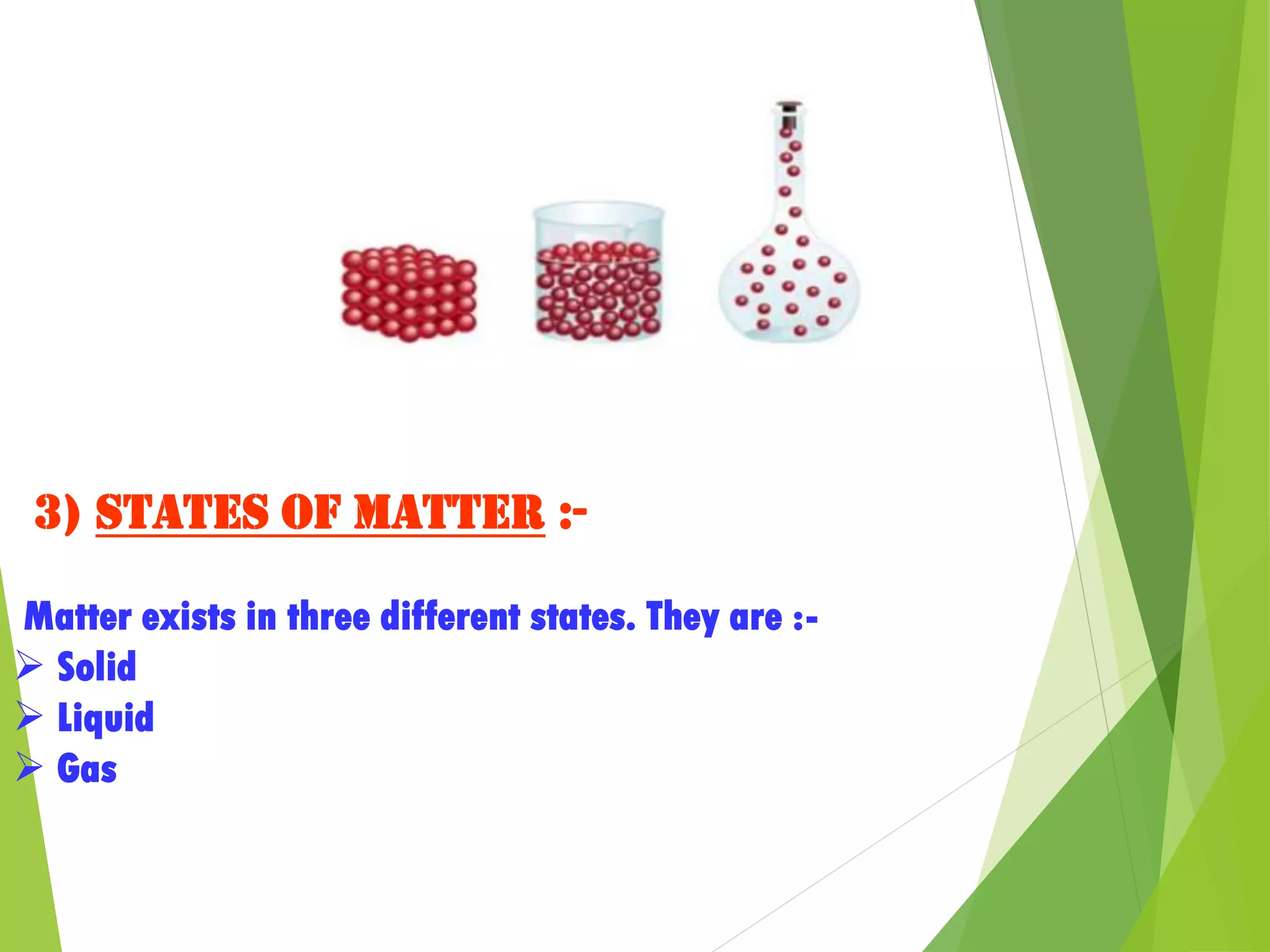
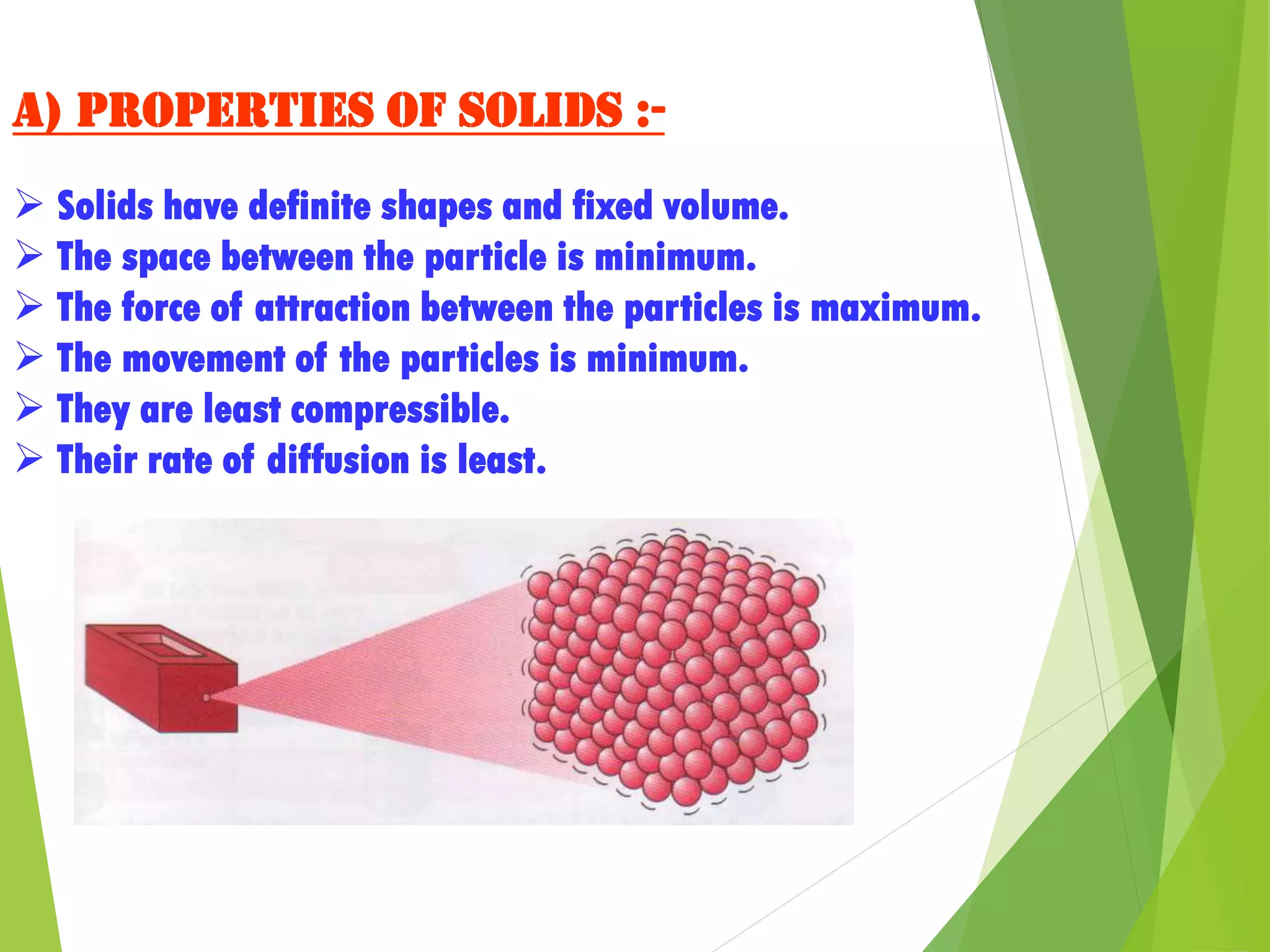
