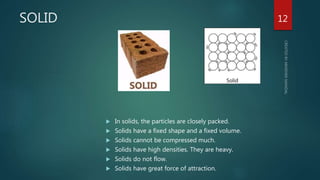
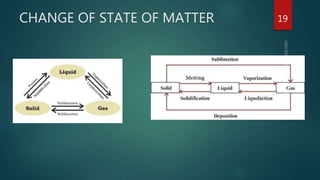
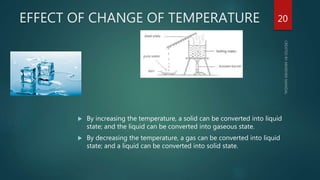
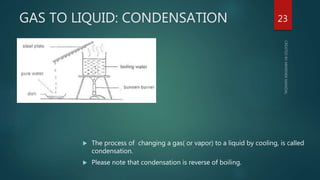
The document discusses the characteristics and classification of matter, defining it as anything that occupies space and has mass, with particles that are small, spaced apart, in constant motion, and attract each other. It details the states of matter (solids, liquids, gases, Bose-Einstein condensate, and plasmas), and explains processes like melting, vaporization, condensation, freezing, sublimation, and the effects of temperature and pressure on these states. Key concepts include diffusion, latent heat, and factors affecting evaporation.