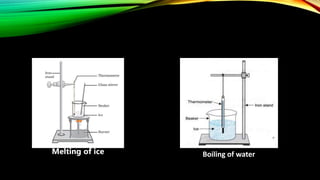
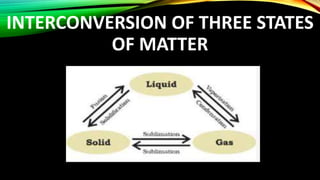
The document discusses the nature of matter, which is composed of tiny particles and can exist in solid, liquid, and gaseous states, each with distinct characteristics. It explains how particles of matter are in constant motion, how they interact through forces of attraction, and how changes in temperature or pressure can lead to changes in state. Additionally, it describes phenomena such as diffusion and evaporation, along with their influencing factors.