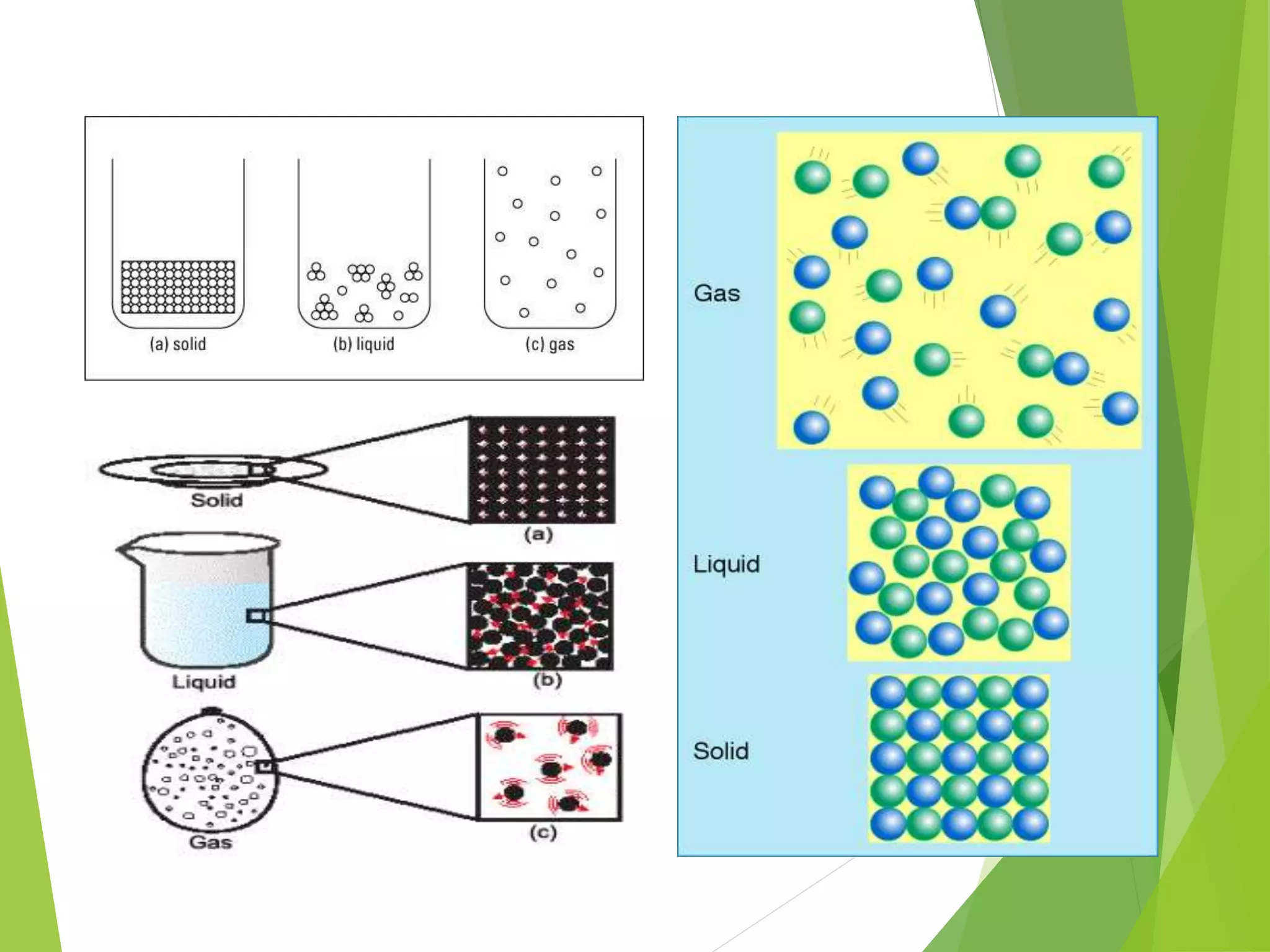
1. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass, and can exist