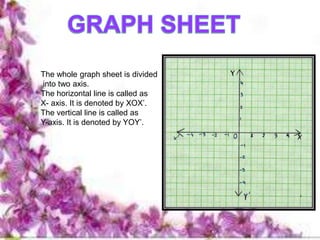
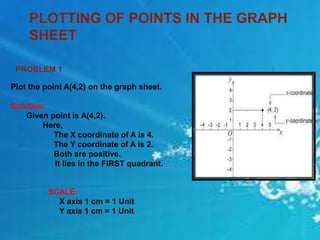
The document provides details of a digital lesson plan for teaching graphs to an 8th grade mathematics class. It includes definitions of key graphing terms like axes, quadrants, and plotting points. It also gives examples of plotting individual points, drawing lines parallel to axes, and drawing lines between two points. The lesson plan aims to help students understand how to draw and interpret graphs through examples and practice problems.