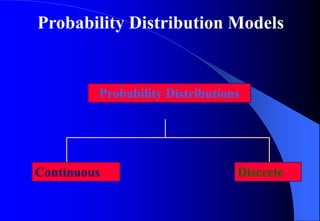
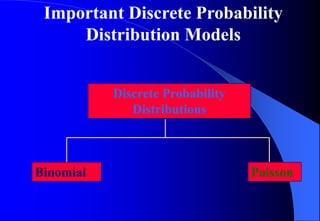
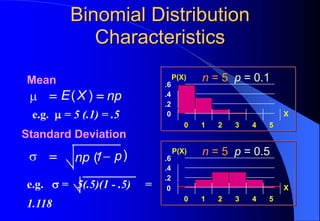
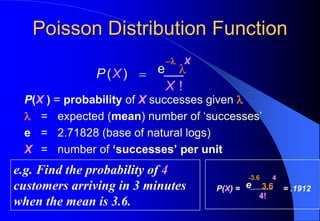
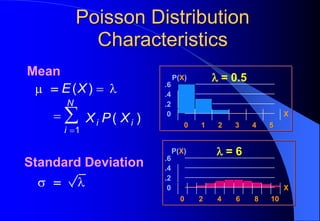
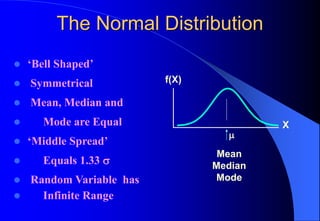
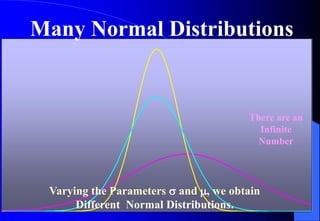
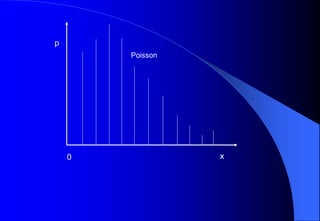
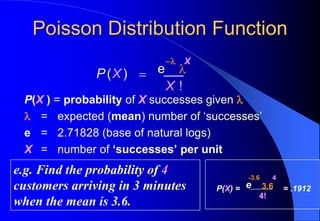
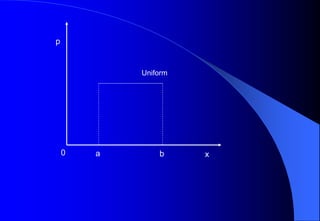
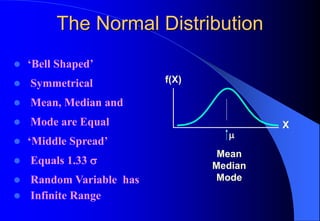
This document contains information about Rohit Bouri's presentation on probability distribution models and functions. It discusses important discrete probability distributions like the binomial and Poisson distributions. It explains the functions, characteristics, and examples of these distributions. It also briefly mentions several continuous probability distribution functions and examples of simulation software.