in three states: solid, liquid, or gas.
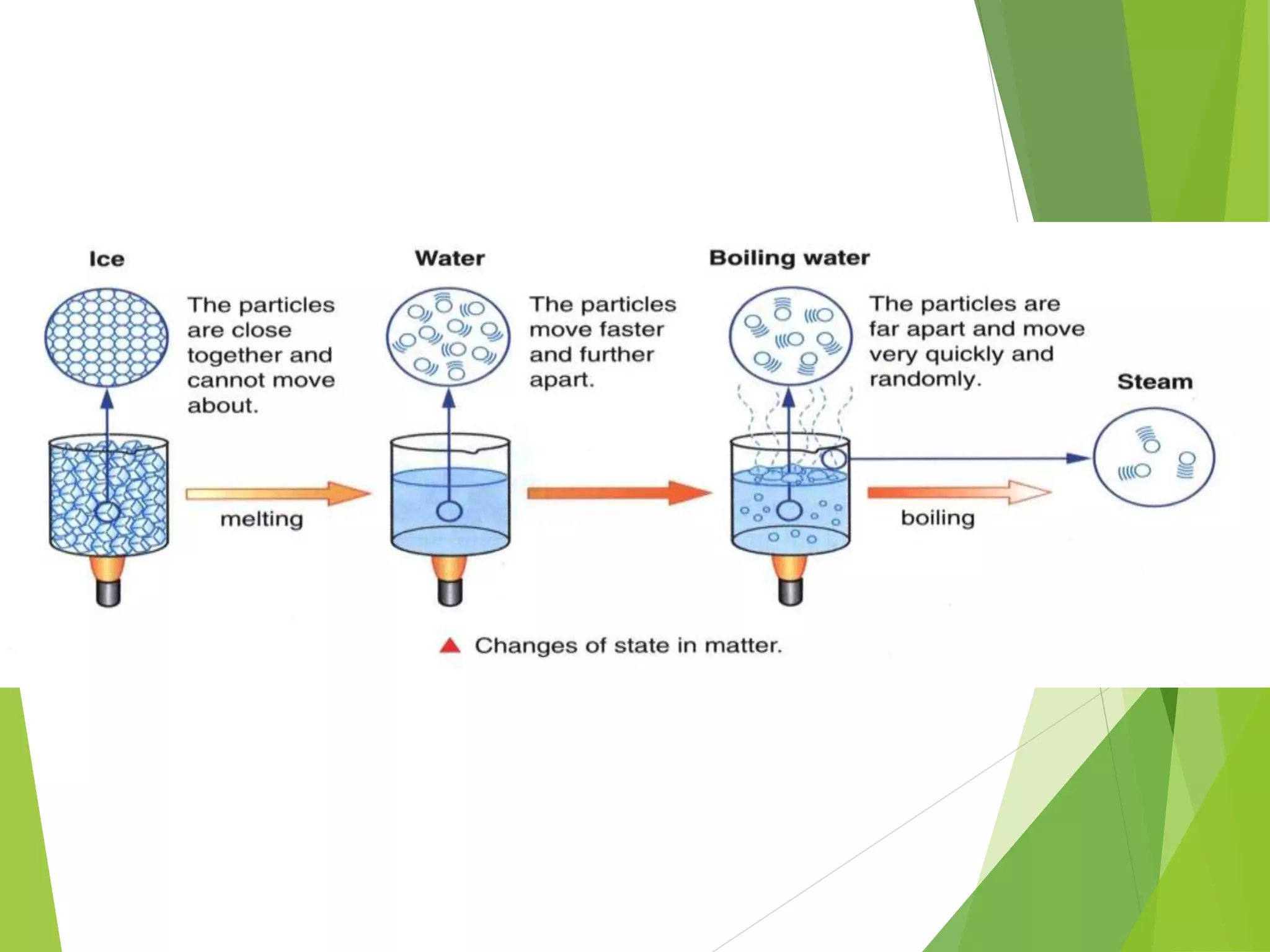
