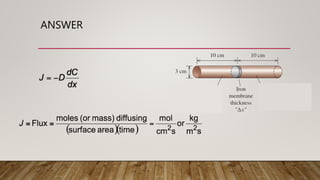
This document discusses diffusion through a membrane and solving related problems. It contains:
1) Information on Fick's first law of diffusion and the Arrhenius equation for calculating diffusion rates.
2) A sample problem calculating the number of nickel ions diffusing through MgO per second given parameters like thickness, temperature, and diffusion coefficient.
3) A multi-part problem designing an iron membrane thickness to allow less than 1% nitrogen loss per hour and 90% hydrogen passage per hour given gas concentrations and diffusion rates at 700C.