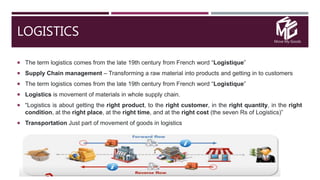
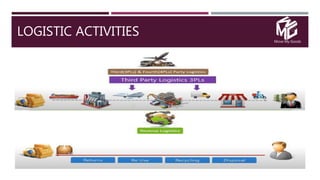
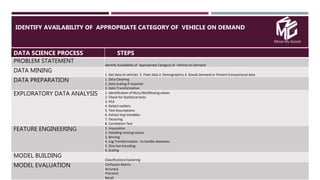
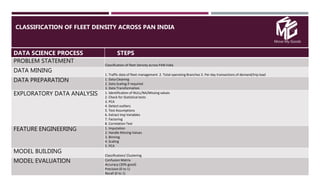
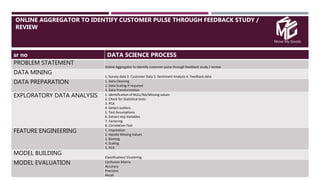
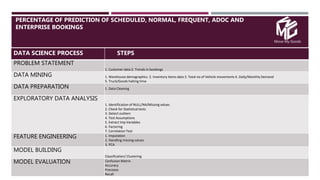
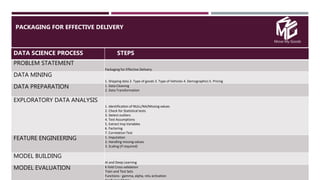
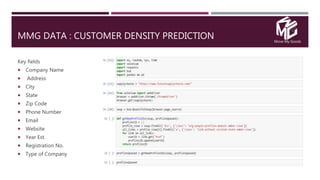
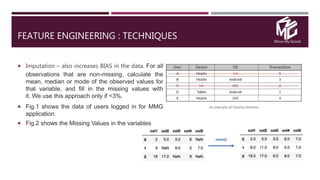
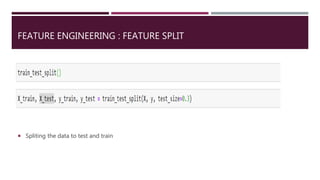
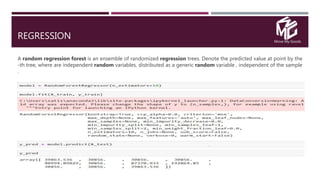
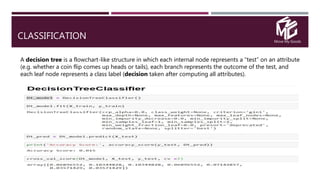
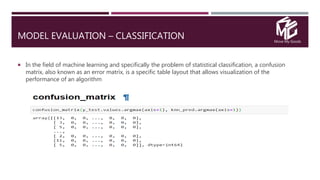
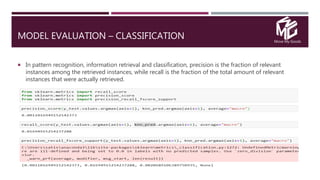
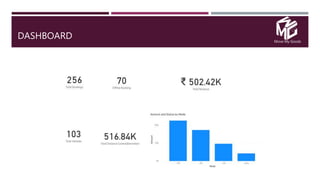
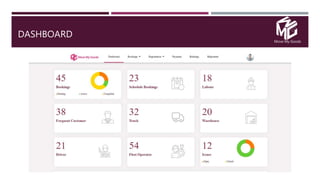
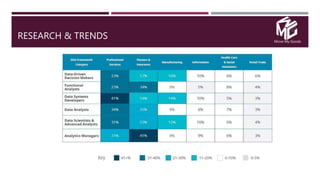
The document discusses the application of data science in the logistics industry, highlighting its impact on efficiency, cost reduction, and job opportunities in India. It emphasizes the growth potential of the logistics sector, driven by digital technology and e-commerce, and outlines various data science processes for optimizing logistics operations and forecasting demand. Key areas included are route optimization, warehouse efficiency, and the use of machine learning for improved decision-making.