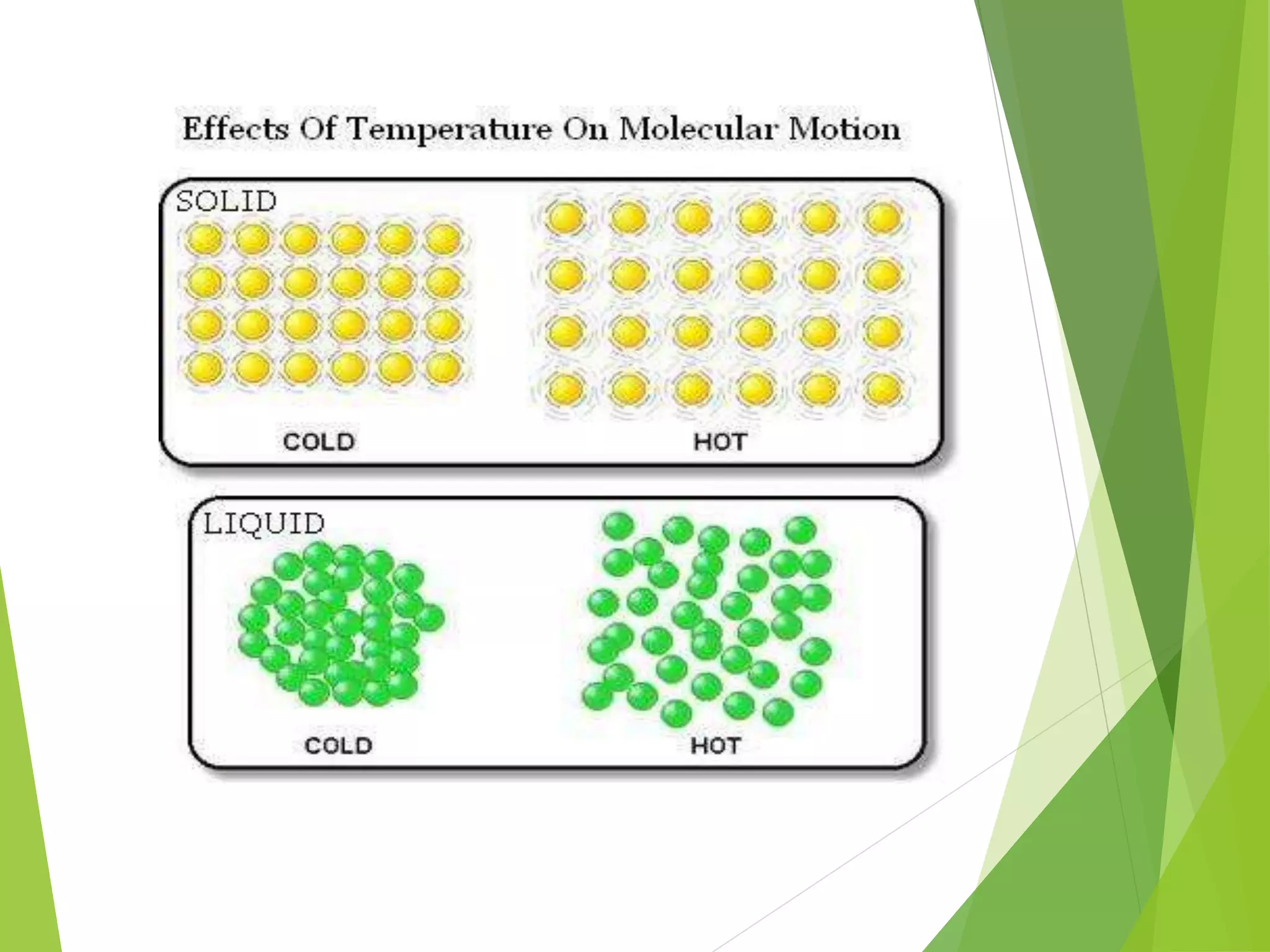
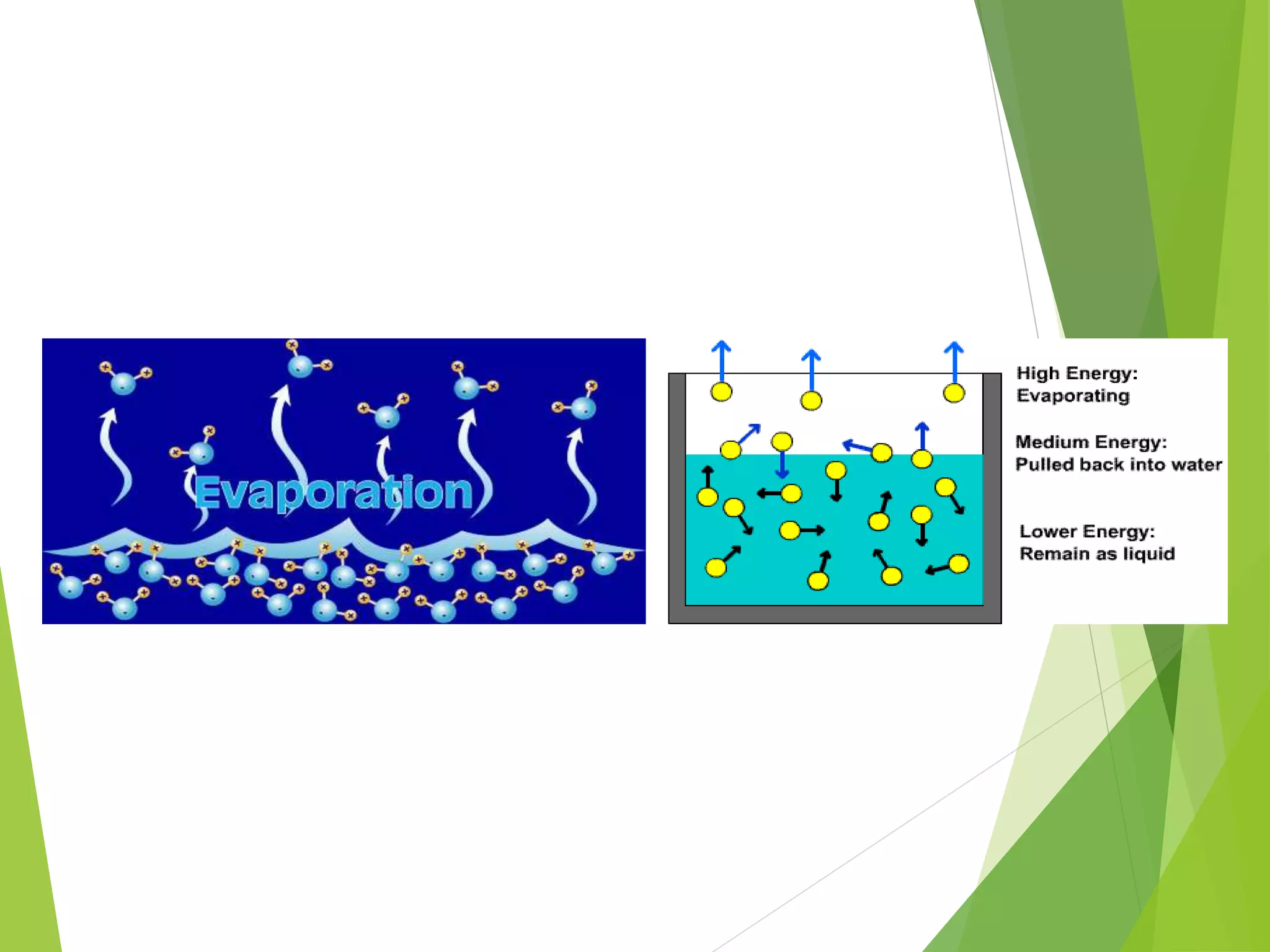
2. The particles that make up matter are very small, continuously moving, and attract one another, though they have space between them.
