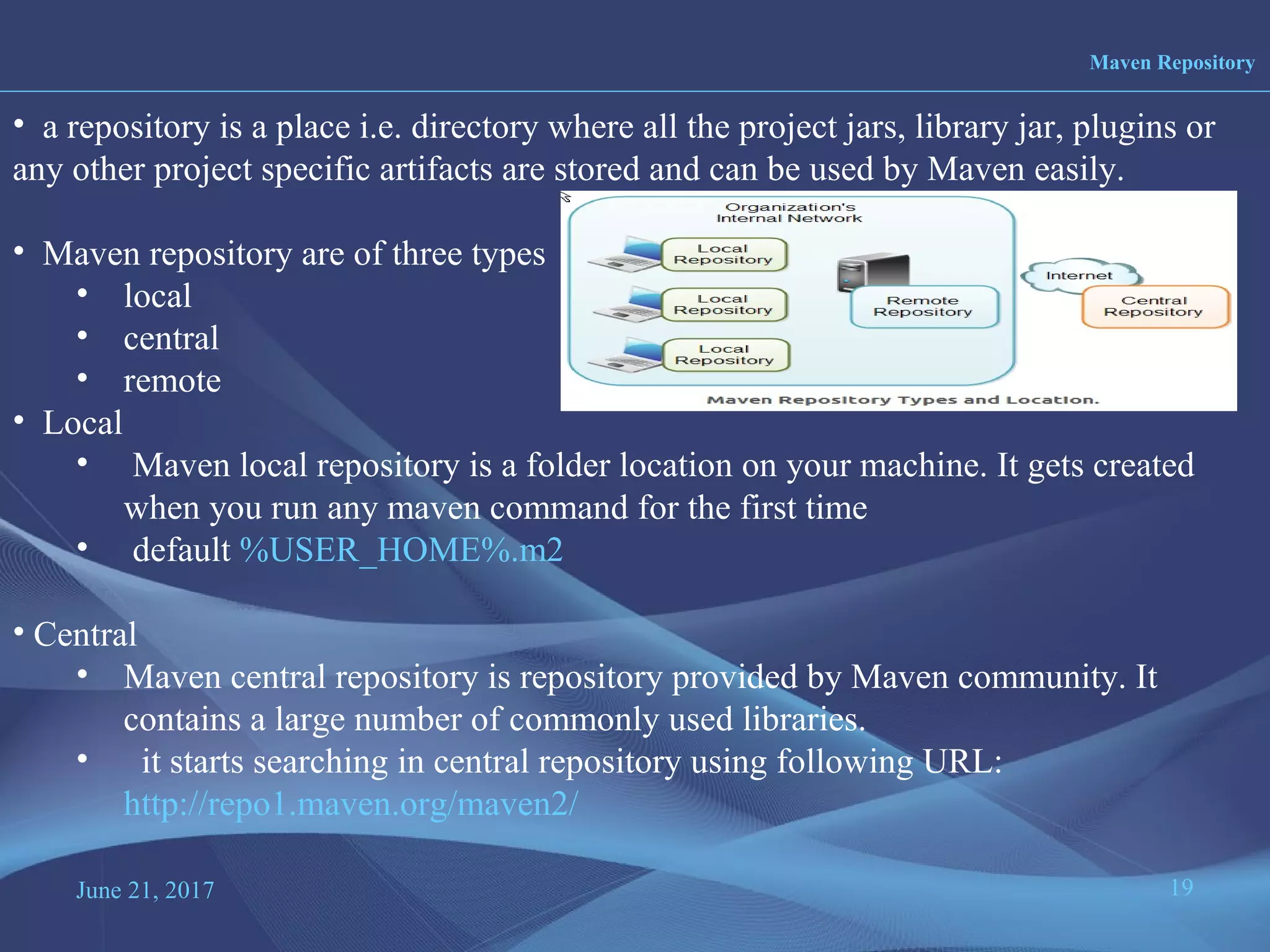
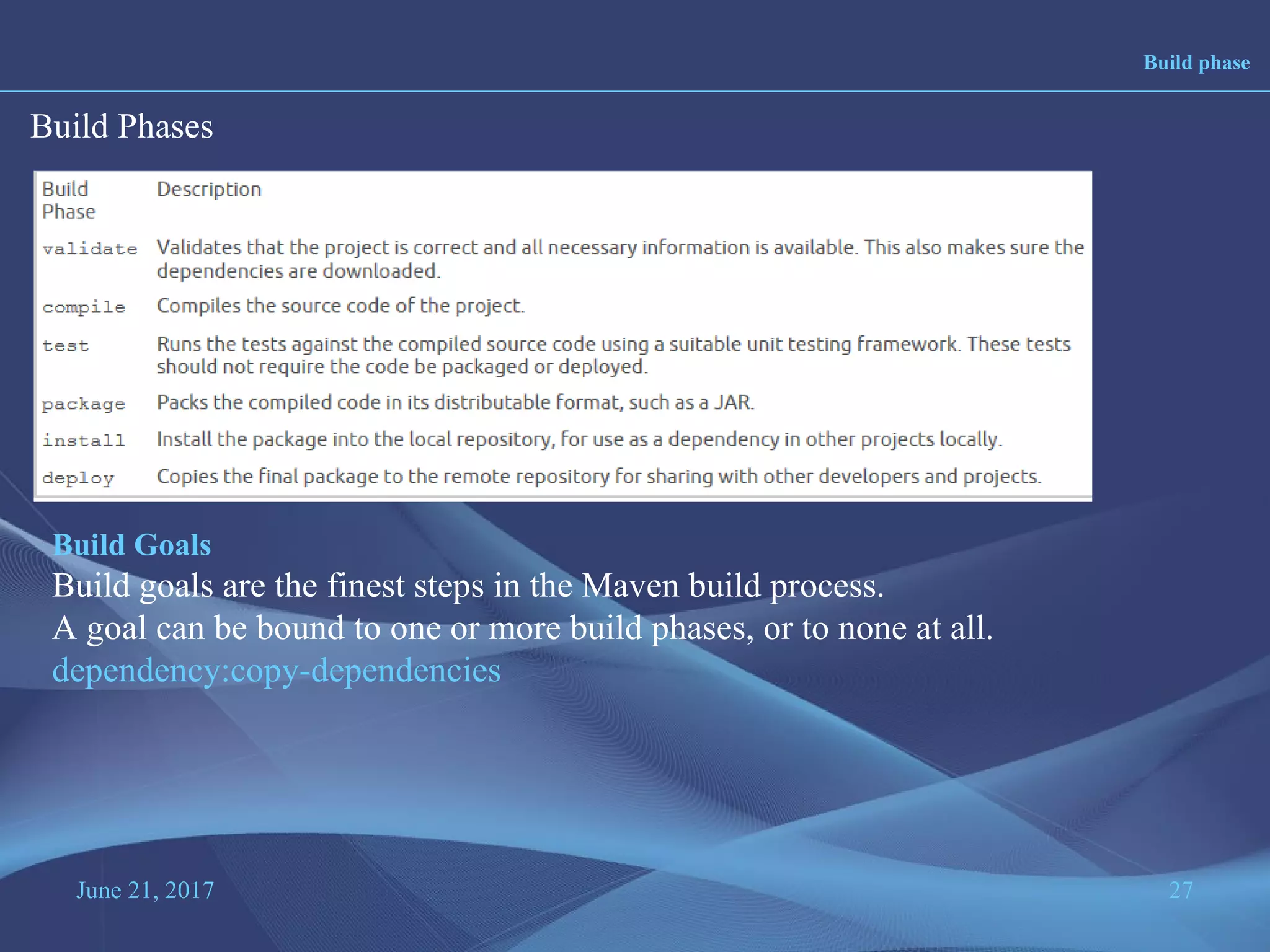
Maven is a project management and build tool that is commonly used for Java projects. It uses a Project Object Model (POM) file to manage a project's build, reporting, documentation and dependencies. The POM file contains information about the project like its name, version, dependencies and configuration details. Maven has built-in support for managing multi-module projects through its POM inheritance and module capabilities. It also standardizes project structures and builds through defined phases and goals in its build lifecycles.