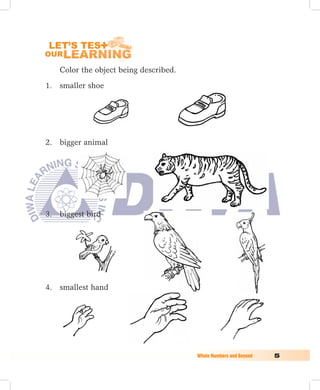
1. This chapter introduces sizes, lengths, heights, and patterns. Objects can be compared as bigger or smaller, taller or shorter, longest or shortest.
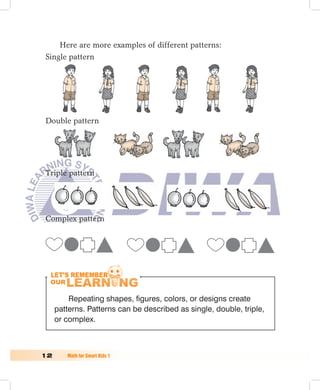
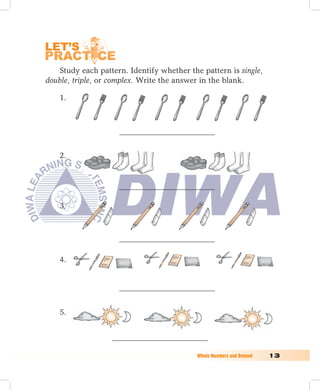
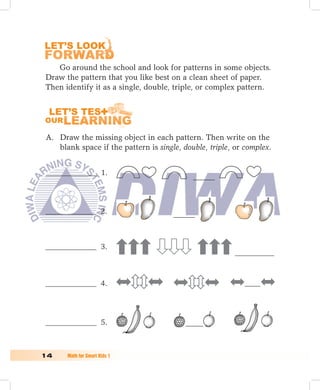
2. Patterns can be single, double, triple, or complex depending on the number of objects that repeat. Repeating shapes, figures, colors, or designs create patterns.
3. Exercises provide practice identifying sizes, lengths, heights, and patterns. Students compare, arrange, identify, draw, and complete patterns of objects.