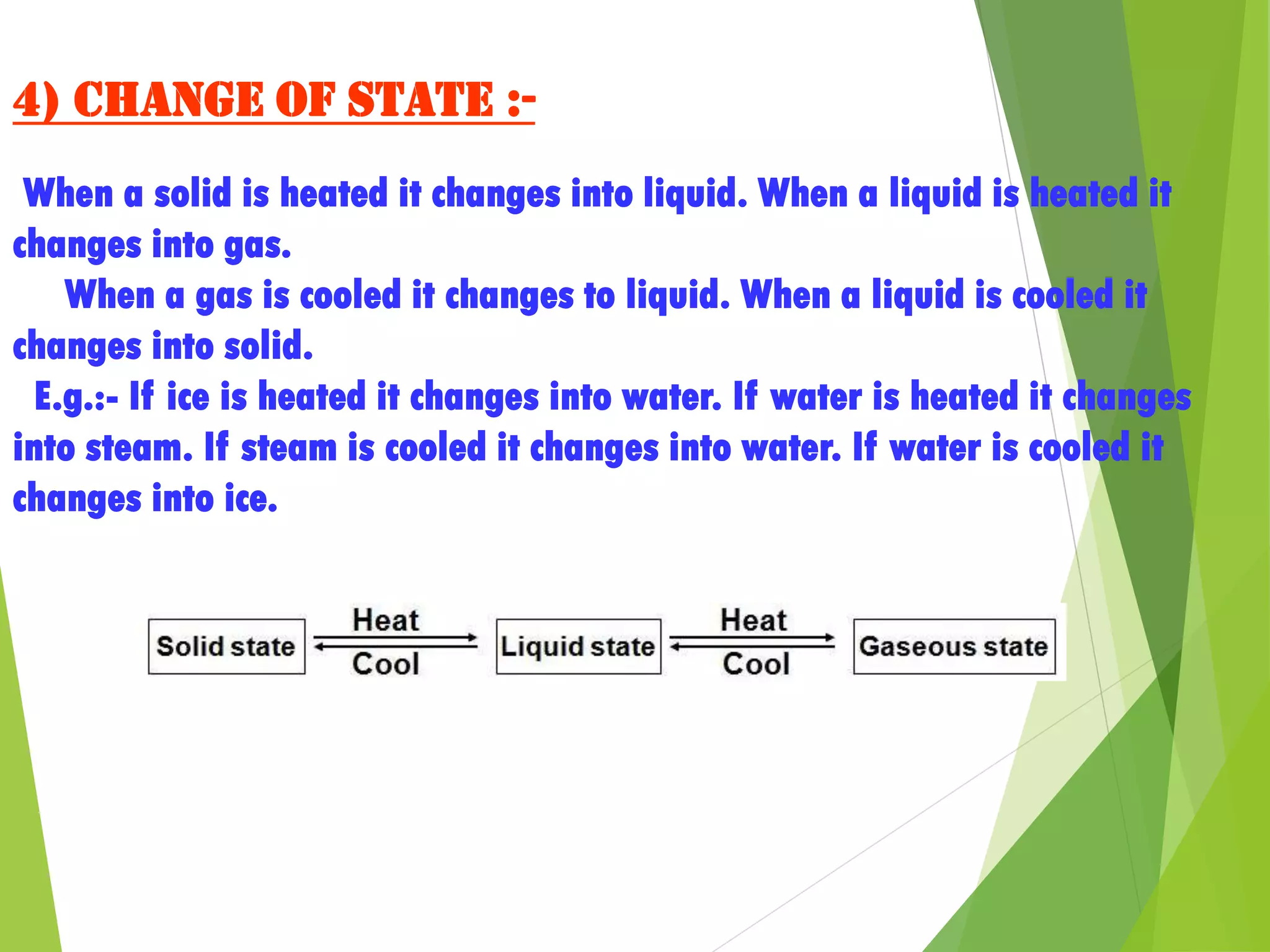
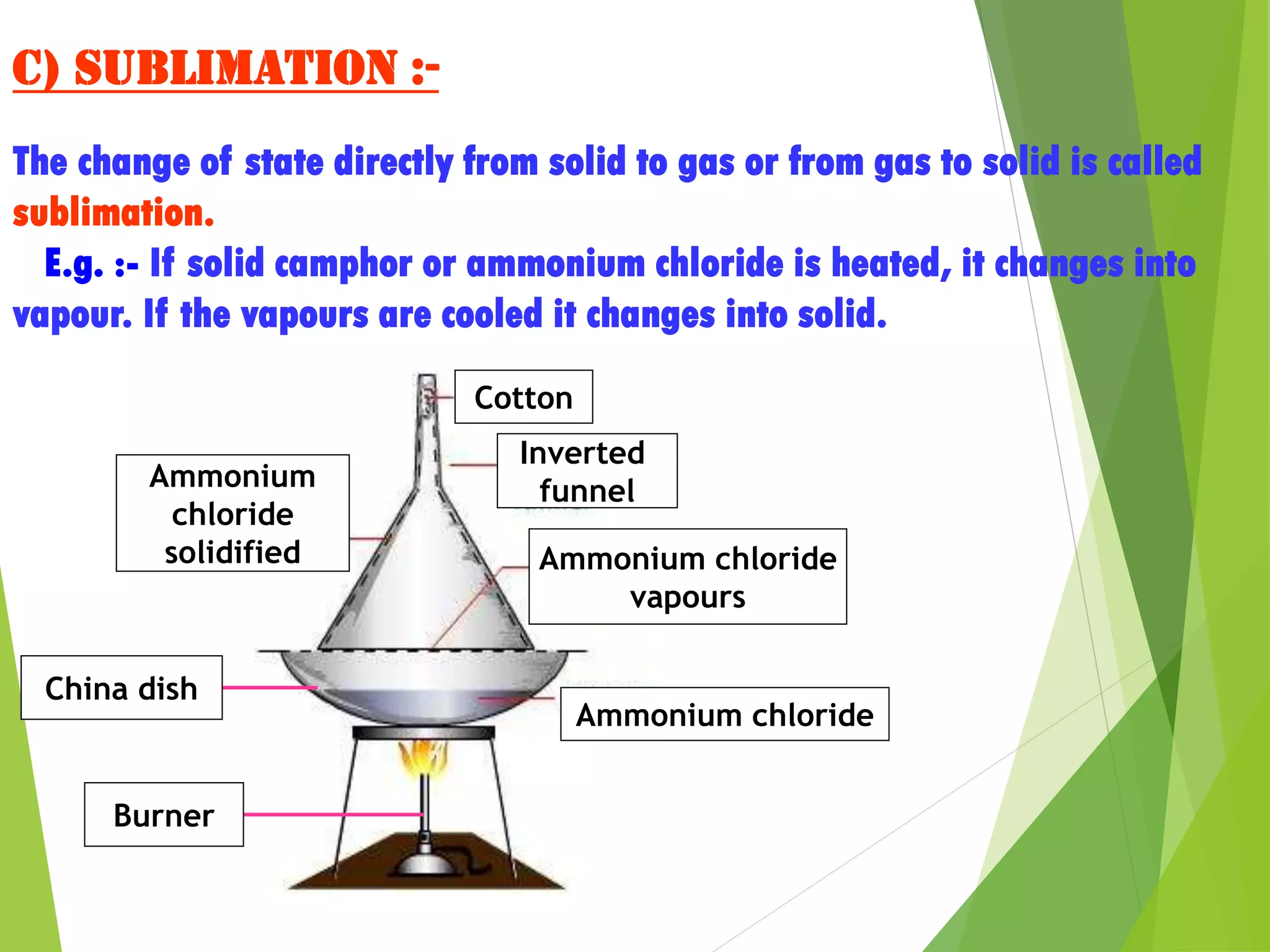
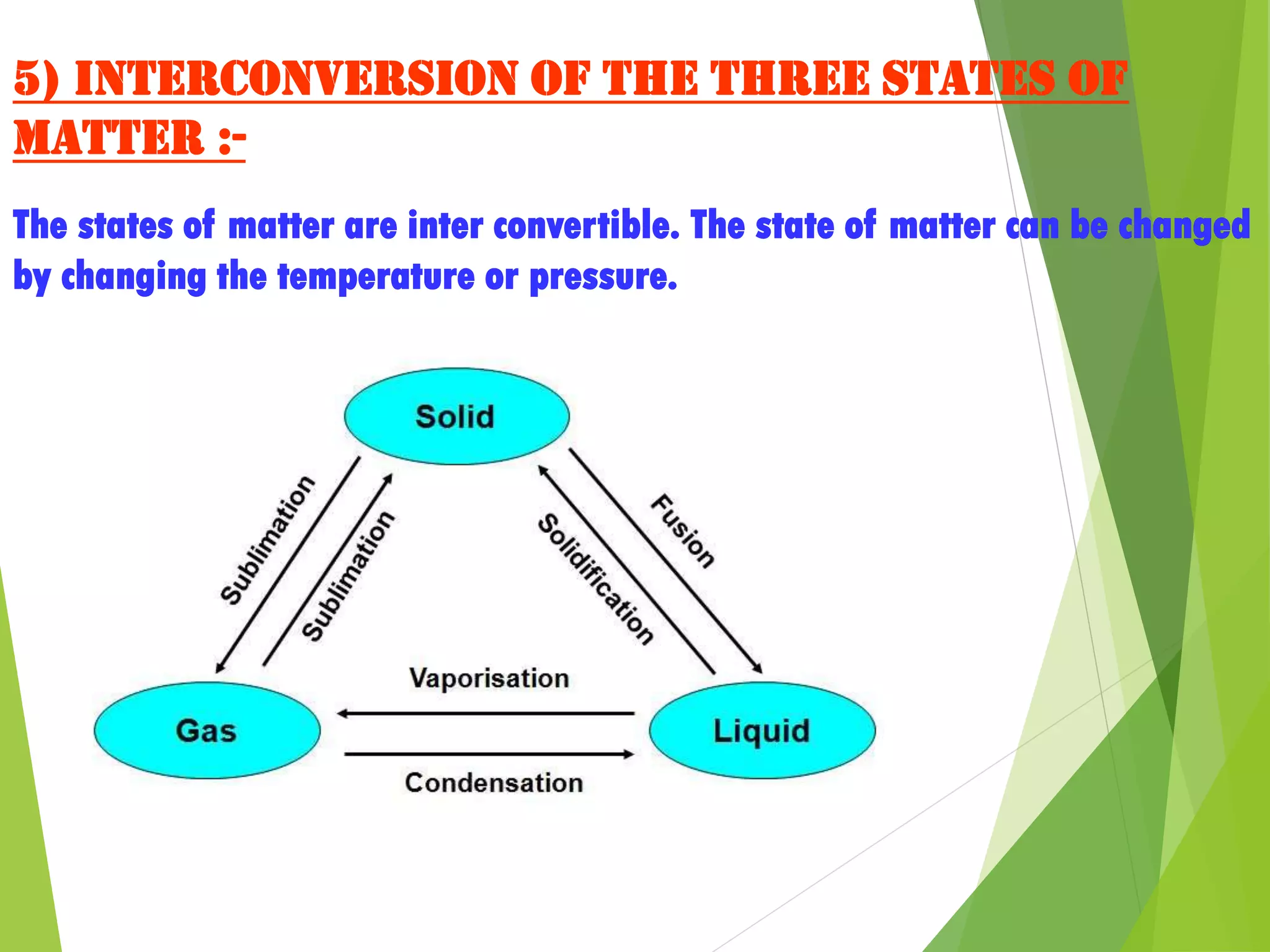
