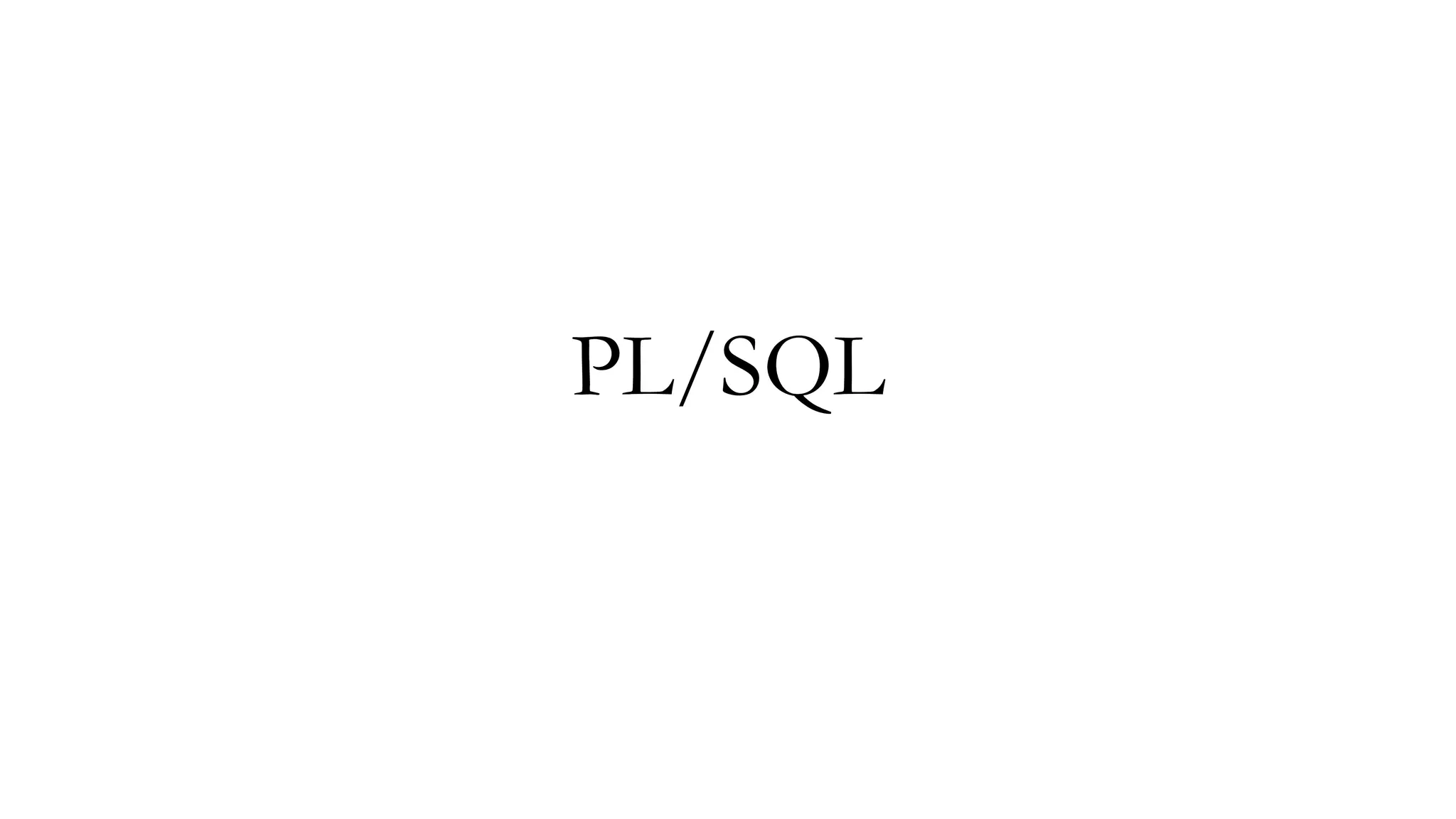
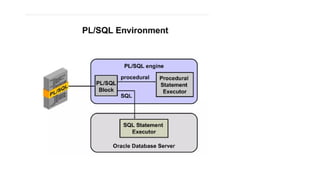
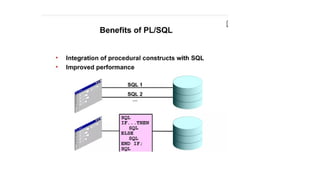
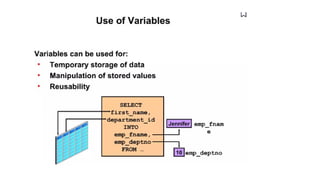
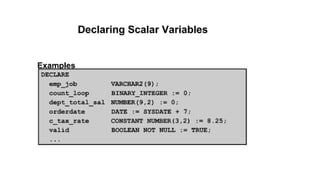
The document discusses PL/SQL programming, highlighting the use of comments, variable declarations, and the dbms_output.put_line statement for displaying information. It explains that PL/SQL is not a standalone language and relies on Oracle tools for user input with substitution variables. Additionally, it describes how to enable and configure output through the dbms_output package in SQL*Plus.