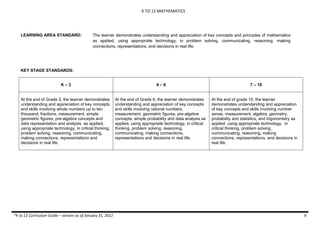
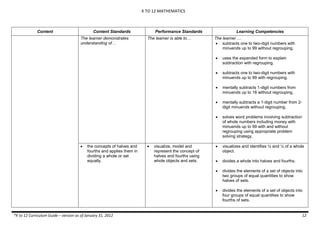
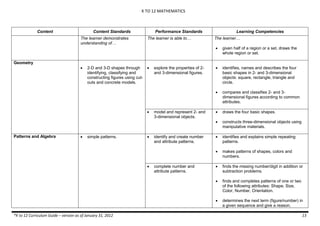
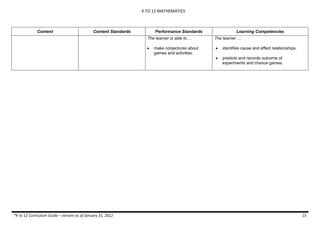
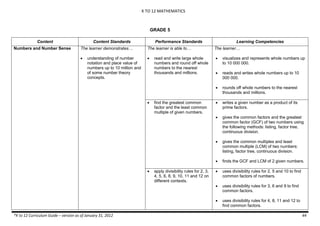
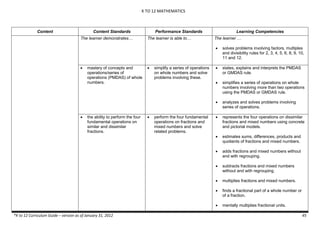
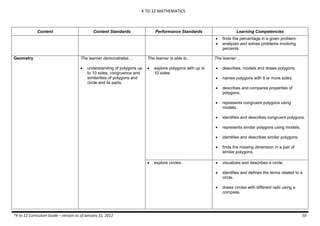
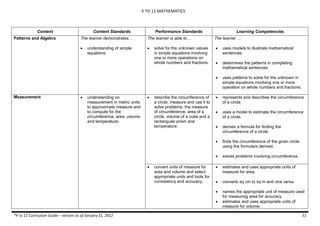
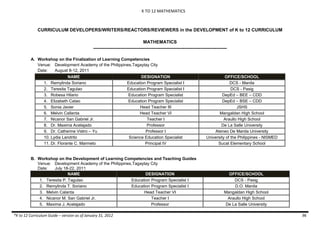
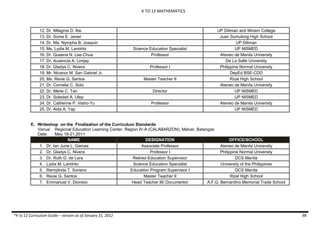
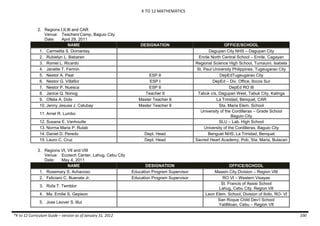
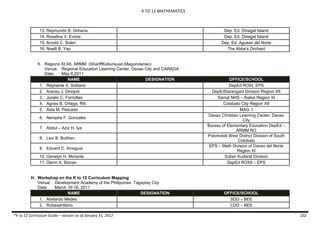
The document provides an overview of the K to 12 Mathematics curriculum guide for the Philippines. It outlines the conceptual framework, which identifies critical thinking and problem solving as the twin goals of mathematics education. It also describes the five content areas - numbers and number sense, measurement, geometry, patterns and algebra, and probability and statistics. Additionally, it provides learning standards and competencies for each grade level from grade 1 to grade 10.