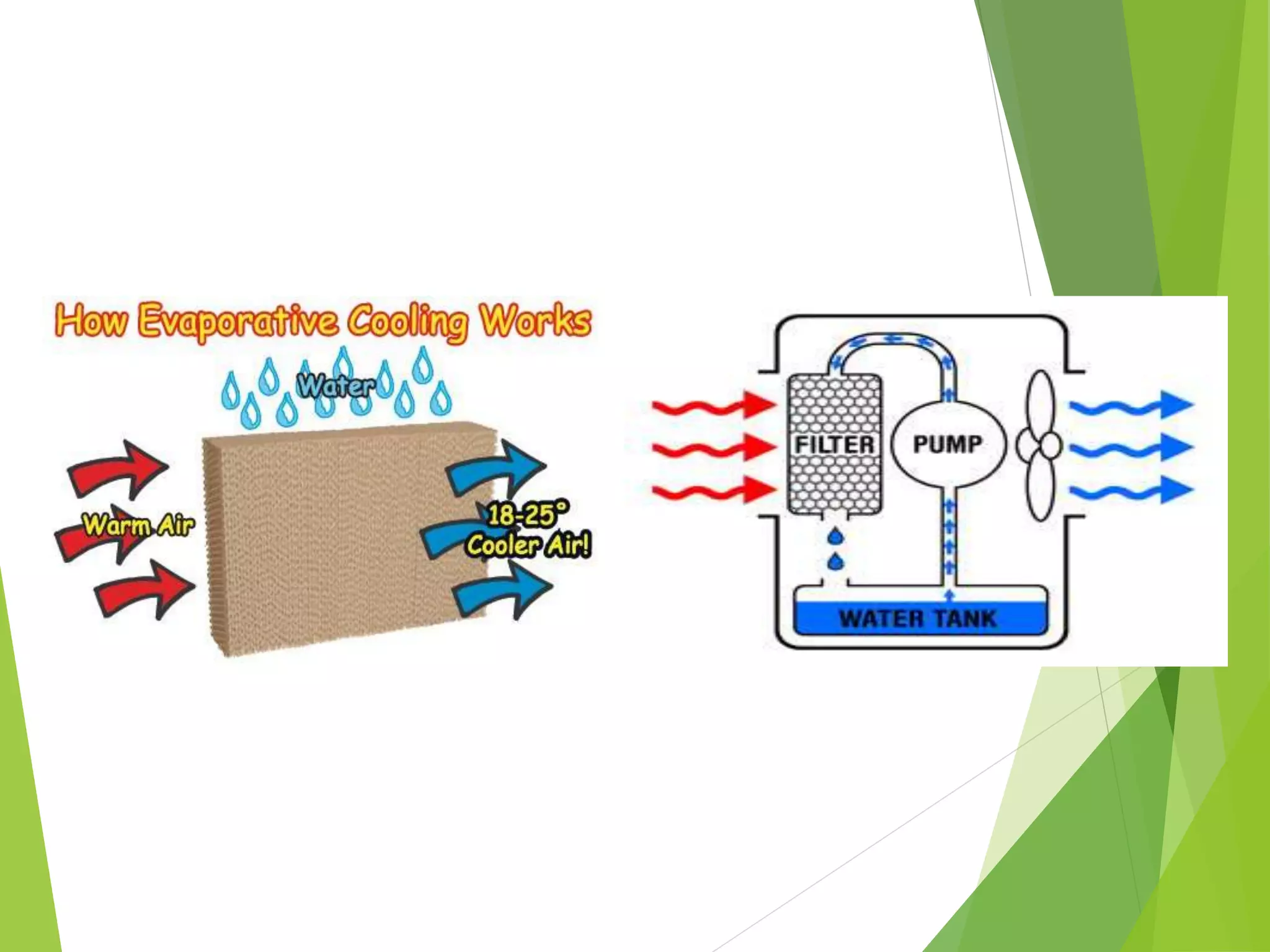
3. The states of matter - solid, liquid, gas - can be transformed by changing temperature or pressure. For example, melting occurs when a solid is heated and its particles gain energy and move freely, transforming it into a liquid.