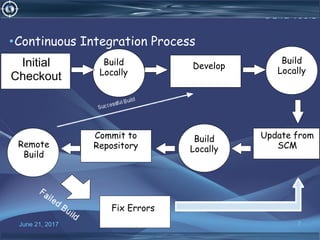
The document discusses continuous integration tools Hudson and Jenkins. Hudson was originally created by Sun Microsystems but later renamed to Jenkins after Oracle acquired Sun. Jenkins is an open source automation server that supports continuous integration practices. It allows developers to integrate code changes frequently and automatically test the code and detect errors. The document compares features of Hudson and Jenkins and explains why Jenkins may be preferable to use.